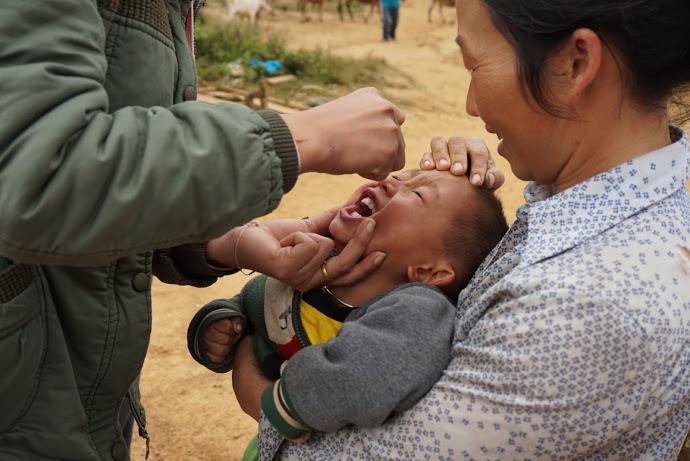
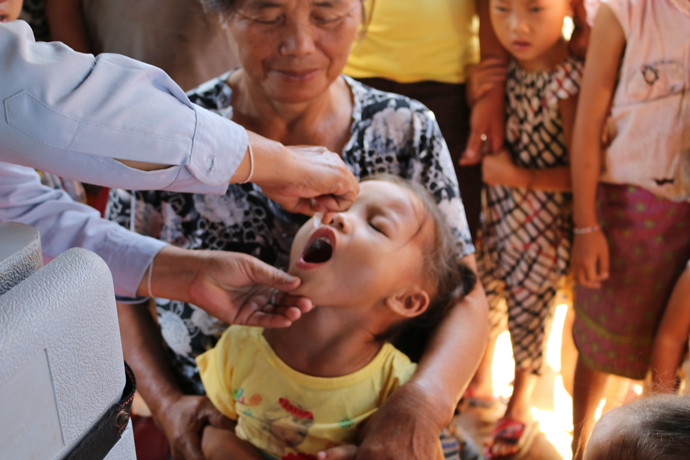
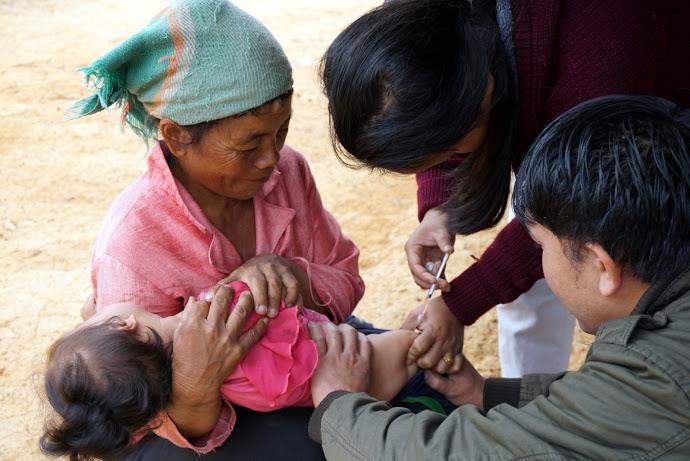
Country: Lao People’s Democratic Republic
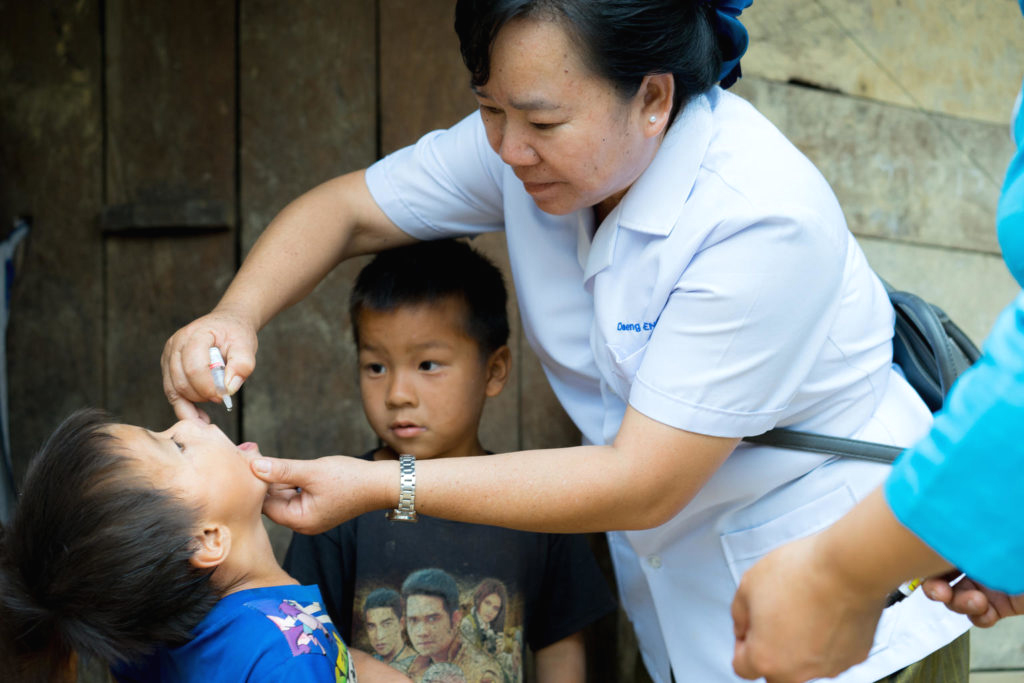
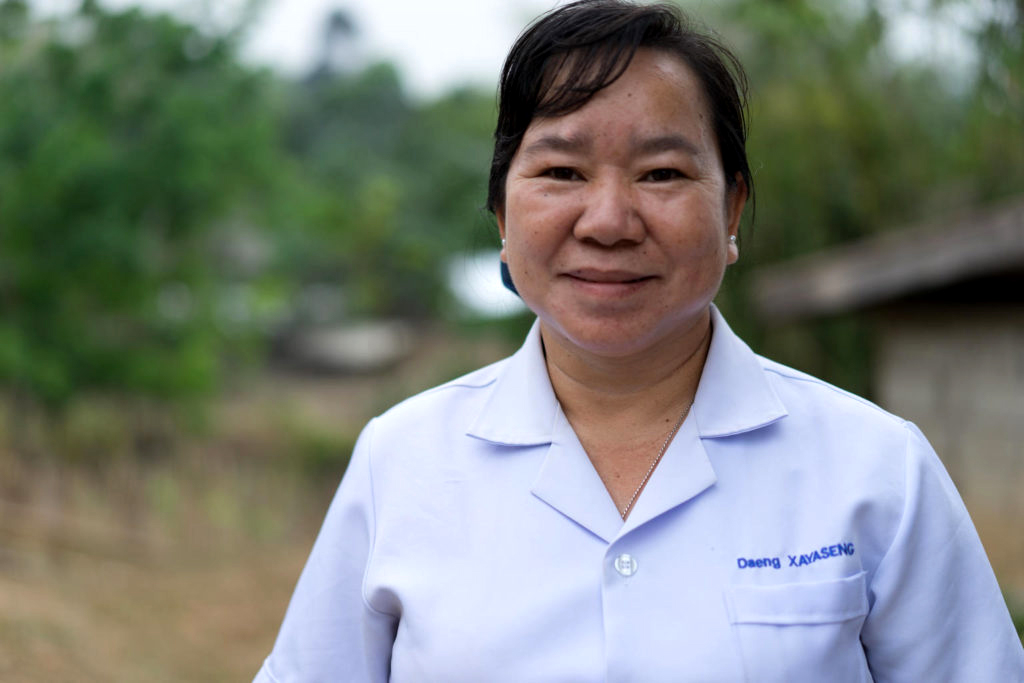
For 15 years Daeng Xayaseng has been travelling through rugged, undulating countryside by motorbike and by foot to deliver vaccines to children in some of the most remote villages in Laos.
It’s hard work but she is determined: “We have a target of children to reach and we’ll achieve that no matter how long it takes,” she says. “We’ll keep working until we reach every child.”
