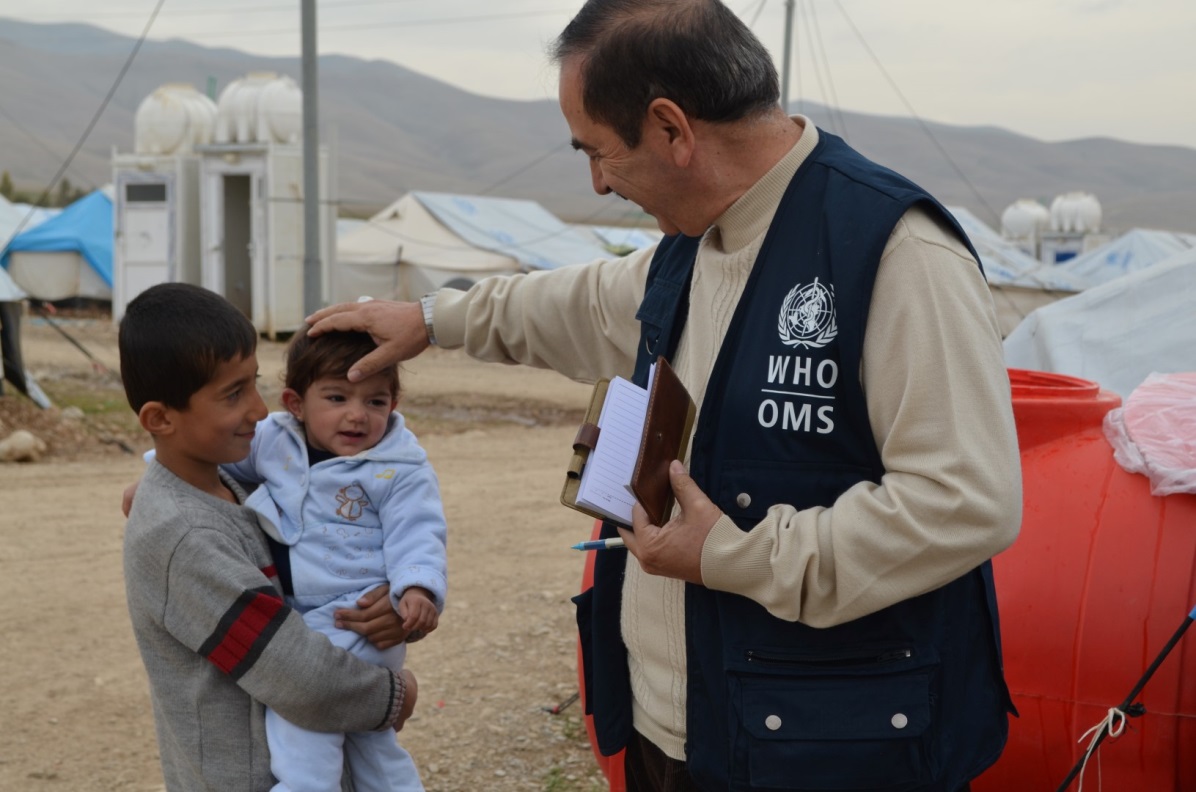
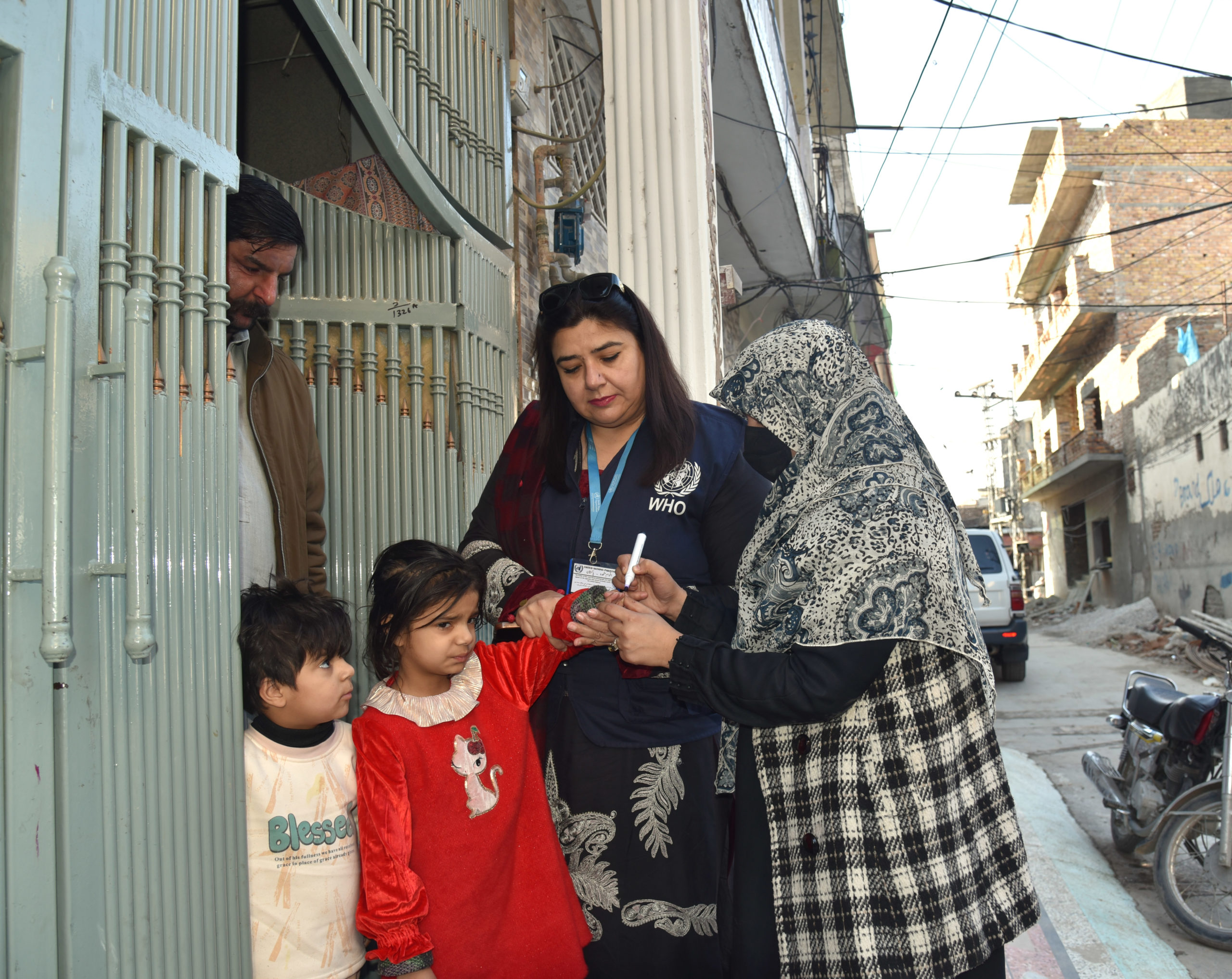
In recent years, the global drive to eradicate polio has seen the virus cornered in fewer places than ever before. Yet polio’s final strongholds are some of the most complicated places in the world to deliver vaccination campaigns. Insecurity and conflict are some of the challenges to delivering vaccines, as well as populations on the move, testing terrain and weather, and weak health systems.
In 2013, polio outbreaks in Central Africa, the Horn of Africa and the Middle East paralysed hundreds of children. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) developed strategies to deliver vaccines and stop the virus, even when access seemed impossible. All three of these outbreaks were put to an end just a year later, by not letting the complexity of the situation undermine the quality of vaccination campaigns.
The valuable lessons learned by the GPEI in tackling these outbreaks are now being used to end polio in the final polio endemic countries – Afghanistan, Nigeria and Pakistan – as well as to stop a newly-detected circulating vaccine-derived polio outbreak in Syria.
Challenges to immunization in emergencies
Disruptions to routine immunization systems and mass displacement caused by conflict can rapidly reduce population immunity, making individuals much more vulnerable to polio outbreaks. Polio eradication relies on being able to repeatedly access over 95% of children with vaccines. Yet emergency settings can interrupt systems that gather data about a population, functioning health facilities, health care personnel, vaccine supplies, cold chains to keep vaccines safe, power supply, financial resources, population demand for vaccines, and disease surveillance. When these factors are at play, the GPEI calls on past experience and adopts new approaches to reach every last child.
Lessons learned in conflict zones
Community acceptance and trust
When there are barriers to access, the first step is to have community trust and acceptance of vaccination. Every community and context is different and calls for a targeted approach to communicate exactly why immunization campaigns need to take place. The polio eradication programme identifies and trains vaccinators from local communities, engages religious figures to support the campaign and gets local leaders on board to advocate for, plan and implement vaccination efforts. The polio programme has seen time and time again that when securing access is a challenge, the answer often lies in the very communities we are trying to reach.
