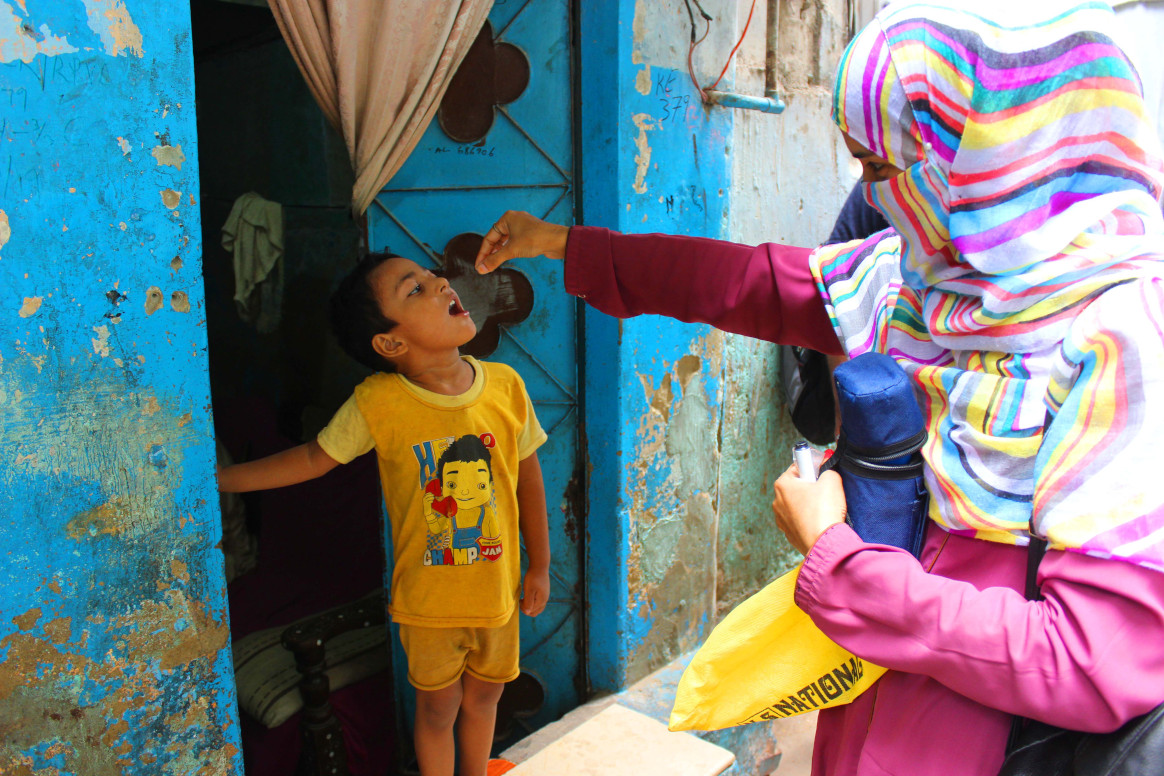
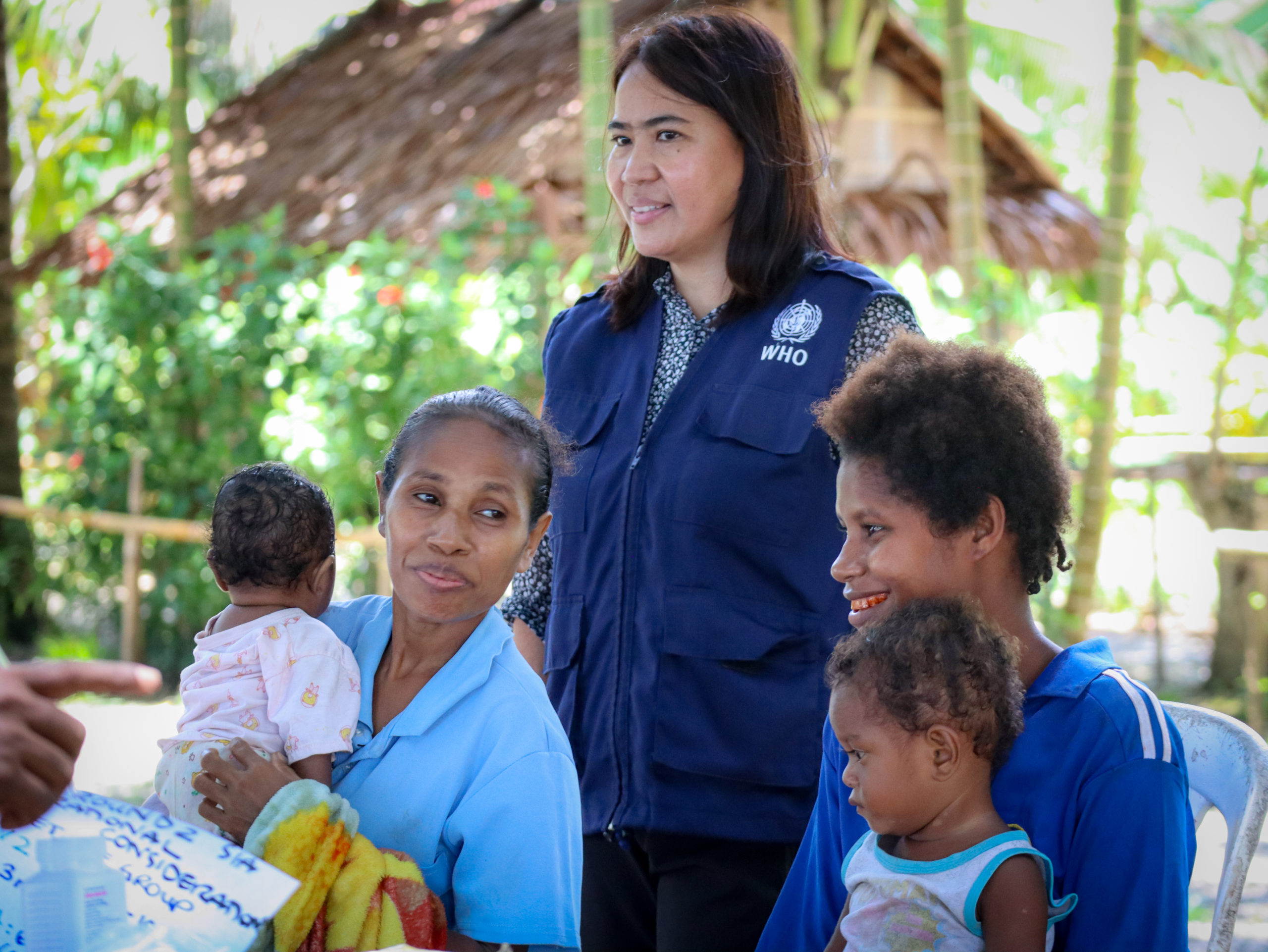
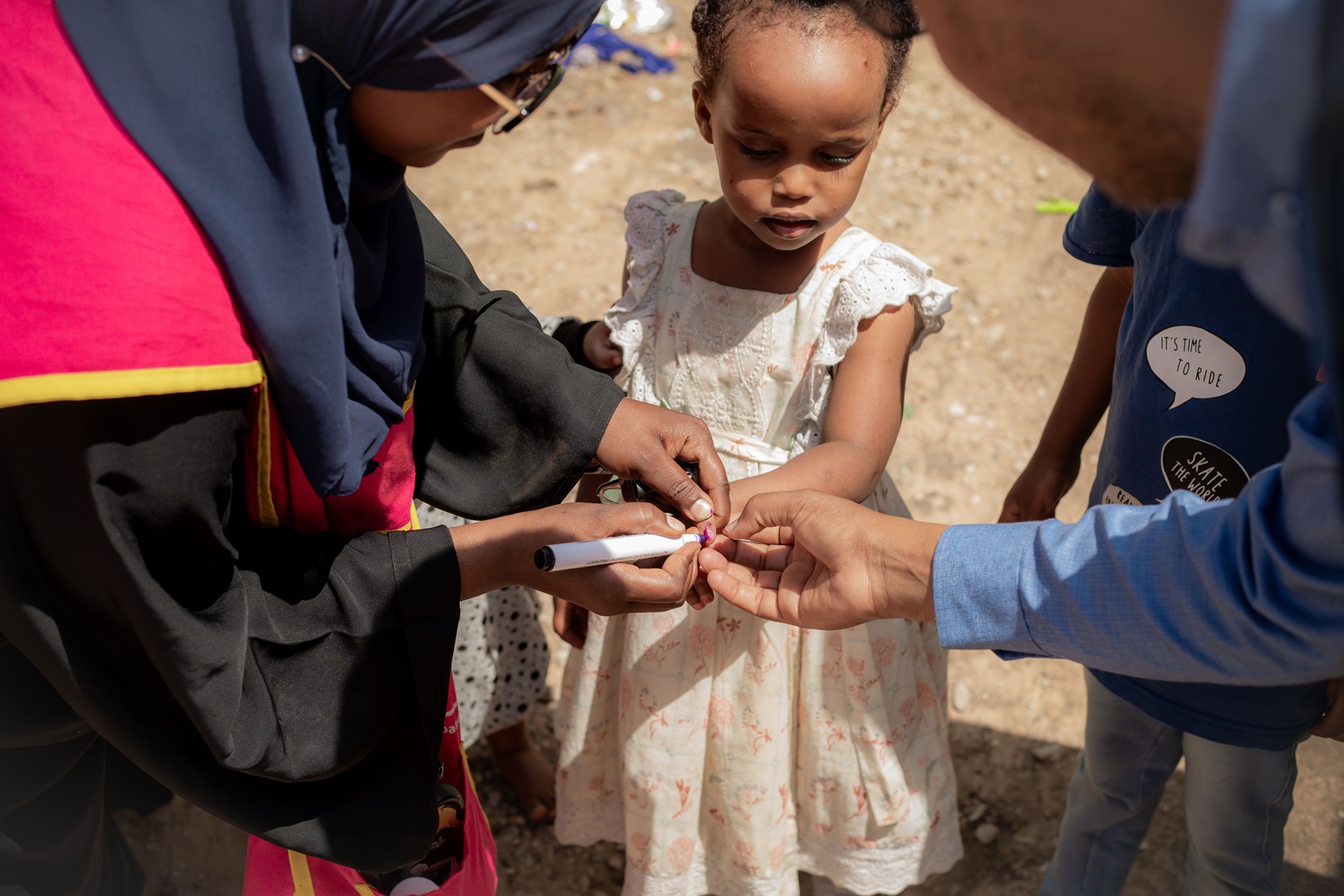