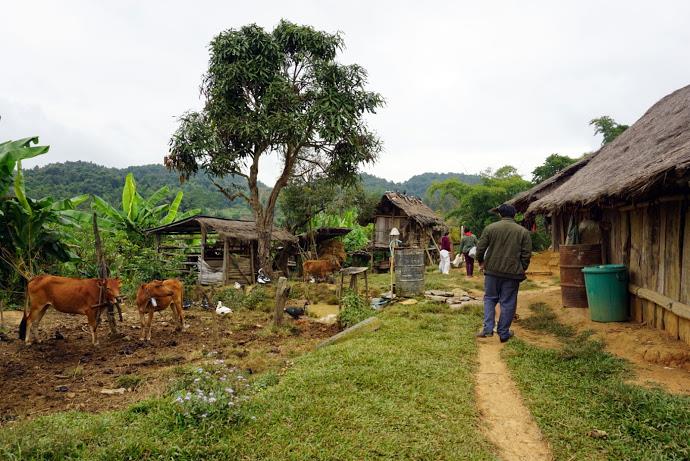
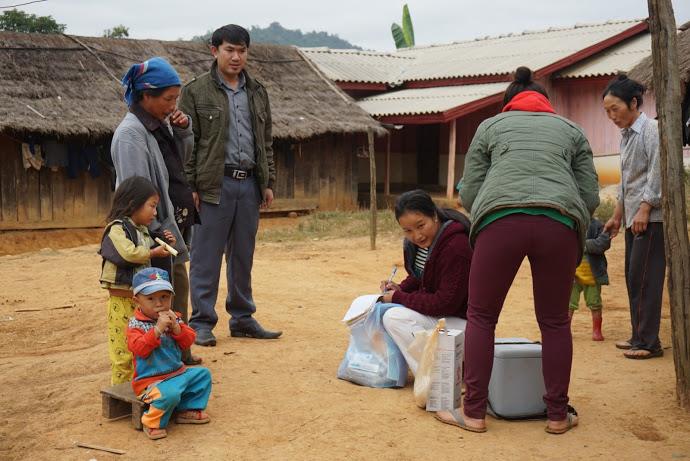
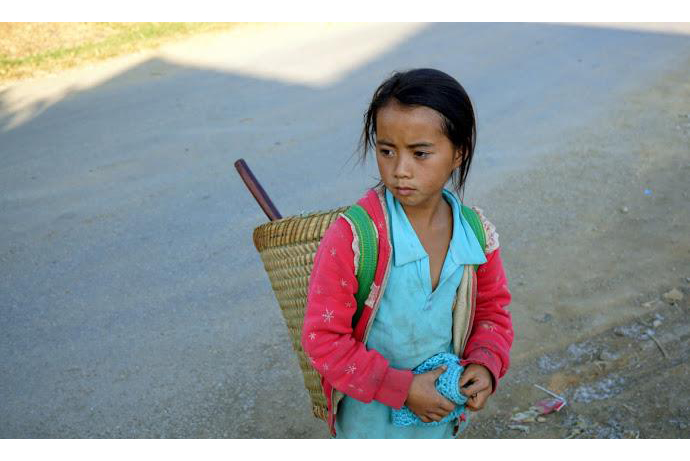
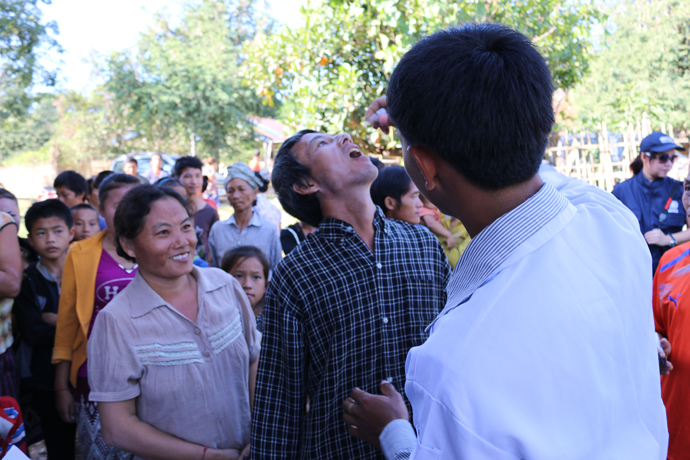
