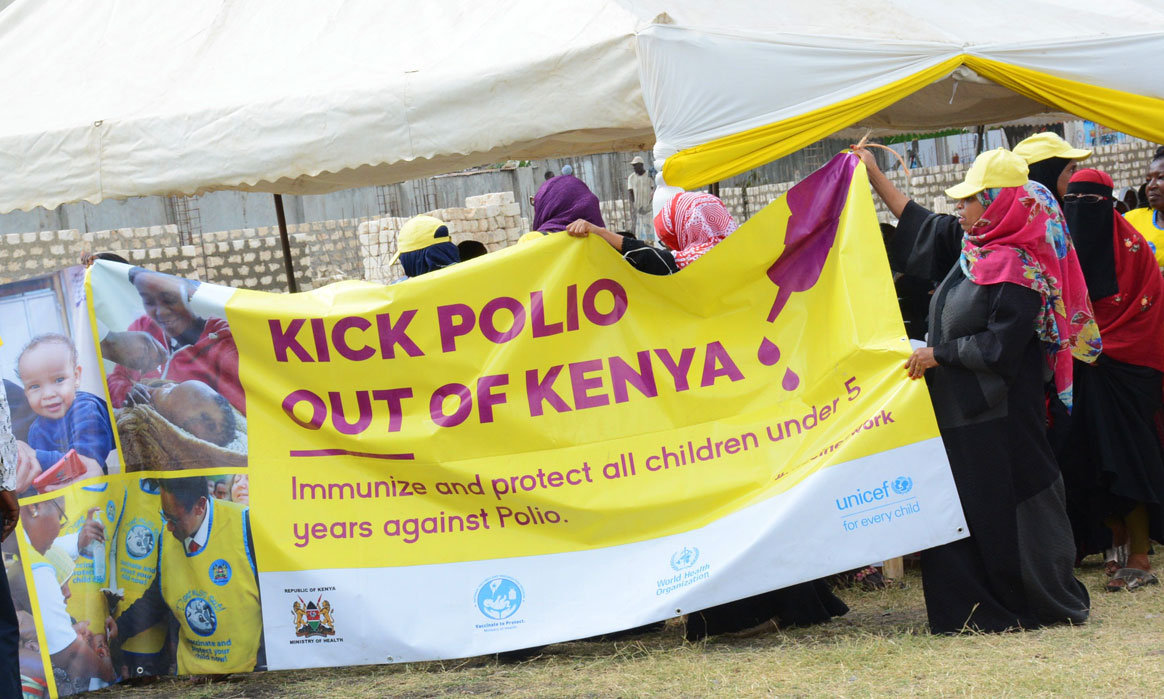
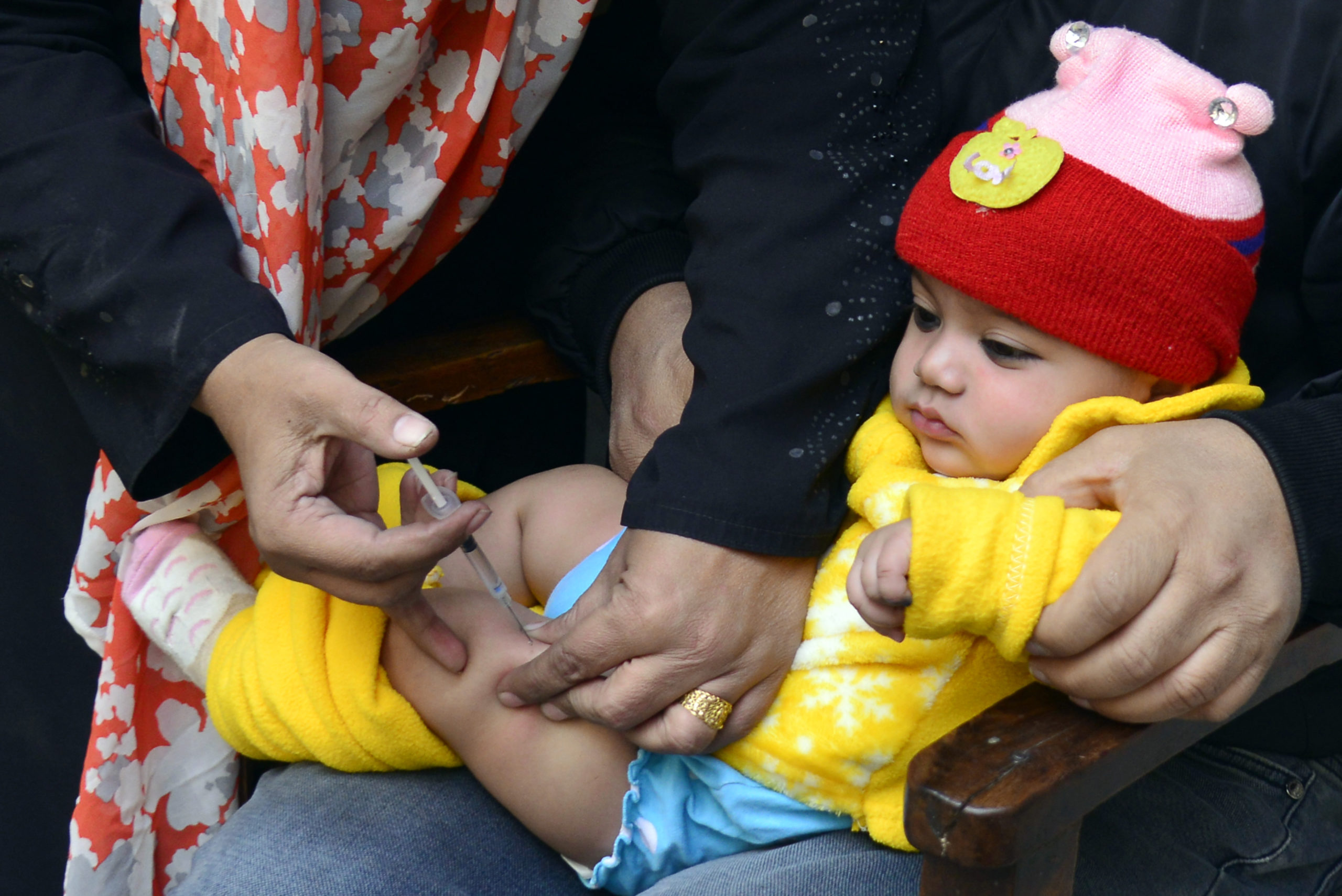
Brazzaville, 19 December 2019 – Kenya, Mozambique and Niger have curbed polio outbreaks that erupted in different episodes over the past 24 months, World Health Organization (WHO) announced.
Transmission of vaccine-derived poliovirus was detected in the three countries in 2018, affecting 12 children. No other cases have since been detected.
“Ending outbreaks in the three countries is proof that the implementation of response activities and ensuring that three rounds of high-quality immunization campaigns are conducted can stop the remaining outbreaks in the region,” said Dr Modjirom Ndoutabe, Coordinator of the WHO-led polio outbreaks Rapid Response Team for the African Region.
“We are strongly encouraged by this achievement and determined in our efforts to see polio eradicated from the continent. It is a demonstration of the commitment by Governments, WHO and our partners to ensure that future generations live free of this debilitating virus,” added Dr Ndoutabe.
Vaccine-derived polioviruses are rare, but these viruses affect unimmunized and under-immunized populations living in areas with inadequate sanitation and low levels of polio immunization. When children are immunized with the oral polio vaccine, the attenuated vaccine virus replicates in their intestines for a short time to build up the needed immunity and is then excreted in the faeces into the environment where it can mutate. If polio immunization coverage remains low in a community and sanitation remains inadequate, the mutated viruses will be transmitted to susceptible populations, leading to emergence of vaccine-derived polioviruses.
No wild poliovirus has been detected anywhere in Africa since 2016. This stands in stark contrast to 1996, a year when wild poliovirus paralysed more than 75,000 children across every country on the continent. The WHO African Region however, is currently facing outbreaks of a rare poliovirus strain known as circulating vaccine derived poliovirus.
