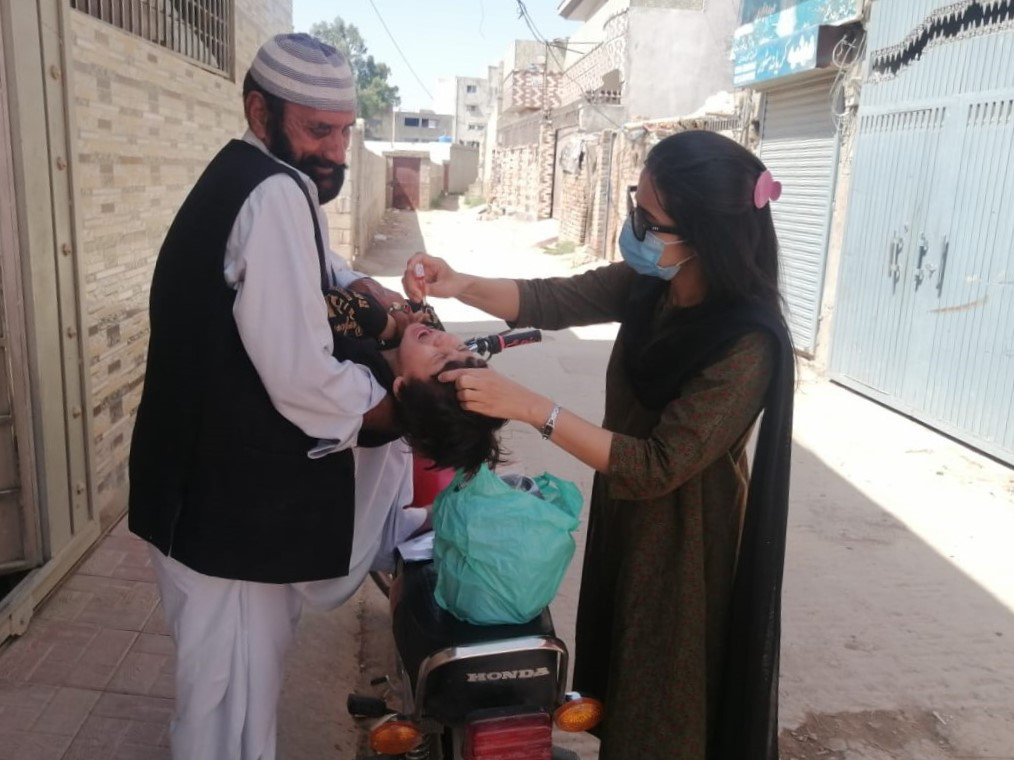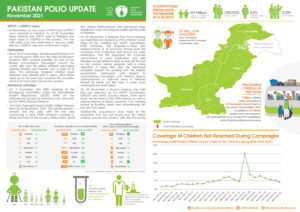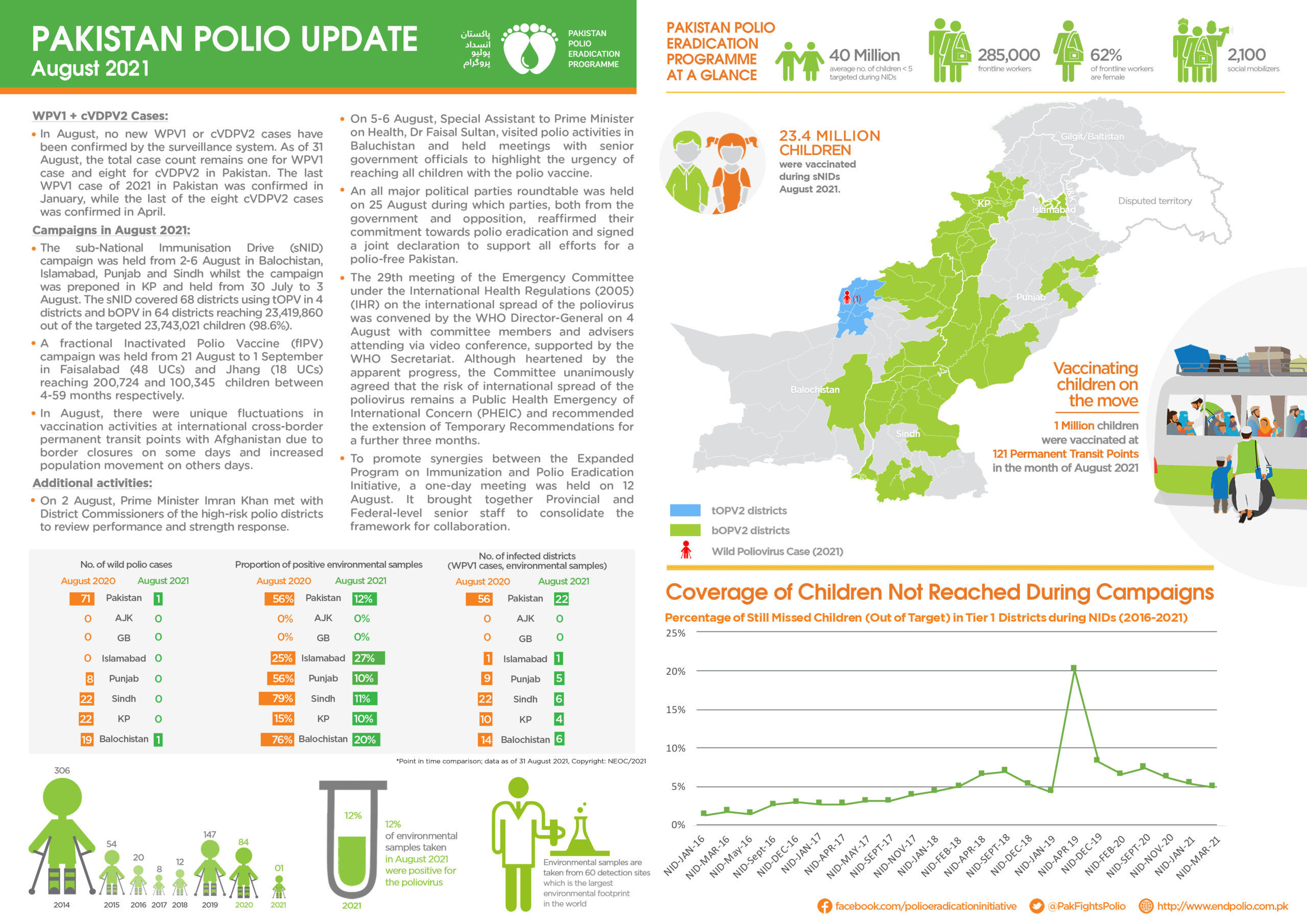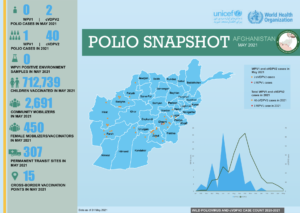
Wild poliovirus transmission in Afghanistan is currently at its lowest level in history. Fifty six children were paralysed by wild polio in 2020. In 2021, the number fell to four. This year to date, only one child has been paralysed, giving the country an extraordinary opportunity to end polio.