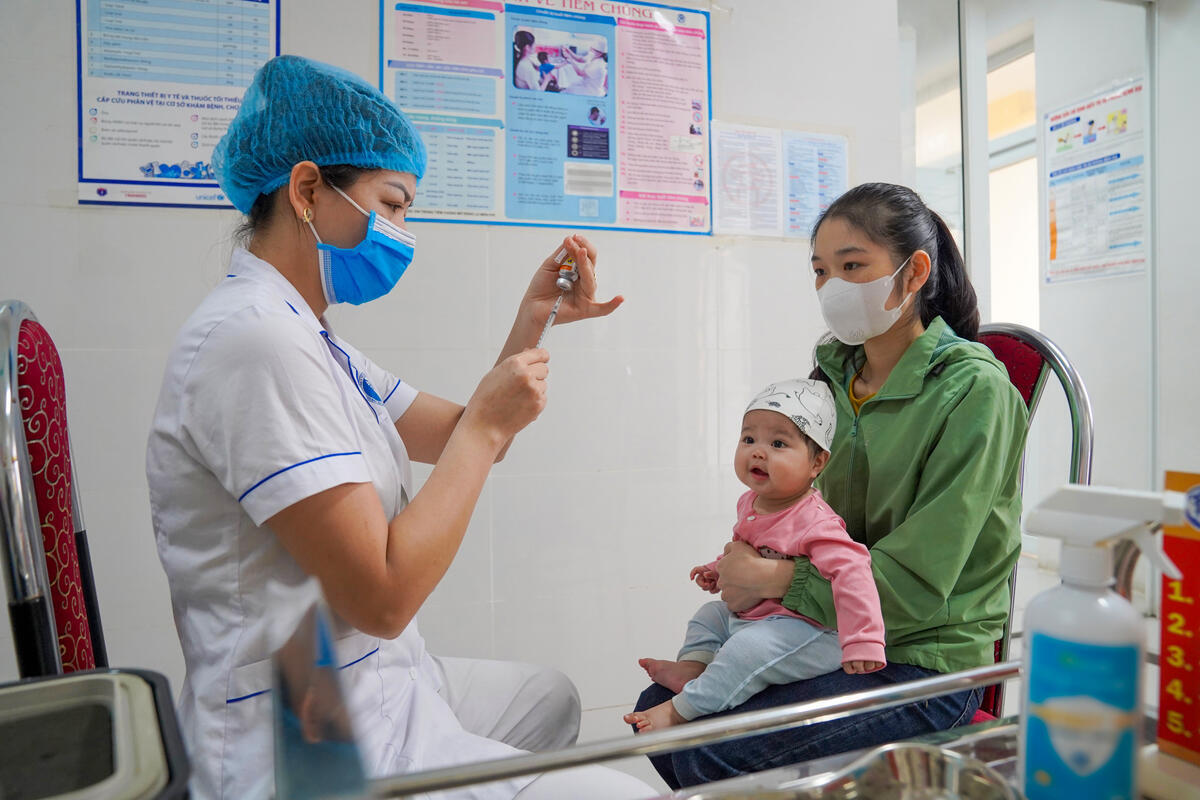
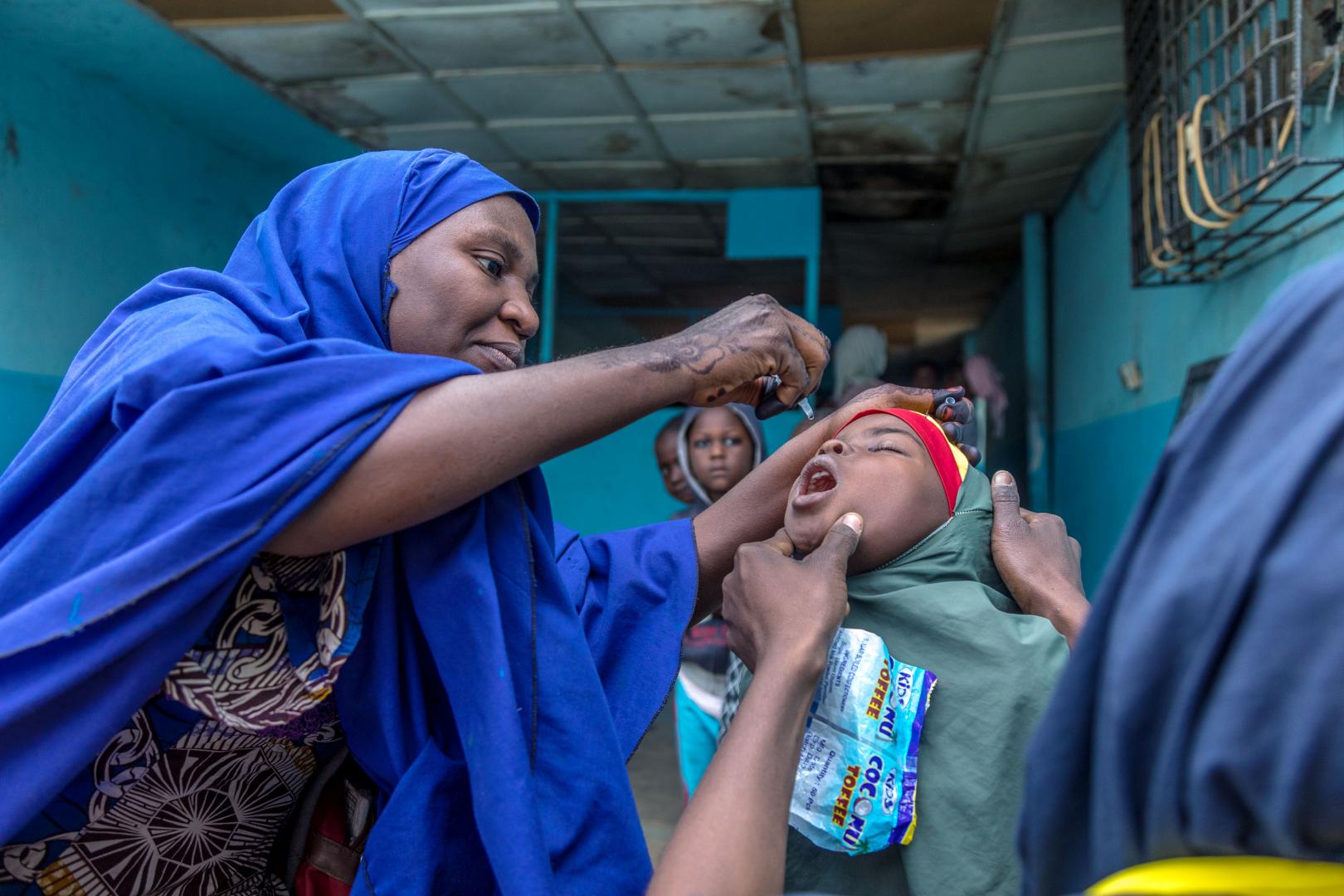
Vaccinators in countries including Afghanistan, Angola, Burkina Faso and Pakistan took to the streets this month to fill urgent immunity gaps that have widened in the under-five population during a four month pause to polio campaigns due to COVID-19.
