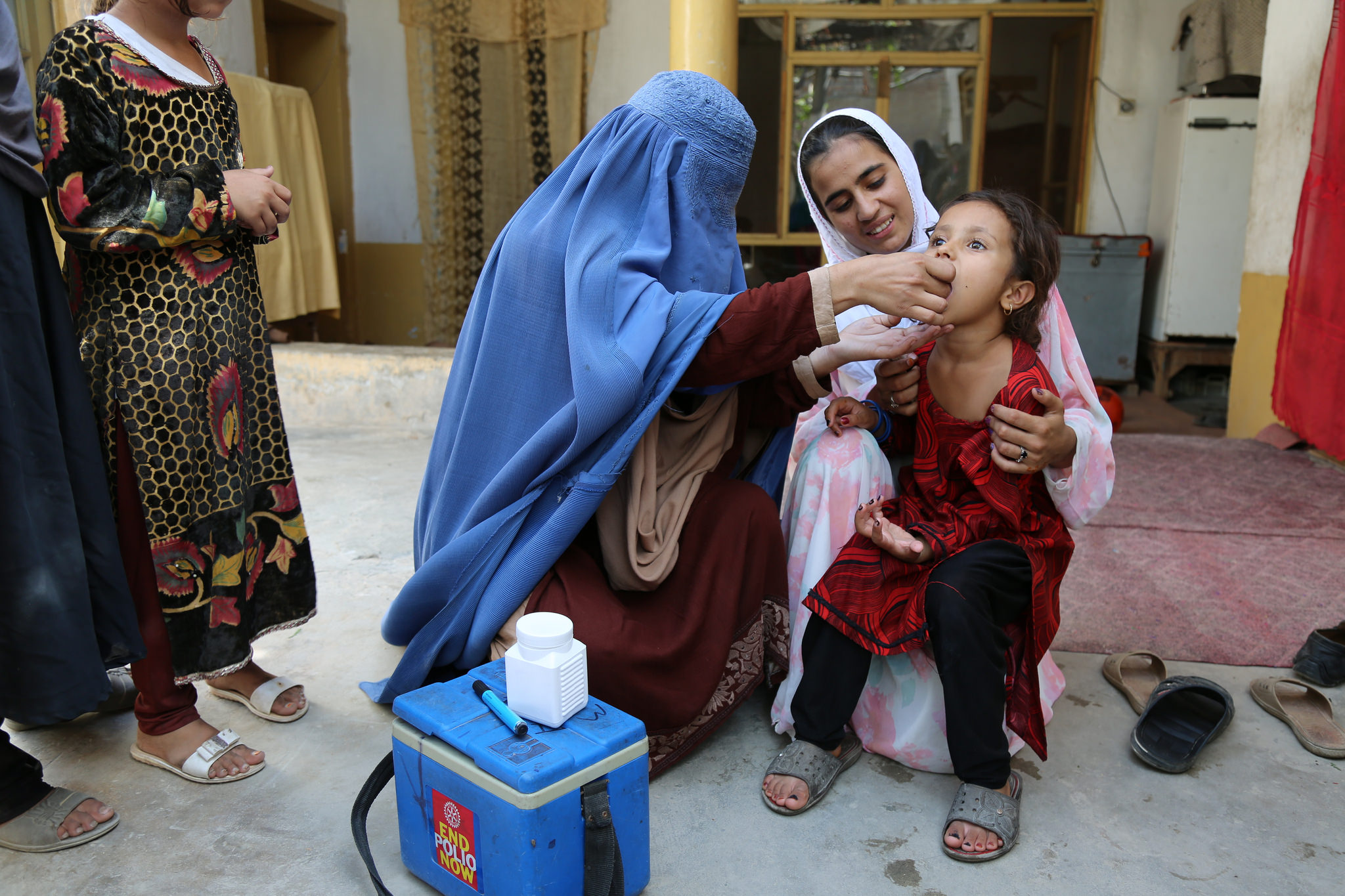
Exciting research is underway on a novel oral polio vaccine for type 2 polio (nOPV2), which – if further trials are successful – could be a potential new tool to provide the same level of protection against poliovirus as the current oral polio vaccine (OPV), but without the same risk of mutating into vaccine-derived poliovirus in under-immunised populations.
