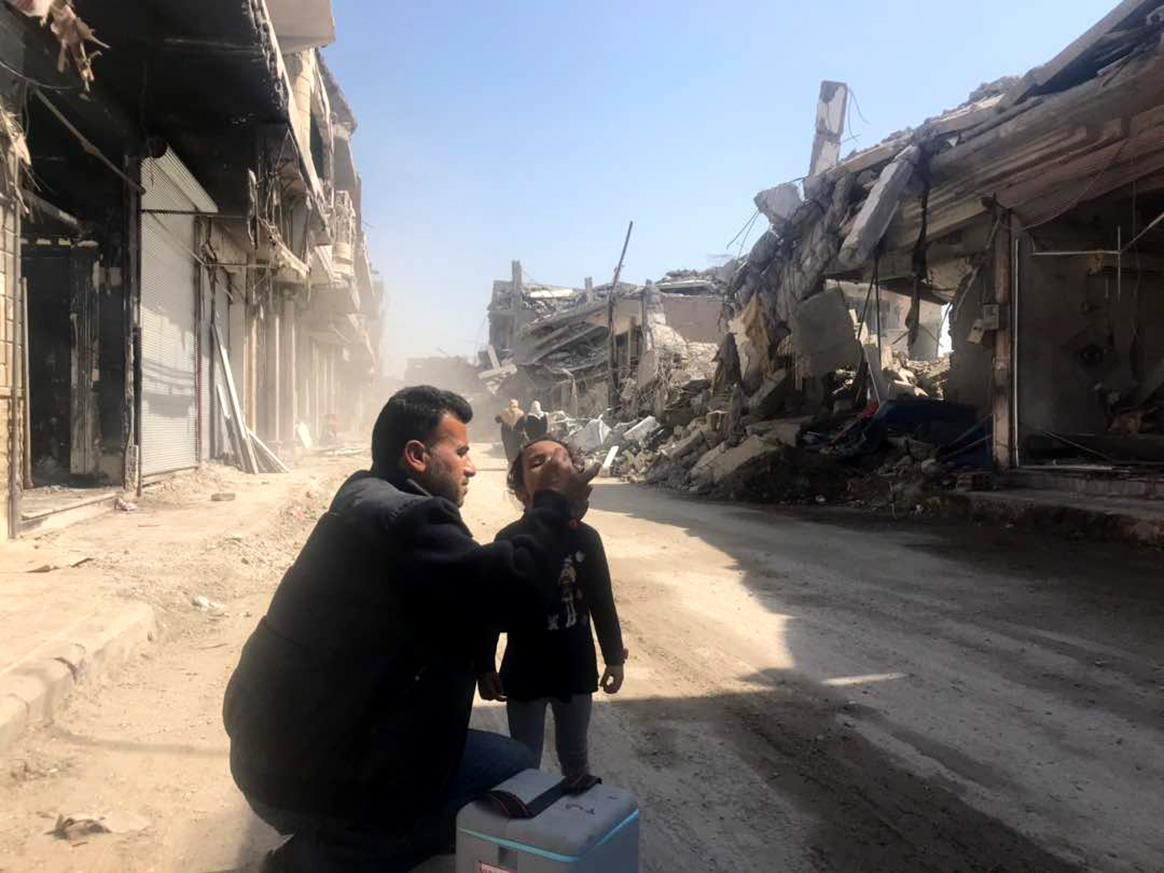
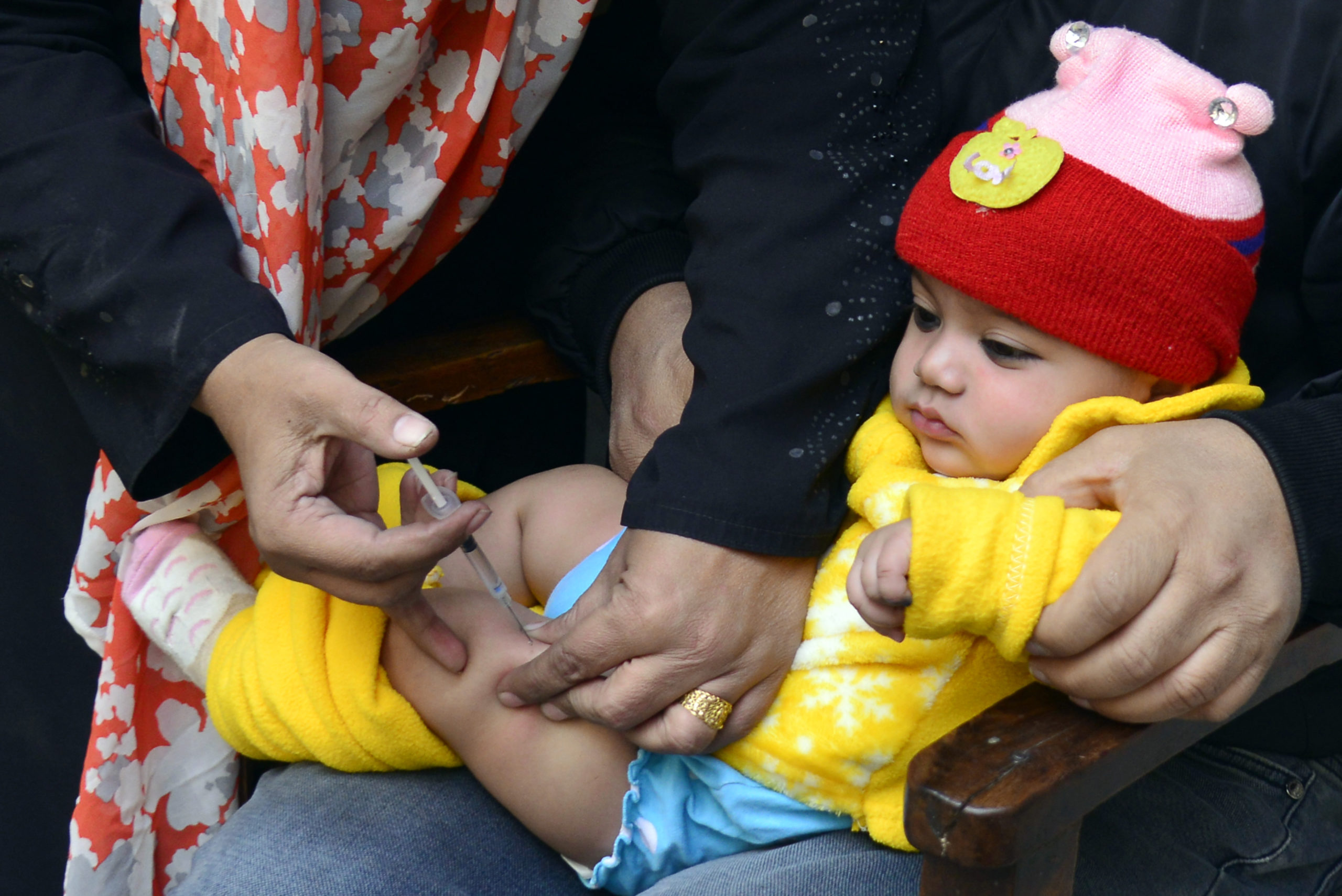
From the front passenger seat of a small utility truck, Mahmoud Al-Sabr hangs out the window, looking for families and any child under five years old to be vaccinated against polio. As the car he travels in dodges rubble and remnants of buildings that once stood tall in Raqqa city, he flicks the ‘on’ switch for his megaphone.
“From today up to January 20, free and safe vaccine, all children must be vaccinated to be protected from the poliovirus that hit Syria for the second time,” he calls, beckoning families with young children who have recently returned to Raqqa city to come outside of their makeshift homes amongst destroyed buildings, to have their children vaccinated.
In 2017, amidst the protracted conflict and humanitarian crisis in Syria, an outbreak of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) was detected, threatening an already vulnerable population.
Due to ongoing conflict, Raqqa city, which was once host to half of the governorates population, had been unreached by any vaccination activity or health service since April 2016. During the first phase of the outbreak response, more than 350,000 resident, refugee and displaced children were vaccinated against polio in Syria, but “Raqqa city remained inaccessible,” says Mahmoud.
In January 2018, polio vaccinators conducted the first vaccination activity in the city since it became accessible again, following the end of armed opposition group control.
There were no longer accurate maps or microplans that vaccinators could use to guide them in their work. Unrecognizable, the city was a picture of devastation with few dwellings untouched by the violence that once caused families to flee. The house-to-house vaccination campaign that usually helps the programme to reach every child under five wouldn’t work here. Teams knew they would have to innovate to seek out families wherever they were residing to vaccinate their children.
“All children must be vaccinated to protect against poliovirus,” Mahmoud echoes around shelled out buildings, and slowly mothers and fathers carrying their children start to appear in the street.