Campaigns resumed in alignment with strict COVID-19 prevention measures, including screening of vaccinators for symptoms of COVID-19, regular handwashing, provision of masks and a ‘no touch’ vaccination method to ensure that distance is maintained between the frontline worker and child. Only workers from local communities provided house-to-house vaccination to prevent introduction of SARS-CoV2 infection in non-infected areas.
Although necessary to protect both health workers and communities from COVID-19, the temporary pause in house-to-house campaigns, coupled with pandemic-related disruptions to routine immunization and other essential health services, has resulted in expanding transmission of poliovirus in communities worldwide. Modelling by the polio programme suggests a potentially devastating cost to eradication efforts if campaigns do not resume.
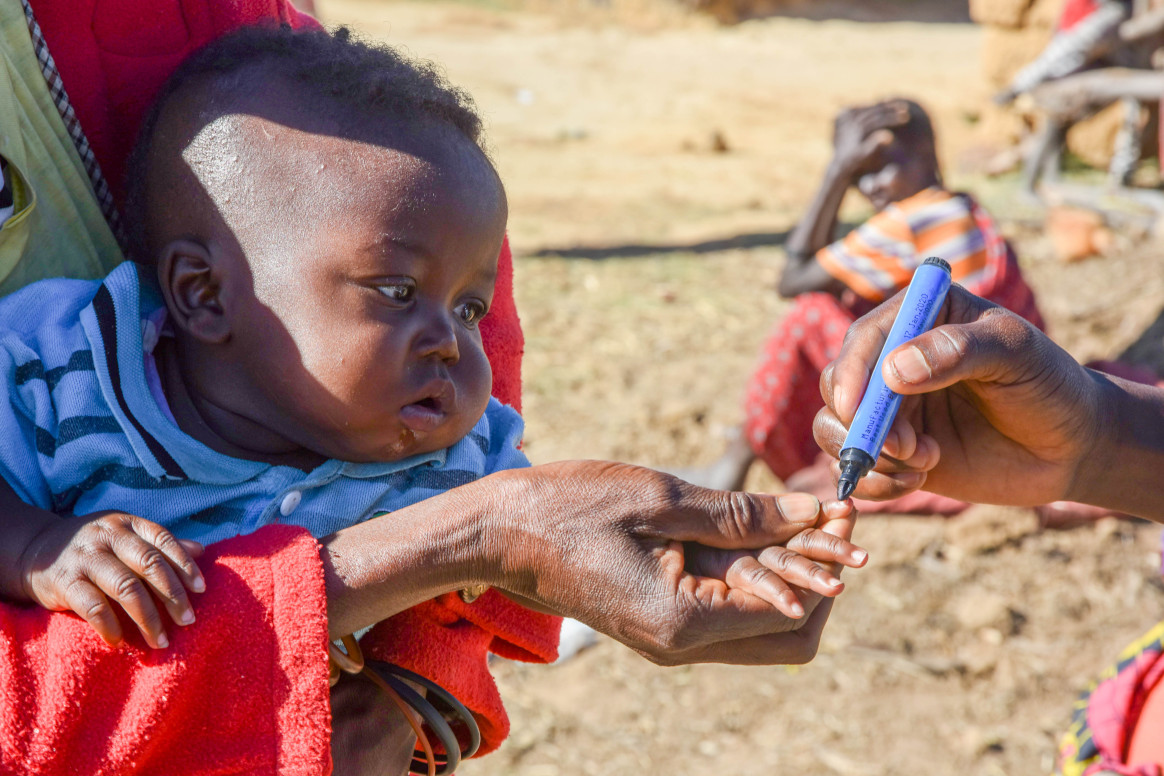

In Afghanistan, 7858 vaccinators aimed to vaccinate 1 101 740 children in three provinces. Vaccinators were trained on COVID-19 infection control and prevention measures and were equipped to answer parents’ questions about the pandemic. Through the campaign, teams distributed 500 000 posters and 380 000 flyers featuring COVID-19 prevention messages.
In Angola, 1 287 717 children under five years of age were reached by over 4000 vaccinators observing COVID-19 infection prevention and control measures. All health workers were trained on infection risk, and 90 000 masks and 23 000 hand sanitizers were distributed by the Ministry of Health.
In Burkina Faso, 174 304 children under five years of age were vaccinated in two high-risk districts by 2000 frontline workers. Vaccinators and health care workers were trained on maintaining physical distancing while conducting the vaccination. 41 250 masks and 200 litres of hand sanitizer were made available through the COVID-19 committee in the country to protect frontline workers and families during the campaign.
