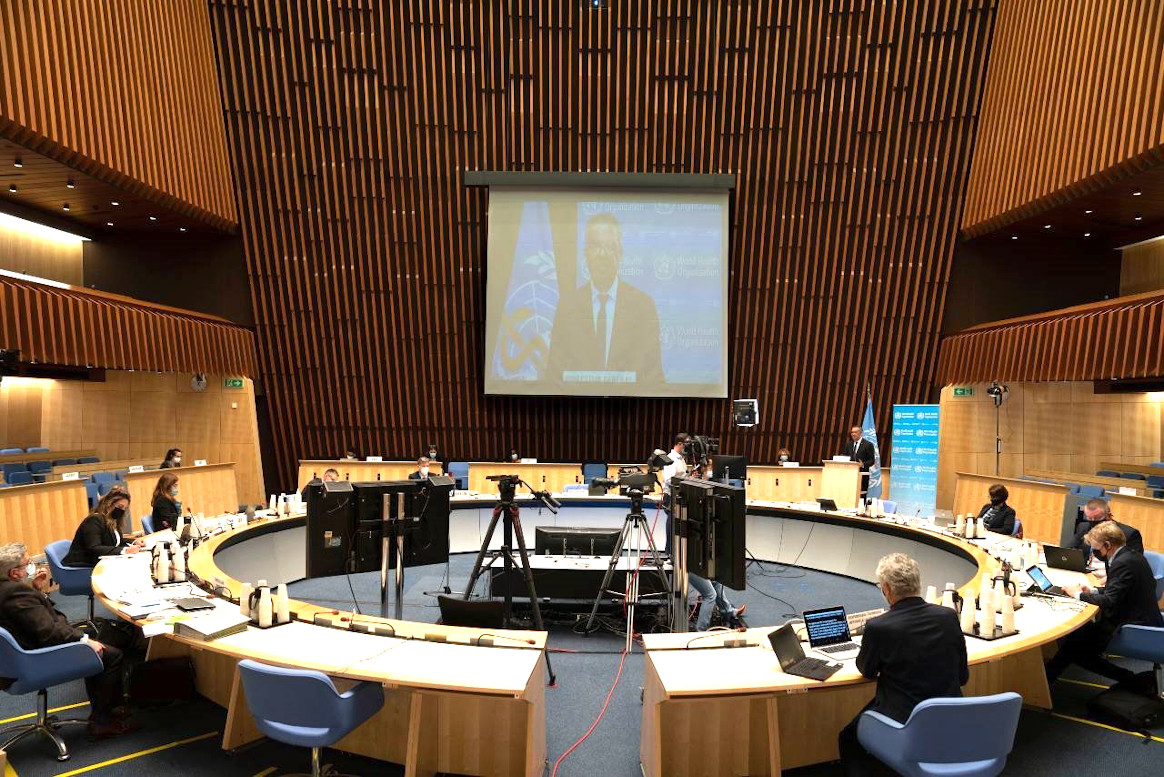
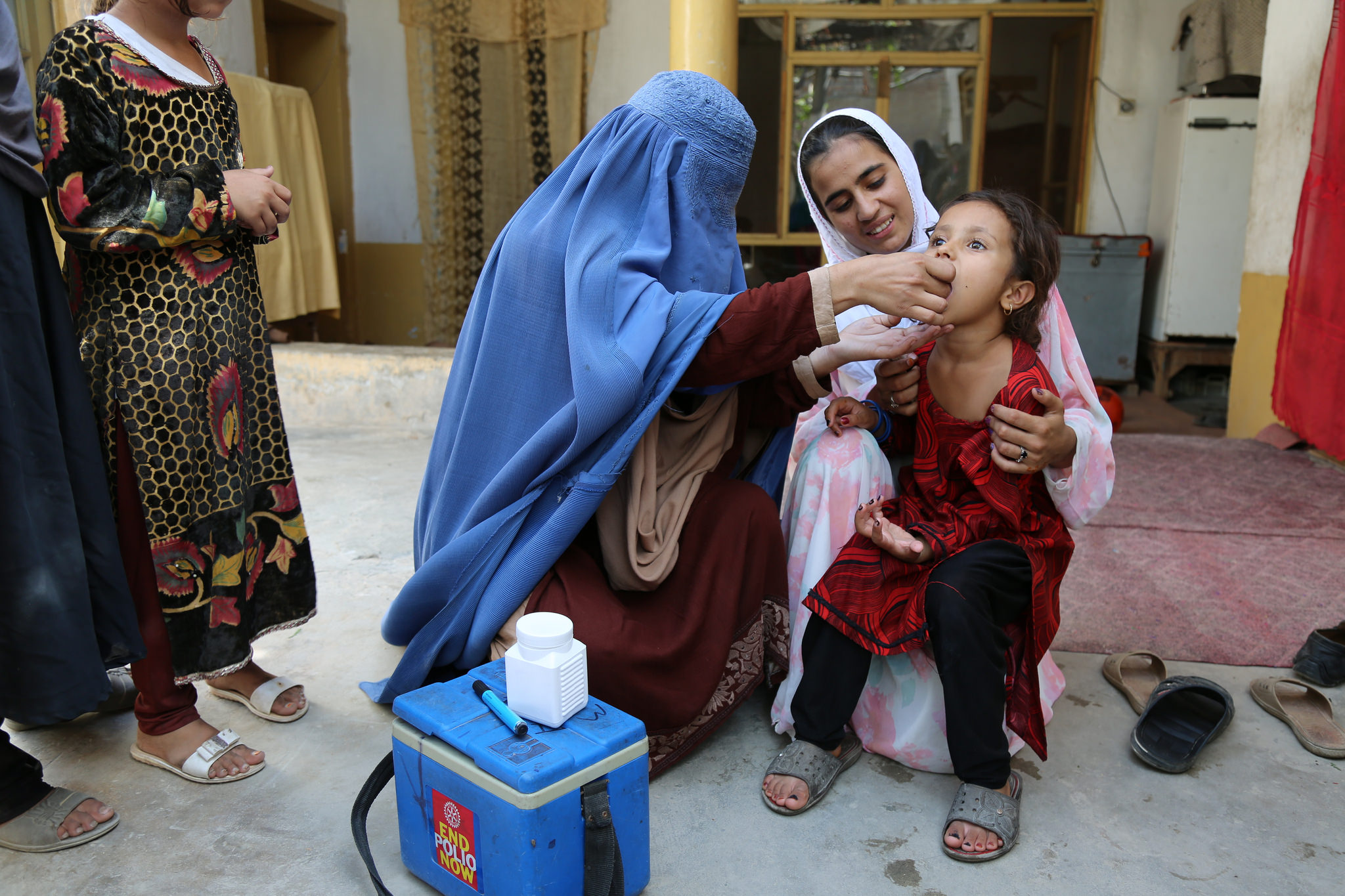
Meeting virtually at this week’s WHO Executive Board (EB), global health leaders and ministers of health urged for concerted and emergency efforts to finally rid the world of polio, noting a global and collective responsibility to finish the disease once and for all. Delegates also reiterated their support for the sustainable transitioning of polio assets, recognizing that successful polio transition and polio eradication are twin goals.
Noting that endemic wild poliovirus is now restricted to just two countries – the lowest number in history – with the African region being certified as wild polio-free in August 2020, delegates urged intensified efforts to wipe out the remaining chains of transmission of this strain and prevent global resurgence. The representatives of both Pakistan and Afghanistan demonstrated strong commitments to this goal and urged collective responsibility to achieve success. Delegates also expressed strong appreciation for the establishment of the Eastern Mediterranean Ministerial Regional Subcommittee on Polio Eradication and Outbreaks, by WHO Regional Director Dr Ahmed Al-Mandhari, which focuses on critical barriers to overcome to achieve zero poliovirus.