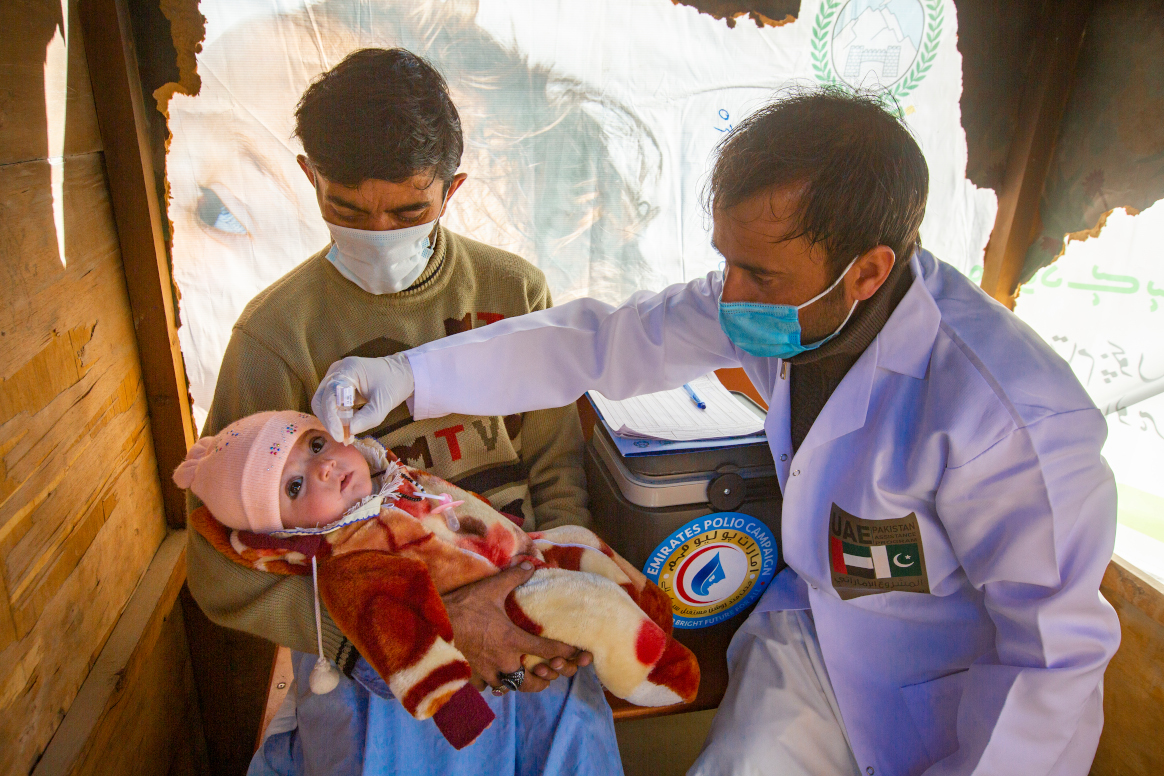
The resumption of nationwide polio vaccination campaigns targeting 9.9 million children has been a critical step. Since 2018, local-level bans on polio vaccination activities in some districts controlled by the Taliban had significantly reduced the programme’s ability to vaccinate every child across the country. With access to the entire country following the August transition, seven nationwide vaccination campaigns took place between November 2021 and June 2022, and a sub national campaign targeting 6.7 million children in 28 provinces took place in July. Of the 3.6 million children who had been inaccessible to the programme, 2.6 million were reached during the November, December and January campaigns. With improved reach to previously inaccessible children throughout the February to July campaigns, the number children has been reduced to 0.7 million. Further campaigns are planned for the remainder of the year.
With Afghanistan and Pakistan sharing one epidemiological block, the two countries continue to coordinate cross border activities. December and May’s campaigns were synchronized with Pakistan’s national campaigns, focusing on high risk populations including nomadic groups, seasonal workers and communities straddling both borders.
Improved access also had a significant impact on polio surveillance activities. Afghanistan’s surveillance indicators remained above global standards throughout the transition. With access to all districts since August, the quality of activities has improved significantly including early case detection and reporting.
In June, the first review of the polio surveillance system in six years took place with WHO hosting a team of technical experts including epidemiologists and virologists. A small team visited in 2016 but insecurity and lack of access to much of the country limited the visitors’ movements to Kabul, Herat, Kandahar, Jalalabad, Mazar-e-sharif and Kunduz. This year, the 16-strong team visited 76 districts across 25 of the country’s 34 provinces. The review determined the likelihood of undetected poliovirus transmission in Afghanistan to be low. Recommendations, including upscaling surveillance in the country’s south and south east, are being implemented.