In Pakistan, almost 800 000 children under the age of five were reached by vaccinators in districts where there is an outbreak of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus. Staff were trained on preventive measures to be followed during vaccination, including keeping physical distance inside homes and ensuring safe handling of a child while vaccinating and finger marking them.

“Our early stage analysis suggests that almost 80 million vaccination opportunities have been missed by children in our Region due to COVID-19, based on polio vaccination activities that had to be paused,” said Dr Hamid Jafari, Director for Polio Eradication in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. “That’s close to 60 million children who would have received important protection by vaccines against paralytic polio.”
Over the coming months, more countries plan to hold campaigns to close polio outbreaks and prevent further spread, when the local epidemiological situation permits.
“Our teams have been working across the Region to support the COVID-19 response since the beginning of the pandemic, as well as continuing with their work to eradicate polio,” said Dr Hamid Jafari. “We must now ensure that we work with communities to protect vulnerable children with vaccines, whilst ensuring strict safety and hygiene measures to prevent any further spread of COVID-19”.
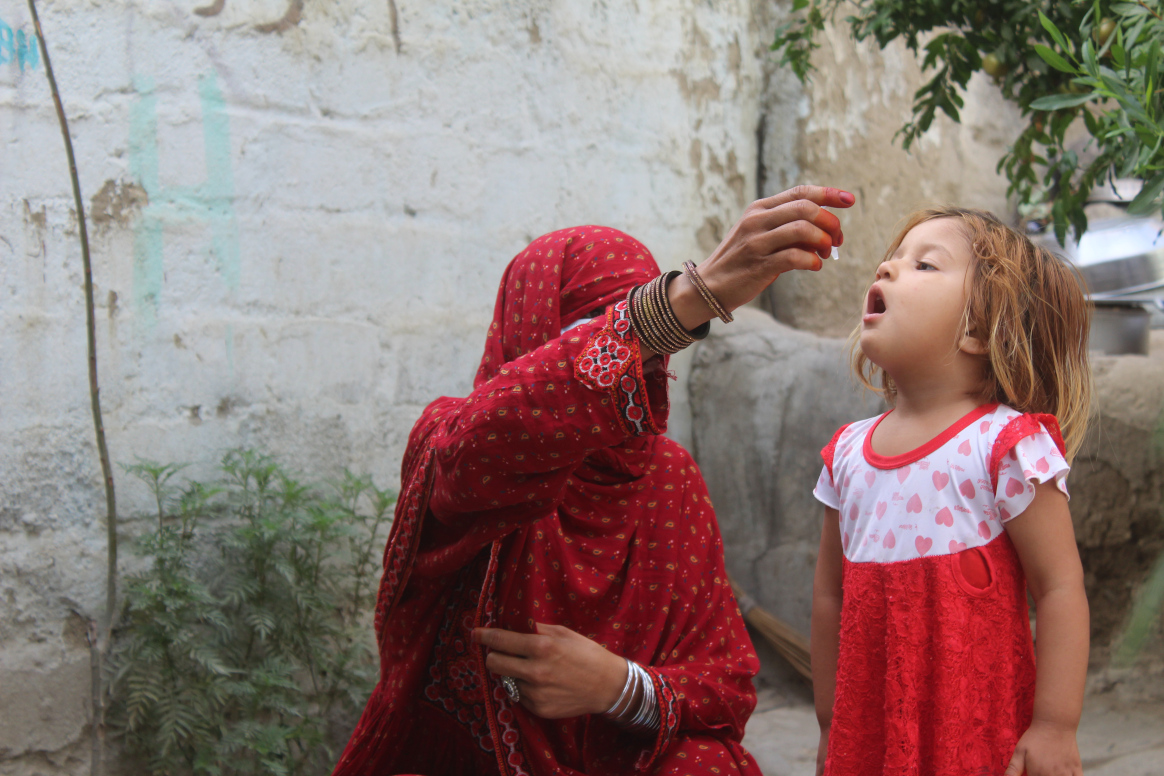

Dr Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa, commented, “We cannot wait for the COVID-19 pandemic to be contained to resume immunization activities. If we stop immunization for too long, including for polio, vaccine-preventable diseases will have a detrimental effect on children’s health across the region.”
“The campaigns run by the Polio Eradication Programme demonstrate that mass immunization can be safely conducted under the strict implementation of COVID-19 infection prevention and control guidelines.”