Women Leaders in Polio Eradication: Heather Monnet
By asking polio eradicators to “put on their gender glasses”, Heather Monnet is a driving force behind the GPEI gender strategy.

Throughout her career as a Resource Mobilization Officer for WHO’s polio eradication programme, Heather Monnet has held onto her vision of a polio-free world. A respected communicator with a deep understanding of the polio programme, she was one of the first in the programme to realize that considering gender is crucial to defeat the poliovirus. Since 2017, she has successfully “led from behind”, supporting the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) to develop a gender strategy and workstream which has become a model for other United Nations programmes, and which is designed to overcome some of the most intractable challenges facing polio eradicators.
Describing her motivation, Heather describes “putting on her gender glasses”. She explains, “We had reached a point where it seemed like we had turned nearly every stone to eradicate polio, and yet we had not defeated the disease. At the same time, the introduction of the sustainable development goals had led to an increasing awareness of gender. I began to think more about how gender affects health and health-seeking behaviors.”
“I was not, and am still not a gender expert, but as Member States began to speak more about this issue, it was increasingly on my radar. Putting on my “gender glasses”, I realized that gender was an unexplored intersection for polio eradication, and it could be transformative for our work.”
The case for considering gender
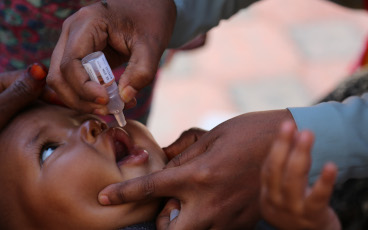
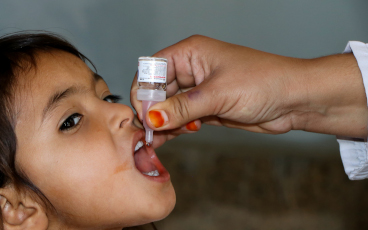
In polio eradication, areas where gender intersects with health delivery include exploring whether boys and girls are equally as likely to receive the polio vaccine, and if gender norms impact whether mothers are able to take their children to health centres for routine immunization.
In some places, such as in Nigeria, women are often more effective at delivering the polio vaccine than men, as it is more culturally acceptable for them to interact with mothers and enter homes to vaccinate the smallest children. The GPEI Gender Technical Brief showed how the presence of female health workers in Pakistan has been associated with substantial increases in tetanus vaccine coverage, attended births, and full immunization coverage of children.
To explore and respond to the gender dynamics of polio eradication, the GPEI has published a comprehensive gender equality strategy. A dedicated gender analyst works in the polio programme at WHO headquarters, and gender focal points have been appointed at regional levels and in some country offices. Data is now routinely disaggregated by sex, and there has been a concerted effort to use gender analyses to inform programme policy. The team are currently engaged in implementing the GPEI gender strategy as well as supporting efforts to mainstream gender across WHO, including through a dedicated gender data working group.
Advocating for consideration of gender within the programme has not always been easy. Heather explains, “The polio programme is huge and so many people are involved. Encouraging people to put on their ‘gender glasses’ even for five minutes can be a challenge. But what is really encouraging is that once we educate people about how gender impacts their work, they often have an “aha” moment.”
“The next and crucial steps are striving to ensure that the gender strategy is implemented. This requires all those involved in polio to be engaged – whether it’s designing a gender-inclusive microplan, collecting sex-disaggregated data during a campaign, or considering how gender impacts the way we pay vaccinators. As we integrate gender into our work, we also need to identify the building blocks to ensure that this workstream is sustainably mainstreamed. This is not dependent on one person – rather it takes everyone having exposure.”
Polio Gender Champions
The GPEI gender workstream is supported by Polio Gender Champions, who work to raise the voices of those engaged in the programme. Champions include Senator Hon Marise Payne, Australian Minister for Foreign Affairs and Minister for Women, Wendy Morton, Minister of European Neighbourhood and the Americas at the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office in the United Kingdom, and Arancha González Laya, who is the Spanish Minister for Foreign Affairs, European Union and Cooperation.
Heather explains that the vision and leadership of the gender champions is crucial for achieving change. “The gender champions amplify the voices of those who don’t have a megaphone on the global stage and whose voices need to be heard. For instance, female frontline workers have a lot to say, but their voices aren’t always listened to. Our gender champions raise up these voices from the field.”
