GPEI – a brief review of 2023 and full focus on 2024
As the year draws to a close, efforts intensify against the virus in 2024
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative has two goals laid out in its current strategy: to interrupt all remaining transmission of endemic wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) and to stop all outbreaks of variant poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2). 2023 was a critical year for progressing on each of these, and while our urgent and diligent work to end polio must continue into 2024, the GPEI achieved incredible things in the past twelve months.
Continuing work in endemic countries
Despite significant geo-political and environmental challenges in the two remaining WPV1-endemic countries, Pakistan and Afghanistan, the polio programme has continued to reach greater numbers of children with polio vaccines.
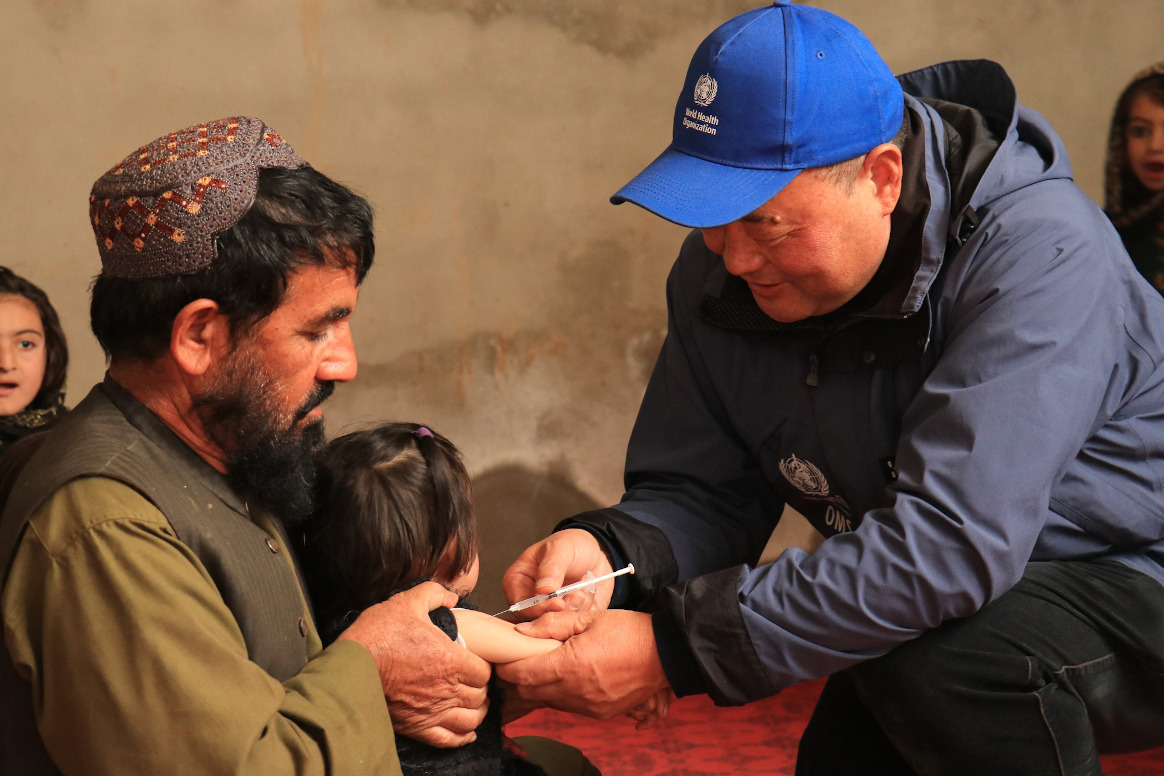

Wild polio transmission was beaten back to just a handful of districts in eastern Afghanistan and the southern area of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in Pakistan. In both countries, efforts are increasingly focused on reaching and vaccinating the last remaining ‘zero dose’ children – children who have received no vaccines of any kind. The number of these missed children continues to dwindle, with the success of improved collaboration with the national immunisation program, new efforts like Pakistan’s Nomad Vaccination Initiative and focused vaccination activities at border crossings between the two countries. Just one family of the virus remains endemic in each country, and coupled with this increasing geographic restriction, the situation resembles the end of wild polio eradication efforts in former virus hotspots like India, Nigeria and Egypt.
In addition, after a wild poliovirus outbreak that was confirmed in southeast Africa in early 2022, neither Malawi nor Mozambique has reported a WPV case since August 2022 thanks to a concerted subregional emergency response across five neighbouring countries. We are hopeful that this outbreak will be officially closed in the coming months, affirming that countries have what it takes to protect children from this devastating disease and keep wild polio out of Africa.
Progress on variant polio outbreaks
Thanks to the novel oral polio vaccine type 2 (nOPV2), strong political commitment and community-based efforts to reach more children with the vaccine, the number of cases of variant poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) continued to decline in 2023.
Nearly 1 billion doses of nOPV2, a comparably safe, effective, but more genetically stable version of the existing type 2 oral polio vaccine (mOPV2), have now been administered across 35 countries, protecting millions of children from illness and paralysis.
Emergency response to variant polio outbreaks is continuing, notably in the most consequential geographies for the programme—where children are at the highest risk of encountering and spreading poliovirus. In northern Nigeria, for example, variant polio cases have fallen by 90% since a peak in 2021, thanks to concerted commitment from government, unique community programs to improve the reach of vaccines and the extensive rollout of nOPV2. Across these consequential geographies, the programme will continue to focus on increasing access, acceptance and campaign quality, which have helped make incredible progress in Nigeria, and continue to innovate until we end polio for good everywhere.
Finally, In September 2023, after a massive vaccination response in the shadow of ongoing war, Ukraine officially stopped its outbreak of type 2 variant polio that began in 2021. New York, London and Jerusalem, where high-profile outbreaks began in 2022, have not detected the virus in recent months. Still, the emergence of polio in these areas is a reminder that as long as poliovirus exists anywhere, it is a threat to people everywhere.
A global effort
Most importantly, thanks to the efforts of the GPEI and its partners, health workers vaccinated more than 400 million children in 2023, preventing an estimated 650,000 cases of paralysis from polio and saving the lives of up to 60,000 children. Building full, healthy futures was at the core of Rotary International’s mission when it began this fight to end polio for good in 1985, and when the GPEI was launched in 1988—35 years ago.
This year, the Independent Monitoring Board (IMB) conducted a rigorous mid-term review of the GPEI’s progress towards its strategic goals. This welcome counsel is already helping inform and guide the GPEI’s own ongoing analysis and strengthening of its strategic approaches to achieve a polio-free world, as the programme published its initial response to the mid-term review, under the guidance of the Polio Oversight Board (POB).
Achieving and sustaining a polio-free world has proven harder – and taken longer – than anyone could have imagined. But making history is never easy, and we are confident that together we can eradicate a second human disease from this earth, and build stronger, more resilient health systems along the way.
2023 has firmly set the stage for success. With the complexities of the world today, this programme still inspires to bring about the very best in our humanity.
Thank you to all who have contributed to this effort so far and continue to do so. Let us double down and make the dream of a polio-free world a reality.