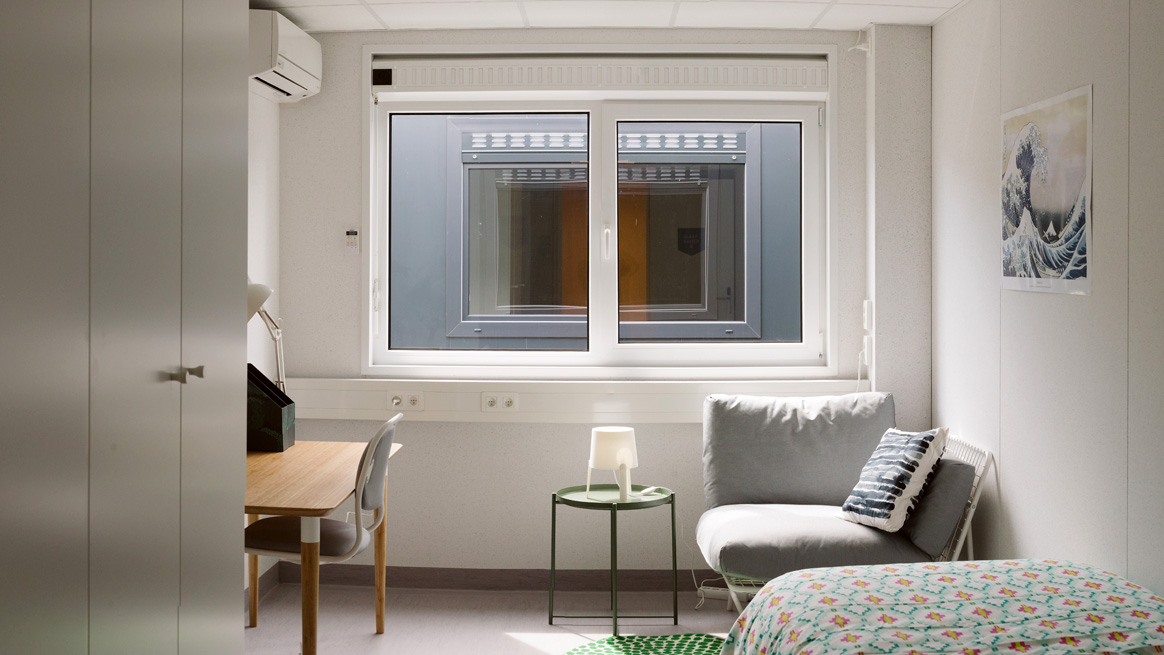
Results from a phase I study to test two nOPV2 candidates were published in The Lancet in early June 2019. The study, led by the University of Antwerp in partnership with a global consortium of researchers and funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, was conducted in 2017 at a unique container park named “Poliopolis” at the University of Antwerp. To test the vaccine, 30 individuals volunteered to spend a month living in the container park – complete with private, air-conditioned rooms, a lounge area and foosball table, fitness room, dining area, daily schedules of entertainment, exercise and health check-ups.
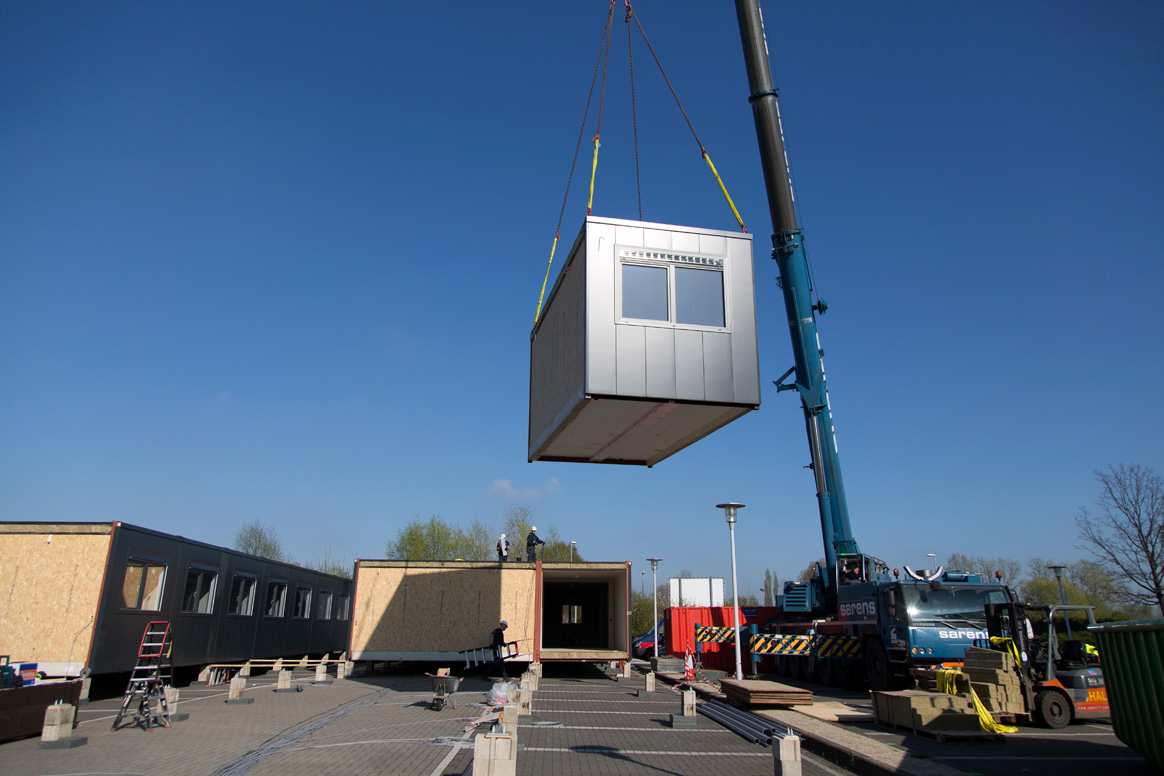

The initial findings from this study are promising, showing that the two vaccines tested at Poliopolis are safe and produce the immune response needed to protect individuals against polio. Results from phase II trials are expected in the coming months, which is when the program will learn whether nOPV2 is a tool that can ultimately be deployed for children at risk of poliovirus transmission.
About nOPV
The nOPV2 vaccine candidates were designed by a consortium of scientists from the UK National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC), the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and manufactured by Bio Farma – with several other institutions playing key roles in the development process. Current clinical trials testing the vaccine candidates are taking place in Belgium and Panama. If ongoing and future trials are successful, nOPV2 could be kept in stockpiles and used in case of a VDPV2 outbreak in the near future or after eradication. This would make it a potentially vital tool for keeping the world free of all forms of the poliovirus.

OPV, which has been responsible for reducing the number of global polio cases by over 99% since the launch of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) in 1988, remains the best available tool to eradicate wild poliovirus. It is a safe and effective vaccine that will continue being used widely.
This exciting research on nOPV, however, is just one more way in which the GPEI has continued to innovate to overcome hurdles over the past three decades. We look forward to seeing the results of further research that will tell us if we can add this vaccine to our “toolbox” to protect all children from polio.