| In Pakistan, a number of Religious Support Persons have been recruited based on the guidance of the Islamic Advisory Group for polio eradication, to address concerns of local communities about polio vaccinations in some challenging areas of the country. This has resulted in enhanced community acceptance of immunization, with refusal rates of less than 1.5%, as well as broader child welfare interventions. |
Opportunistic vaccination campaigns
When different forces make populations periodically inaccessible, vaccination schedules can be interrupted and leave pockets of people unprotected against polio. In these situations, health authorities try to reach children in whatever ways are possible. Transit points can be set up around insecure areas, to vaccinate children as they enter or leave; vaccinators work with local leaders to track and reach populations on the move; communities within the inaccessible areas can store and deliver vaccines themselves; and brief periods of calm can be used to bring vaccines and other essential health services into villages through a health camp.
| In Pakistan, over 350 transit points have been set up in recent years along borders and near areas with access challenges. This is one of the innovative approaches that have reduced the percentage of children missed on vaccination campaigns from 25% in 2014 to 5% in 2017. |
Negotiated access
In the most challenging situations, when all other approaches are not able to overcome the severity of vaccination challenges, the programme has negotiated access by engaging non-state actors, governments, religious figures and local leaders. Reiterating the humanitarian principle of “neutrality,” the GPEI works with all parties to a conflict to highlight the importance of vaccination campaigns, and secure agreements to access targeted communities for specific periods of time.
| In the past, negotiating access to conflict zones was comparatively simple to today. In the 1980s, days of tranquillity were first used in the Americas, through negotiation with two groups – often the government and the opposition group. In many areas where polio persists, there are many different actors and groups engaged in conflict, so negotiation is more complex. It includes identifying who is appropriate to negotiate with in any given district or area, and, importantly, finding appropriate negotiators. Often, third party partners such as the International Committee for the Red Cross are engaged to negotiate operations of vaccination campaigns in security-compromised areas, and in areas where vaccination bans have been imposed by local authorities. |
Conflict and insecurity continue to pose significant challenges to eradication. Our best chance of ending polio for good in conflict zones lies in learning from these lessons and adhering to the principles of neutrality in health.