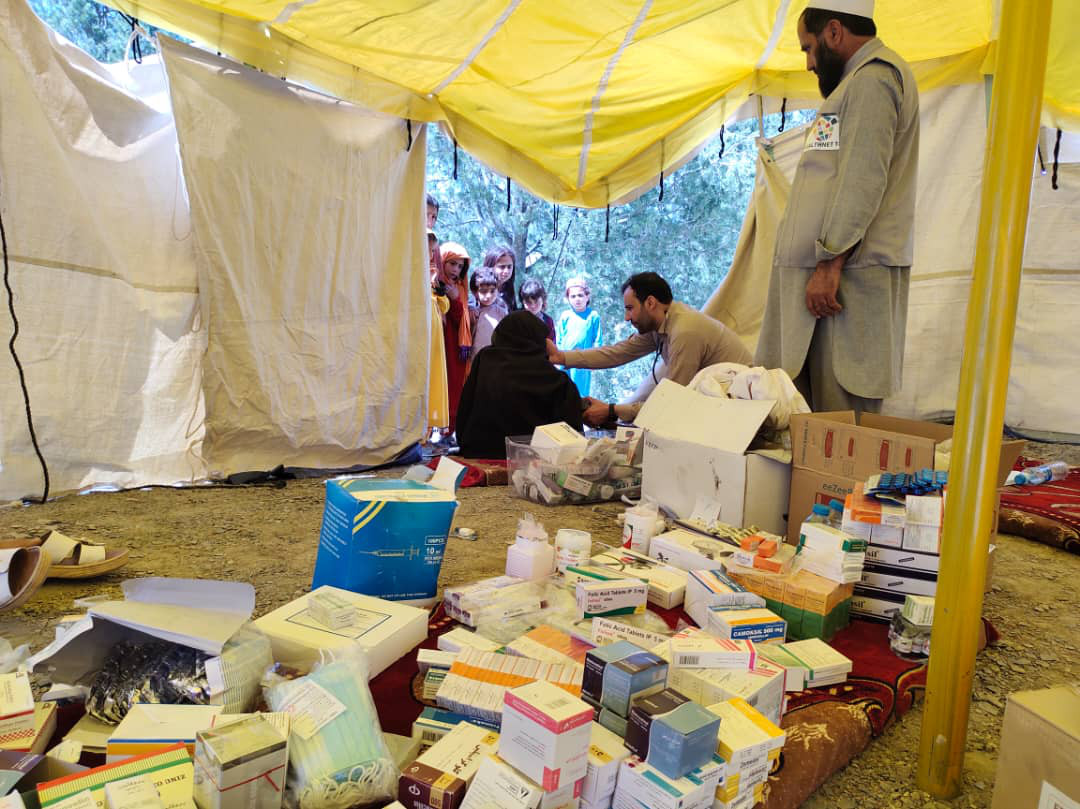
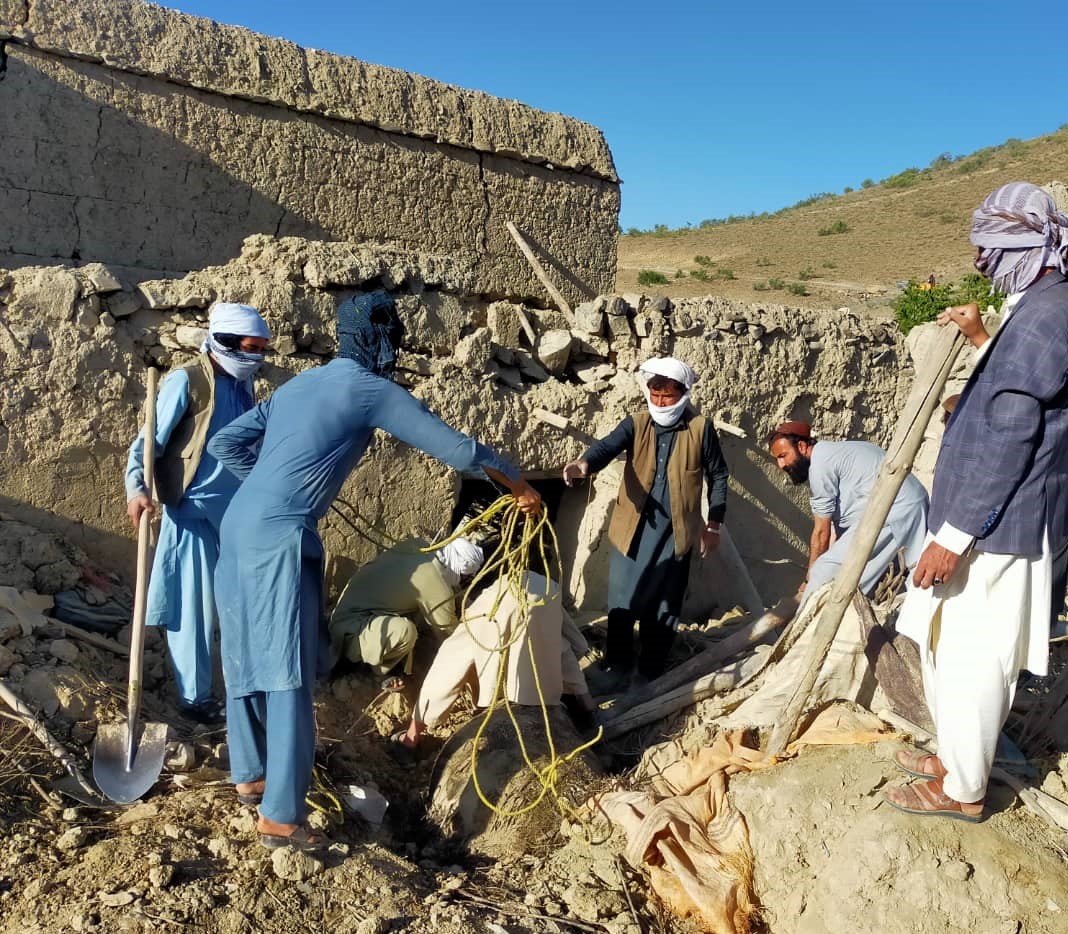
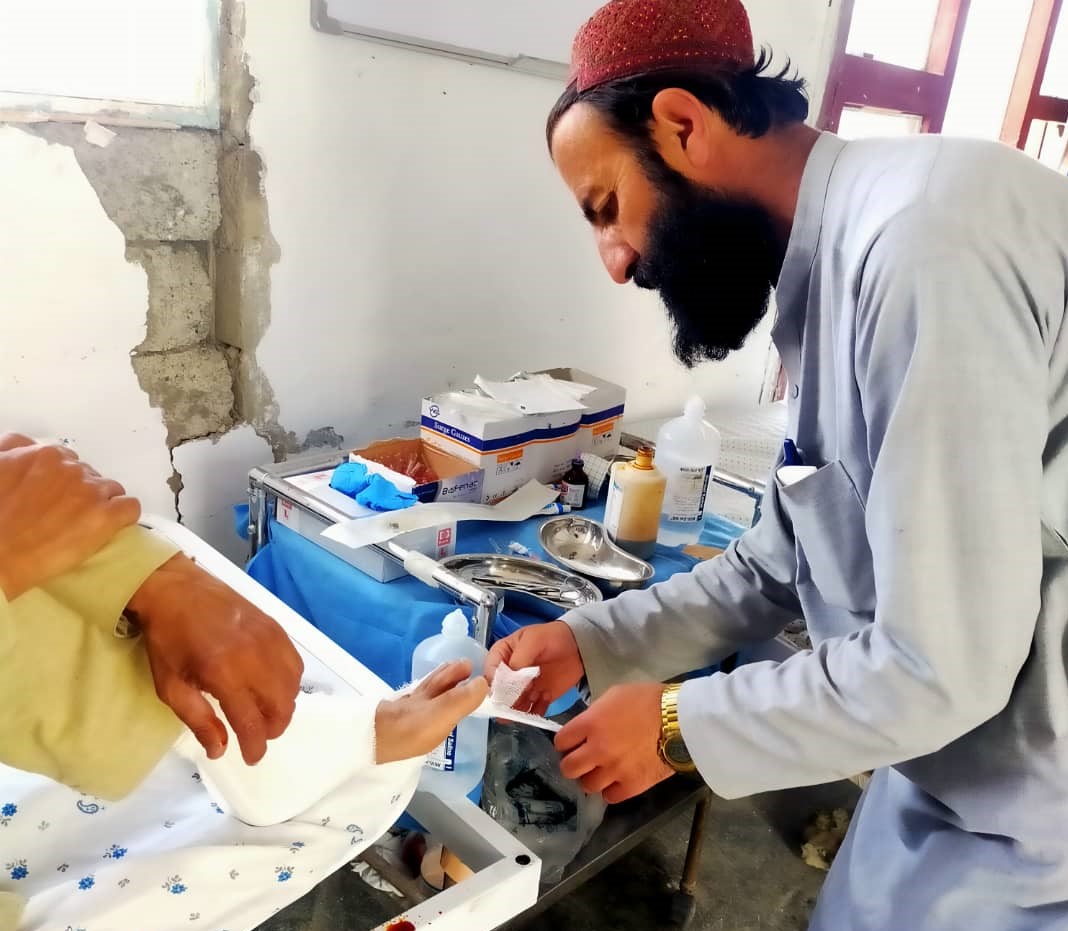
With more than twenty years on the ground in Afghanistan, the polio programme continues to leverage its extensive operational capacity to deliver better health outcomes for all Afghans. In the face of an unprecedented humanitarian crisis, in addition to day-to-day polio activities, polio staff continue to regularly monitor the functionality