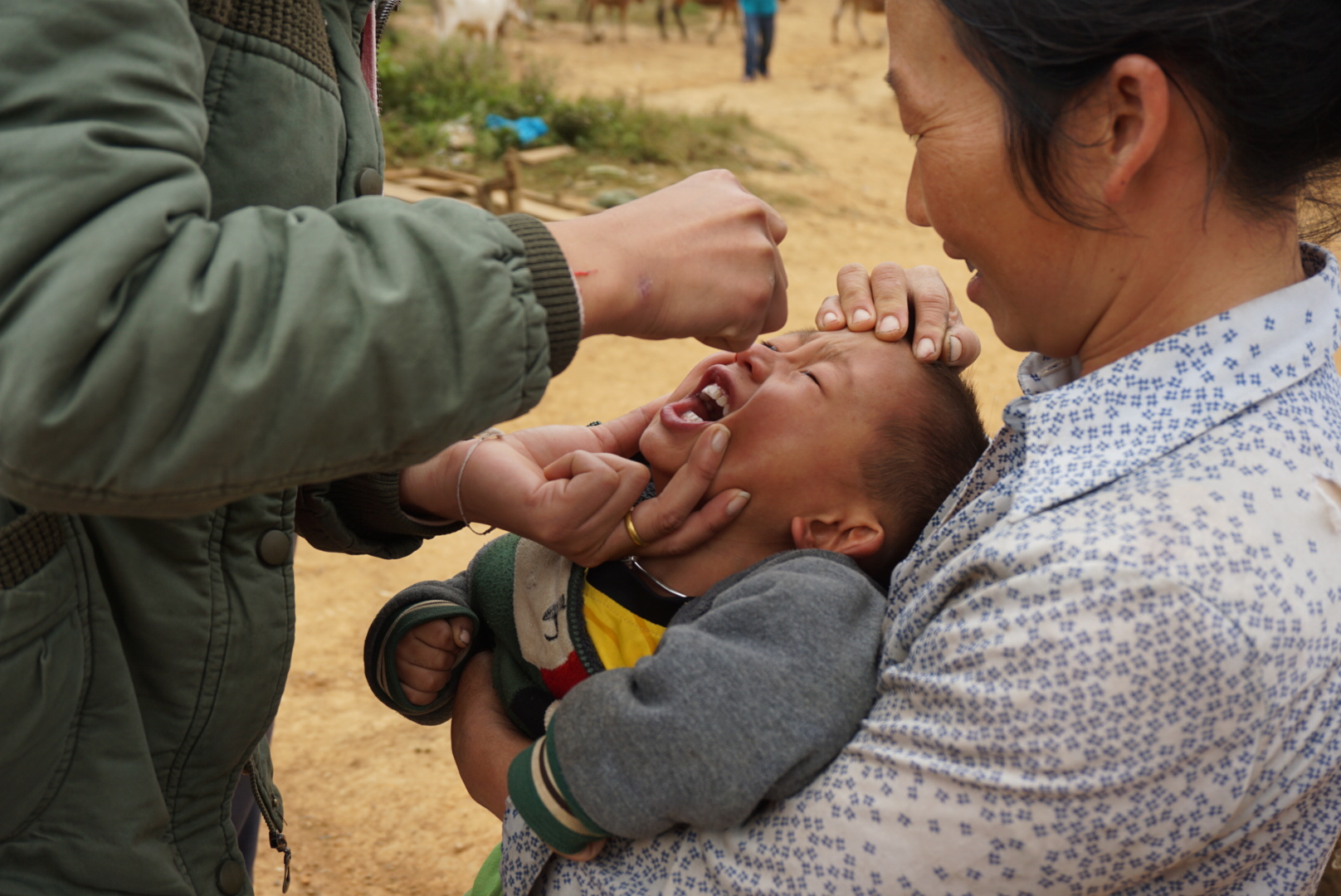
Today her team visits Nampoung village, 4 hours north of the capital of Laos, to deliver polio vaccines.