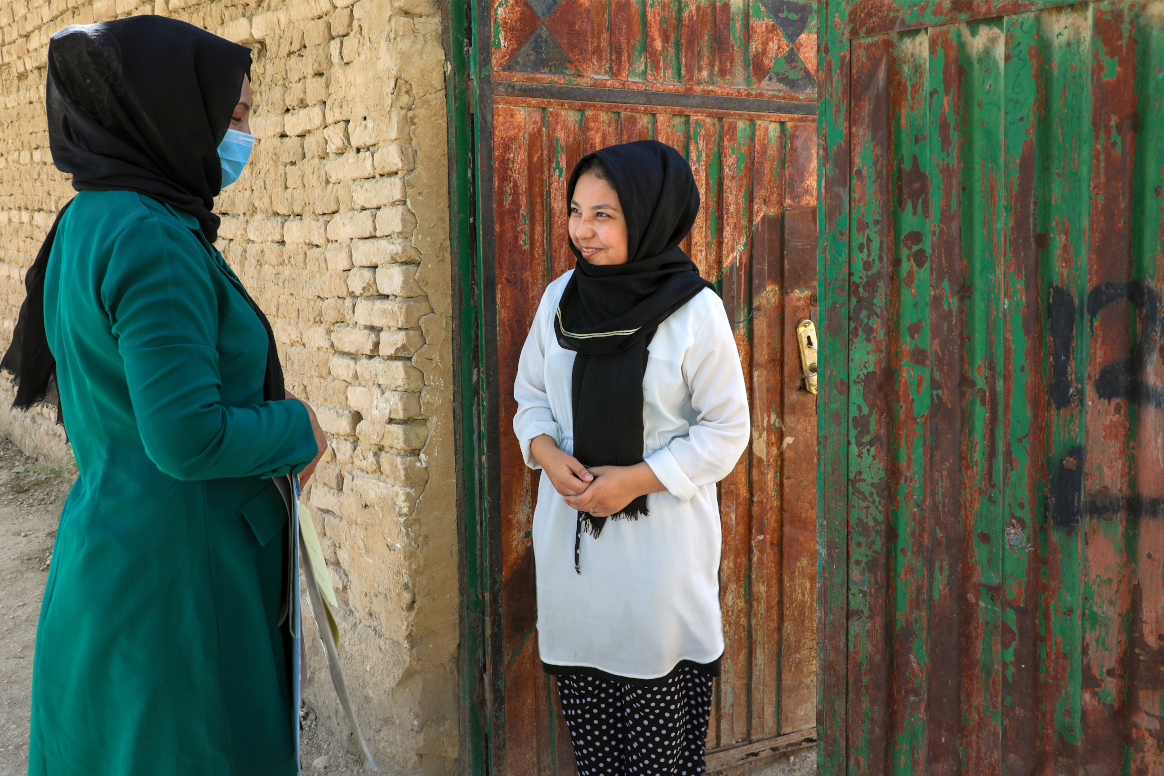

“This feeds into our attempts to improve the way that health is delivered. We know that most healthcare is delivered by women, but the systems to deliver it are designed by men. Practical steps to support women employed by the programme may include ensuring that polio vaccination training materials can be understood by individuals with lower literacy, and ensuring that there are safe, private bathrooms available for women to use during long campaign days. When we plan routes to deliver vaccines from house to house, we should consider that women might prefer to take a different route which gives them a greater feeling of personal security. Women may not feel comfortable speaking about these issues to a male supervisor, so we must also ensure that enough female supervisors are recruited and trained. Gender champions are key to keeping these issues high on the global agenda.”
Over the last few years, the GPEI’s gender work has been recognized in multiple high-level forums, and is leading the way for other programmes. Heather identifies two moments when she felt particularly proud – when the Polio Oversight Board adopted and endorsed the GPEI gender strategy, and at a high-level meeting hosted by the Government of the United Arab Emirates in advance of the Reaching the Last Mile Forum in November 2019, during which the Canadian representative described GPEI’s gender strategy as one of the strongest in global health and noted that it should stand as an example for others.
Heather explains, “I have been inspired by what we have achieved – we have planted the seeds and the soil is now being nourished. Our work on gender is growing into something amazing – and the world is watching what it will become.”