of health facilities across the country as well as support ongoing vaccination campaigns including measles and COVID 19. WHO’s polio team in the southeast were among the first responders following the devastating earthquake in Paktika and Khost provinces in June. In addition to providing critical health care, the team’s experience working among local communities provided the foundations of an assessment tool that mapped affected communities and ensured accurate data guided a focused response in the immediate aftermath.
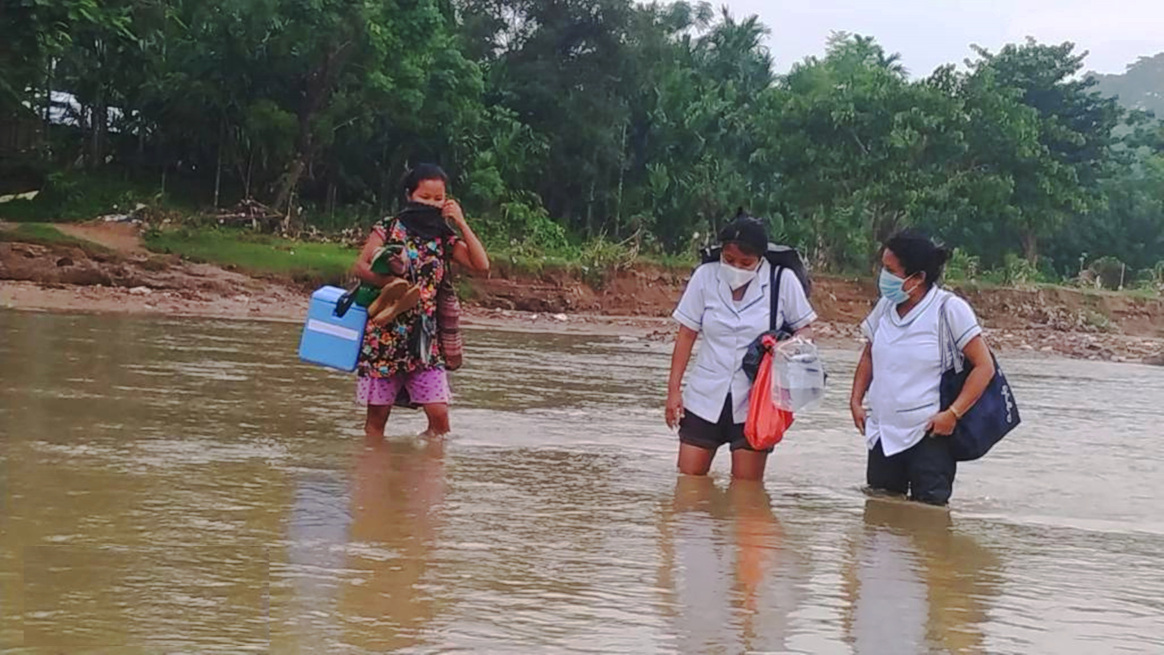
Although the number of children paralysed by polio has reduced significantly in Afghanistan, the threat is far from gone and the programme faces significant challenges. While access has improved across the country, accessing every child though house to house vaccination remains a challenge in some areas leaving immunity gaps and, with them, children at risk.