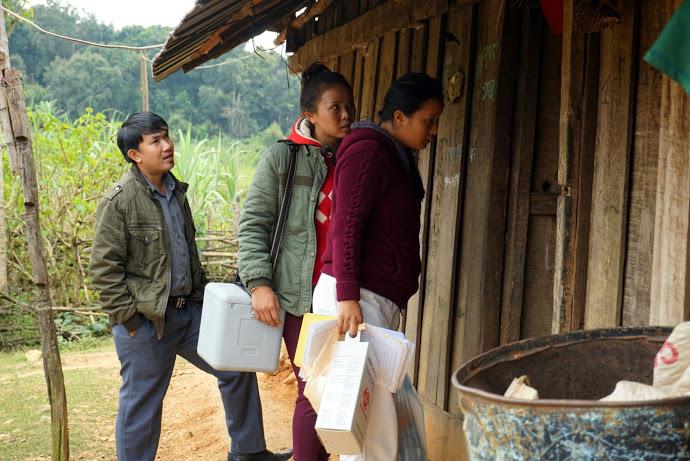
“For 15 years I’ve been working on campaigns like this,” she says. “Today we’re here with our outreach team to vaccinate children against polio. We’ll also go house to house to make sure no child misses out on being vaccinated.”
“We don’t want there to be another outbreak of polio so we have to reach everyone,” says Daeng. “In order to do that, immunizing every child in remote communities like this is a priority to ensure everyone is protected.”
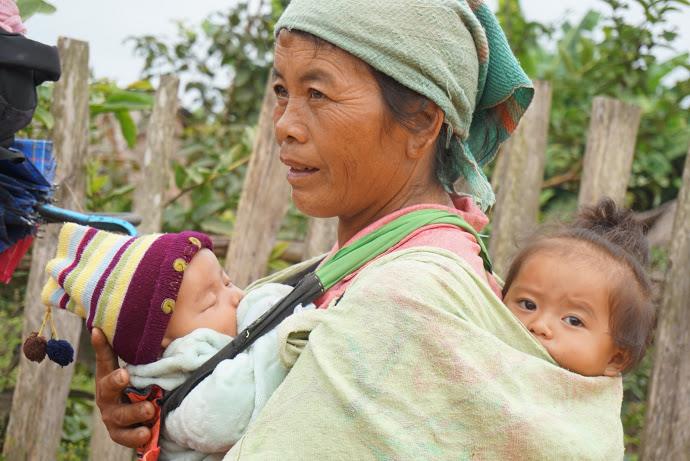
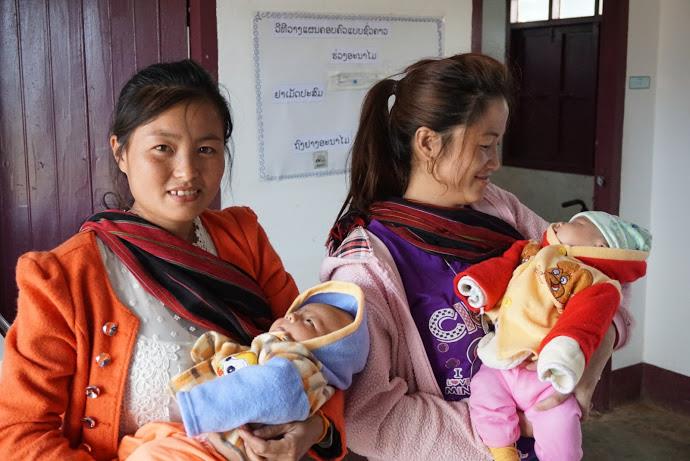
UNICEF and other partners of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative are supporting the Lao Government to reach nearly half a million children under five with potentially life-saving vaccines. More than 7,200 volunteers and 1,400 health workers like Daeng and her team have been mobilized to deliver the oral polio vaccine as well as other vaccinations such as measles-rubella.
“I’m very happy and proud to do this job,” says Daeng once the team has packed up. “I’m proud to do this job to serve the community and help in any way I can.”

Read more:
As of May 2017, Lao People’s Democratic Republic (PDR) is officially no longer infected with circulating-vaccine derived polio virus (cVDPV), according to the International Health Regulations (IHR) Emergency Committee on the international spread of poliovirus.
After an outbreak of circulating vaccine derived poliovirus type 1 (cVDPV1) in 2015 and 2016, the country has now been without cases for over 12 months, with the last case reported in January 2016.
Since the outbreak, WHO, UNICEF and other partners have supported Lao PDR in their outbreak response efforts. This included support for multiple rounds of supplementary immunization activities, expanded social mobilization to raise community awareness and desire to vaccinate, and enhanced acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) surveillance activities to find the virus.