The work of the Rapid Response team starts once the lab confirms that a sample collected from either the environment or a paralysed child is caused by a poliovirus. Every minute that passes from then means that the virus is circulating and risks infecting more children that is why the Rapid Response Team deploys with 72 hours. The team supports local health authorities in the affected country in preparing the risk assessment and outbreak response plan. Then assist with launching the emergency response vaccination campaign, called round zero, within 14 days. A second team then takes over after the first eight weeks and continues the outbreak response activities including ensuring that three more rounds of high-quality vaccination campaigns are conducted.
To end outbreak activities in an affected country national and regional disease surveillance and laboratory teams need to confirm that no polio transmission is detected in samples collected from paralysed children, children in contact, and the environment have been negative for at least nine months. Response to the polio outbreak requires a strong multisector collaboration. In these efforts, WHO with other Global Polio Eradication Initiative spearheading partners: UNICEF, Rotary International, the US Centers for Diseases Control (CDC), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) and other stakeholders have been supporting the Government of Angola in implementing measures to end the transmission of the poliovirus.
Countries still experiencing outbreaks of vaccine-derived poliovirus in Africa are: Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Ghana, Nigeria, Togo and Zambia. The risk factors for these outbreaks include weak routine vaccination coverage, vaccine refusal, difficult access to some locations and low-quality vaccination campaigns, which have made immunization of all children difficult.
Countries of the region experiencing outbreaks are continuing to implement outbreak response, following internationally-agreed guidelines and strengthening surveillance activities to rapidly detect any further cases. To successfully implement the outbreak response required, the engagement of government authorities at all levels, civil society and the general population, is crucial to ensure that all children under the age of five are vaccinated against polio.