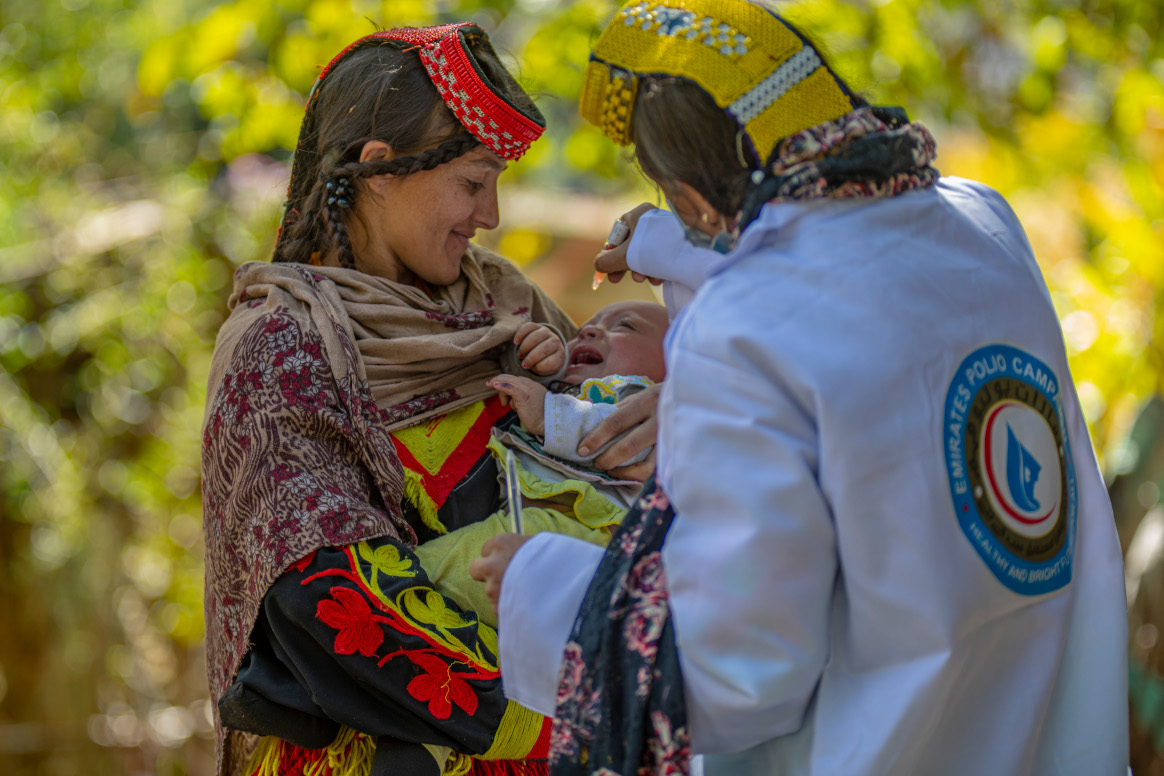
On 24 February, eight polio workers were killed in targeted attacks in the country’s north, not the first time polio workers had come under attack in the course of their life saving work. Four of those killed were women. Female polio workers play a critical role in the programme, building community trust and reaching all children.
The sharp rise in the number of wild polio cases in Pakistan is a cause for concern, and the detection of one case each in Malawi and Mozambique is a reminder of the continued risks of poliovirus and the urgencyrequired to permanently interrupt transmission in both Afghanistan and Pakistan.
While the polio programme has made important progress in the last 12 months, sustaining those gains with high quality campaigns that vaccinate all children and build enough immunity to end circulation of the virus for good is critical. A polio free Afghanistan is within reach – but there is still a long way to go.