Ending the outbreak
In general, an outbreak is considered over following a period of 12 months without the detection of any new polioviruses from an AFP case, a healthy individual or an environmental sample, and with confirmed certification-standard disease surveillance.
An outbreak response assessment (OBRA) team visited the country in March to confirm the virus had, in fact, been stopped. The team, made up of representatives from WHO, UNICEF, and the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, concluded that all evidence suggested the outbreak had been successfully stopped, with all immunity and surveillance indicators meeting rigorous international standards.
At the OBRA meeting, development partners commended the Ministry of Health on its leadership in response to the outbreak. Tremendous progress was made in micro-planning, cold chain and vaccine storage at all levels, as well as nationwide social mobilization and strengthening of AFP surveillance.
Deputy Health Minister of Lao PDR, Dr. Phouthone Muangpak, noted that the Ministry of Health and local authorities need to take ownership to further improve surveillance sensitivity in the country.
Lessons from the outbreak response

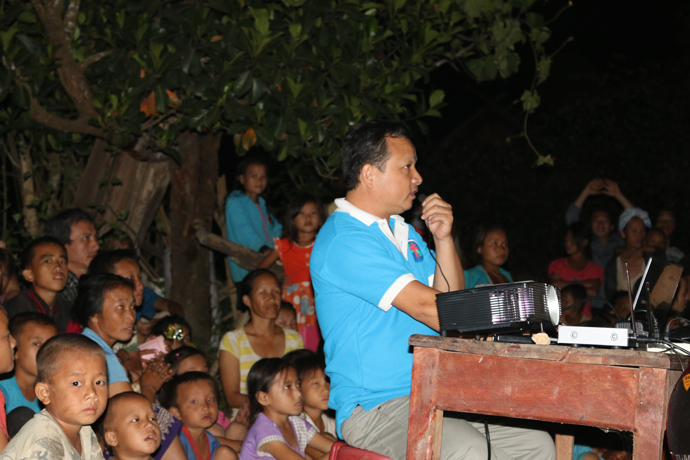
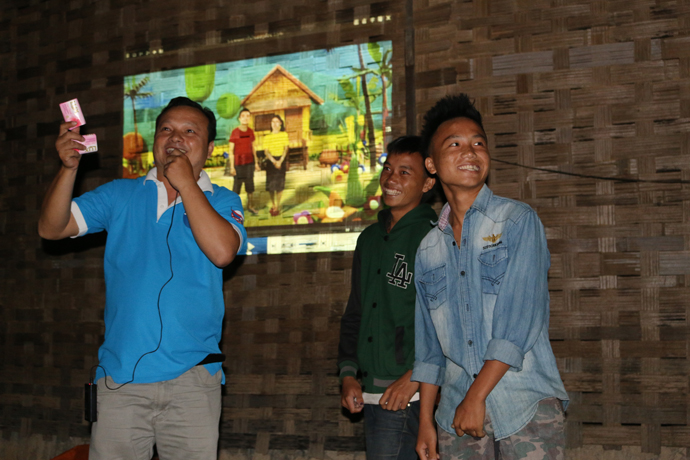
A challenging landscape and diverse ethnic communities added to the challenge of running vaccination schedules in Lao PDR. As the outbreak occurred in an area where vaccination levels had been very low for an extended period of time, campaigns were extended to reach all children under 15, and in some cases even adults. The nuanced cultural, lingual, religious and social needs of the Hmong community called for a response tailored to local needs, especially building an awareness of the importance of vaccines. Impromptu cinemas were set up against bamboo walls to pull in interested families and share information about vaccination campaigns after dark.
Find out more about the response in Lao in this photostory.
Meeting International Health Regulations standards
Information and conclusions from OBRAs are taken into consideration by the IHR Emergency Committee on the Spread of Poliovirus, resulting in this instance in the IHR classification as a state no longer infected with cVDPV1.
Despite being classified as polio-free, the IHR Emergency Committee still categorizes Lao PDR as vulnerable to reinfection. The country must continue to strengthen routine immunization to ensure all children are protected from any polio outbreak that may happen in the future and to maintain the improvements in disease surveillance, to ensure the virus is detected and stopped wherever it may emerge.