The EB urged all stakeholders to follow WHO and UNICEF’s joint emergency call to action, launched 6 November 2020, including by prioritising polio in national budgets as they rebuild their immunization programmes in the wake of COVID-19, and urgently mobilising additional resources for polio emergency outbreak response. To address the increasing global health emergency associated with circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV) outbreaks, delegates expressed appreciation of new strategic approaches, including the roll-out of novel oral polio vaccine type 2 (nOPV2), a next-generation OPV aimed at more effectively and sustainably addressing these outbreaks. This vaccine, which was recently granted a WHO Emergency Use Listing recommendation, is anticipated to be initially rolled-out in the first quarter of 2021. The GPEI is working with countries affected and at high risk of cVDPV2 to prepare for possible use of the vaccine.
Amid the new COVID-19 reality, the EB also expressed deep appreciation for the GPEI’s ongoing support to COVID-19 response. In December 2020, the heads of the GPEI core partners at their final Polio Oversight Board (POB) meeting of the year, confirmed that the polio infrastructure will continue to provide such support, including to the COVID-19 vaccine roll-out.
Member States additionally reiterated their support of polio transition, emphasising the need to ensure sustained, robust public health programming. Several EB members urged for strengthening the links built between the polio, immunization and emergencies programmes during COVID-19 response in the next phase of the pandemic, including for the effective rollout of the COVID-19 vaccine.

Director-General of WHO, Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, commented, “We share the understanding that polio eradication and transition are equally important targets: as we work towards eradication we must think about the future. This is how we will ensure that health systems retain capacity and are strengthened long after polio is ended.”
WHO’s Deputy Director-General, Dr Zsuzsanna Jakab, noted the increasing cross-programmatic integration between polio and other public health programmes, including the introduction of integrated public health teams in countries prioritized for polio transition, bringing together polio, emergencies and immunization expertise. The Regional Director for the African Region, Dr Matshidiso Moeti, emphasised that the work of polio personnel to support the pandemic response, “highlight[s]… the importance of working in interconnected ways going forward.” Dr Al-Mandhari, addressing the delegates, said: “Polio continues to be a public health emergency of international concern. Now is the time to be shoring up the polio programme and mobilizing funding, including domestic funds, so that this remarkable public health and pandemic response mechanism can remain robust and can be integrated into broader public health services across the region. Now is the time for full regional solidarity and mobilization.”
Speaking on behalf of children worldwide, Rotary International – the civil society arm of the GPEI partnership – thanked global health leaders for their continued dedication to polio eradication and public health, sentiments echoed by several other partners, including the United Nations Foundation (UNF). UNF expressed concern about the drop in population immunity, especially for polio and measles, declared support for the joint emergency call to action to prioritize investments for preventing and responding to polio and measles outbreaks, and urged continued focus on strengthening immunization programmes.
The EB discussion will also help inform the finalization of the new strategic plan. This strengthened strategic plan – being developed in broad consultation with partners, stakeholders and countries – is based on best practices and lessons learned, and focuses on fully implementing approaches proven to work. It is expected to be presented to the World Health Assembly in May.
“If we did not know it before, we certainly know now how quickly infectious diseases can spread across the world and wild polio is one such infectious disease. Unlike with COVID-19, where many medical and scientific questions remain unanswered, we know precisely what it takes to stop polio,” said Aidan O’Leary, newly-appointed Director of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative at WHO. “We know how polio transmits, who is primarily at risk and we have all the tools and approaches needed to stop it. That is what this strengthened strategic plan is all about – to bring all the solutions together into a single roadmap to achieve success and through focusing on more effective implementation. What discussions at the EB this week clearly displayed is a strong global sense of commitment and solidarity to do just that: better implementation of what we know works. Together, if we do that, success will follow and we will be able to give the world one less infectious disease to worry about, once and for all.”
Speaking more broadly on global public health issues, the EB welcomed confirmation by the United States of its intention to remain a member of WHO. In a statement by the United States, the country underscored WHO’s critical role in the world’s fight against COVID-19 and countless other threats to global health and health security, confirming it would continue to be a full participant and global leader in confronting such threats and advancing global health and health security.