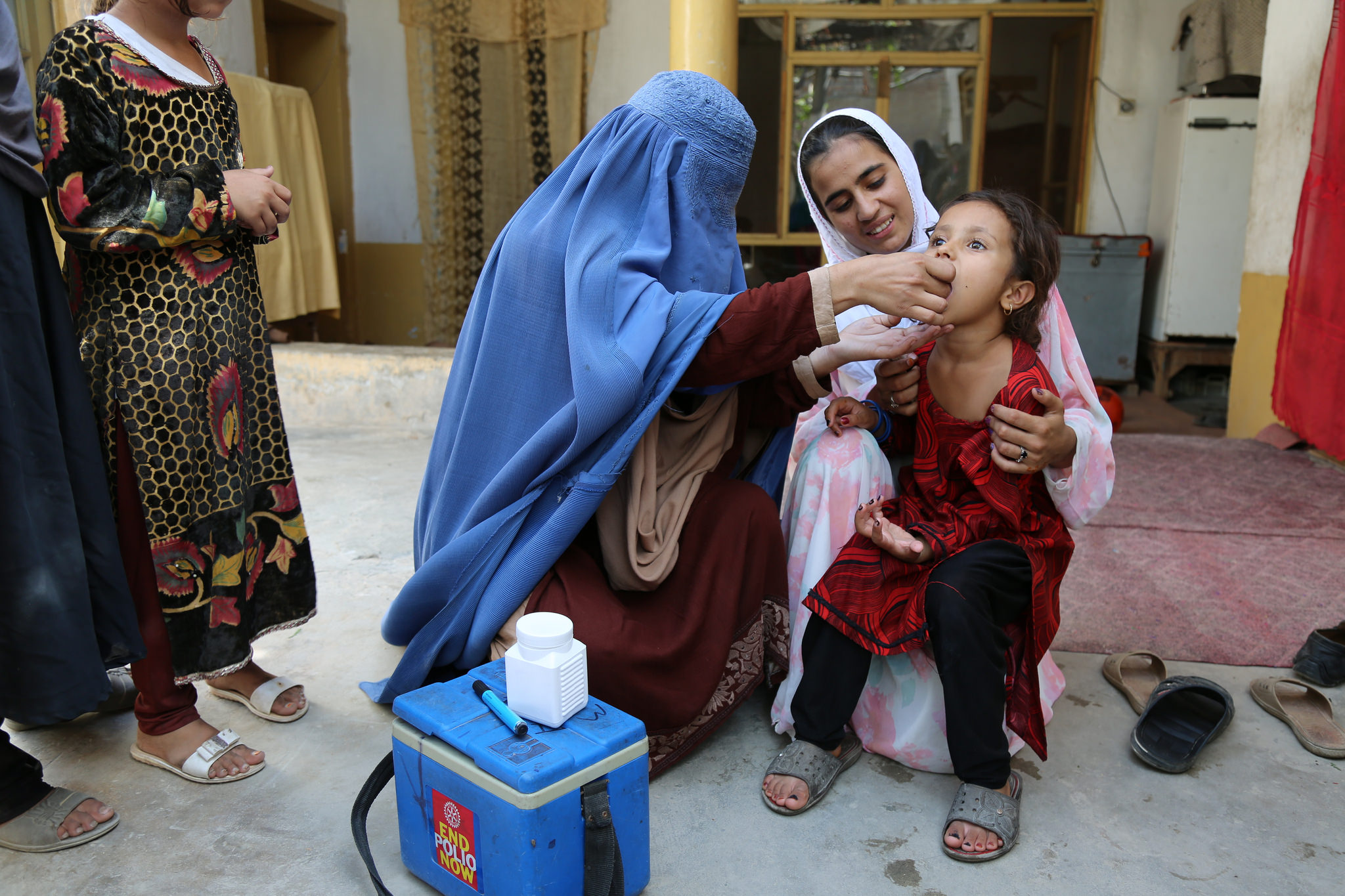
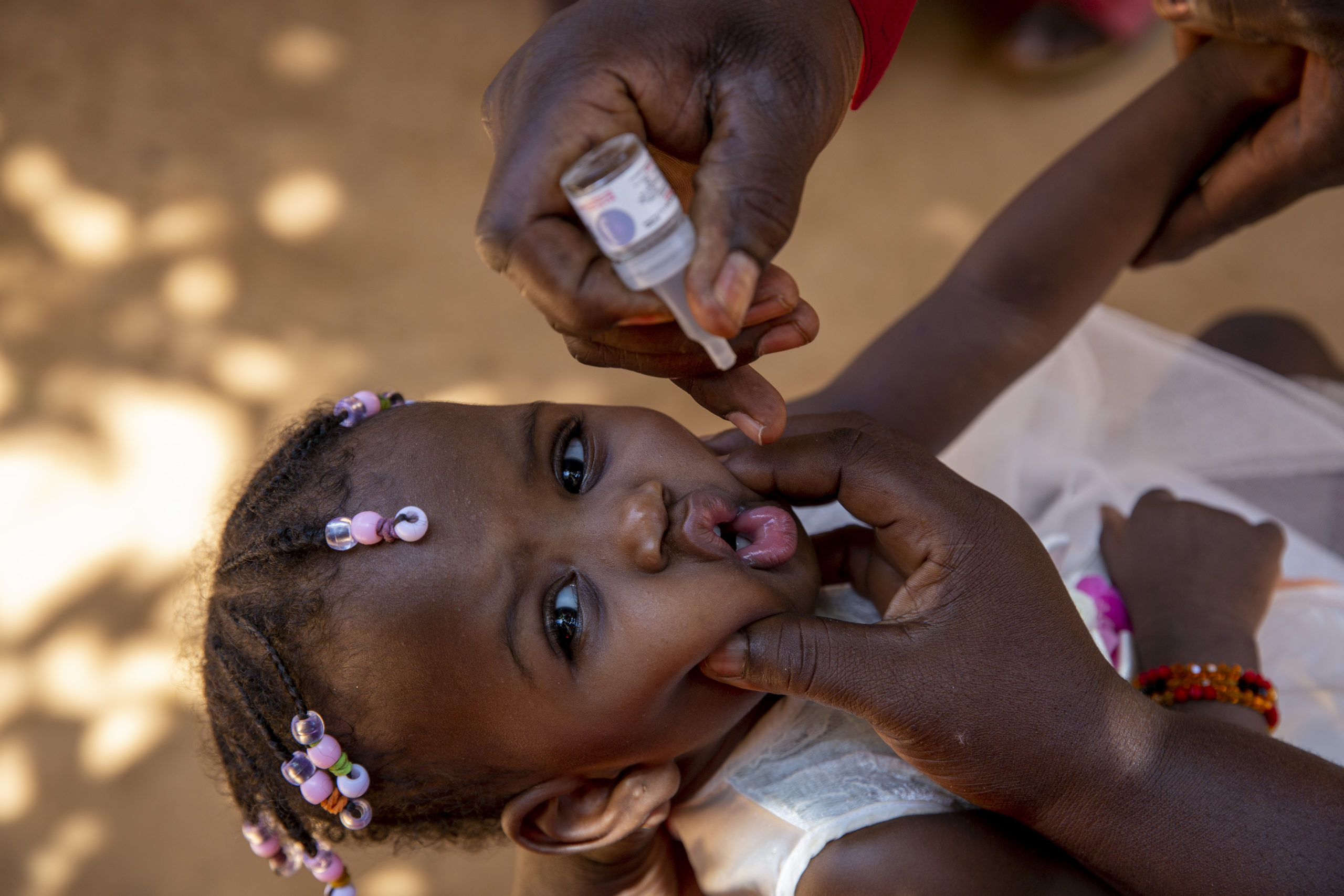
17 February 2022 As a result of ongoing disease surveillance, the Global Polio Laboratory Network (GPLN) has confirmed the presence of type 1 wild poliovirus (WPV1) in a child suffering from paralysis in Tsabango, Lilongwe, Malawi. Analysis shows that the virus is genetically linked to WPV1 that was detected in Pakistan’s Sindh province in October 2019.
The three-year-old girl in Malawi experienced onset of paralysis on 19 November 2021, and stool specimens were collected for testing on 26 and 27 November. Sequencing of the virus conducted in February by the National Institute for Communicable Diseases in South Africa and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed this case as WPV1.
Detection of WPV1 outside the world’s two remaining endemic countries, Pakistan and Afghanistan, is a serious concern and underscores the importance of prioritizing polio immunization activities. Until polio is fully eradicated, all countries remain at risk of importation and must maintain high vaccination coverage to protect all children from polio.
The GPEI is supporting health authorities in Malawi to conduct a thorough assessment of the situation and begin urgent immunization activities in the subregion to mitigate any risk of spread. Surveillance measures are also being expanded in Malawi and neighboring countries to detect any other potential undetected transmission.
As an imported case from Pakistan, this detection does not affect the WHO African Region’s wild poliovirus-free certification status officially marked in August 2020. Malawi last recorded a case of wild poliovirus in 1992. The polio eradication programme has seen importations from endemic countries to regions that have been certified wild poliovirus-free in the past, and has moved quickly to successfully stop transmission of the virus in these areas.
Polio anywhere is a threat to children everywhere. Now is the time for all parties to recommit to ending all forms of polio for good.