Polio in the Syrian Arab Republic
Thirteen cases of wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) have been confirmed in the Syrian Arab Republic.
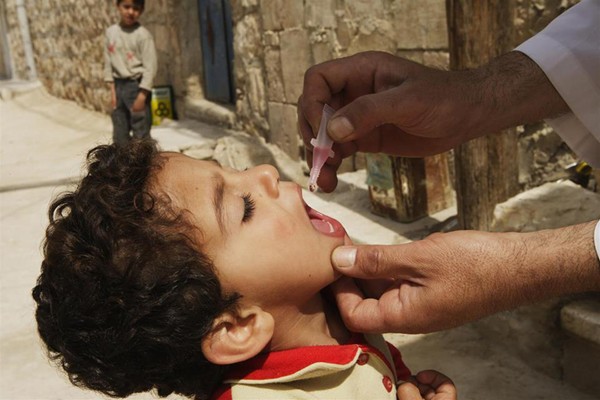
11 November 2013 – Genetic sequencing indicates that the isolated viruses are most closely linked to virus detected in environmental samples in Egypt in December 2012 (which in turn had been linked to wild poliovirus circulating in Pakistan). Closely related wild poliovirus strains have also been detected in environmental samples in Israel, West Bank and Gaza Strip since February 2013. Wild poliovirus had not been detected in the Syrian Arab Republic since 1999.
A comprehensive outbreak response continues to be implemented across the region. On 24 October 2013, an already-planned large-scale supplementary immunization activity was launched in the Syrian Arab Republic to vaccinate 1.6 million children against polio, measles, mumps and rubella, in both government-controlled and contested areas. Implementation of a supplementary immunization campaign in Deir Al Zour province commenced promptly when the first ‘hot’ acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) cases were reported. Larger-scale outbreak response across the Syrian Arab Republic and neighbouring countries will continue for at least 6-8 months depending on the area and based on the evolving situation.
Given the current situation in the Syrian Arab Republic, frequent population movements across the region and the immunization level in key areas, the risk of further international spread of wild poliovirus type 1 across the region is considered to be high. A surveillance alert has been issued for the region to actively search for additional potential cases.
WHO’s International Travel and Health recommends that all travellers to and from polio-infected areas be fully vaccinated against polio.