Mahmoud and Ahmed Al-Ibraim are one of 12 mobile teams that are going street by street, building by building, by car in search of children to vaccinate. Carrying megaphones to alert families of their presence and to tell them of the precious vaccines they carry that will protect their children from the paralysing but preventable poliovirus, they slowly cover areas of the city now unrecognizable.
“No one could enter Raqqa City now for two years,” says Abdul-Latif Al-Mousa, a lawyer from the city who joined the outbreak response as a Raqqa City supervisor for polio campaigns. “So children have not been vaccinated here since that time. Now that people have returned, we are learning where they have returned from and we vaccinate them regardless.”
“We must reach each child with the vaccine to protect them – polio is preventable, why should they suffer more?” Ahmed appeals.
Campaign brings vaccines and familiar faces
Vaccines were not the only thing to return to Raqqa City in January. It was the first time that WHO polio focal point Dr Almothanna could return to Raqqa City after being force to flee under the rule of the armed opposition group. Imprisoned for refusing the demands of the group, friends and neighbours of Dr Almothanna facilitated his escape from the city in 2016.
Dissatisfied but not deterred, Dr Almothanna continued to work with the polio programme, serving the whole governorate except his own city. Over the course of the January 2018 campaign, he worked tirelessly with vaccination teams to ensure more than 20 000 children under the age of five in Raqqa City received a dose of mOPV2 to protect them against polio. For many, it was the first vaccination they had received. In the additional campaigns that followed in March 2018, even more children were reached.
The microplans developed by vaccinator teams in the first vaccination round have become a critical road map for reaching children and families with health services, accounting for the locations of returned families and information about neighbouring families that teams had not yet located. In the second round, the microplans were updated to include new families who had returned.
Syria reported 74 circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus cases between March and September 2017. It has been more than six months since the last case was reported (21 September 2017). Efforts are continuing to boost immunity in vulnerable populations, maintain sensitive surveillance for polioviruses and strengthen routine immunization to enhance the population immunity.