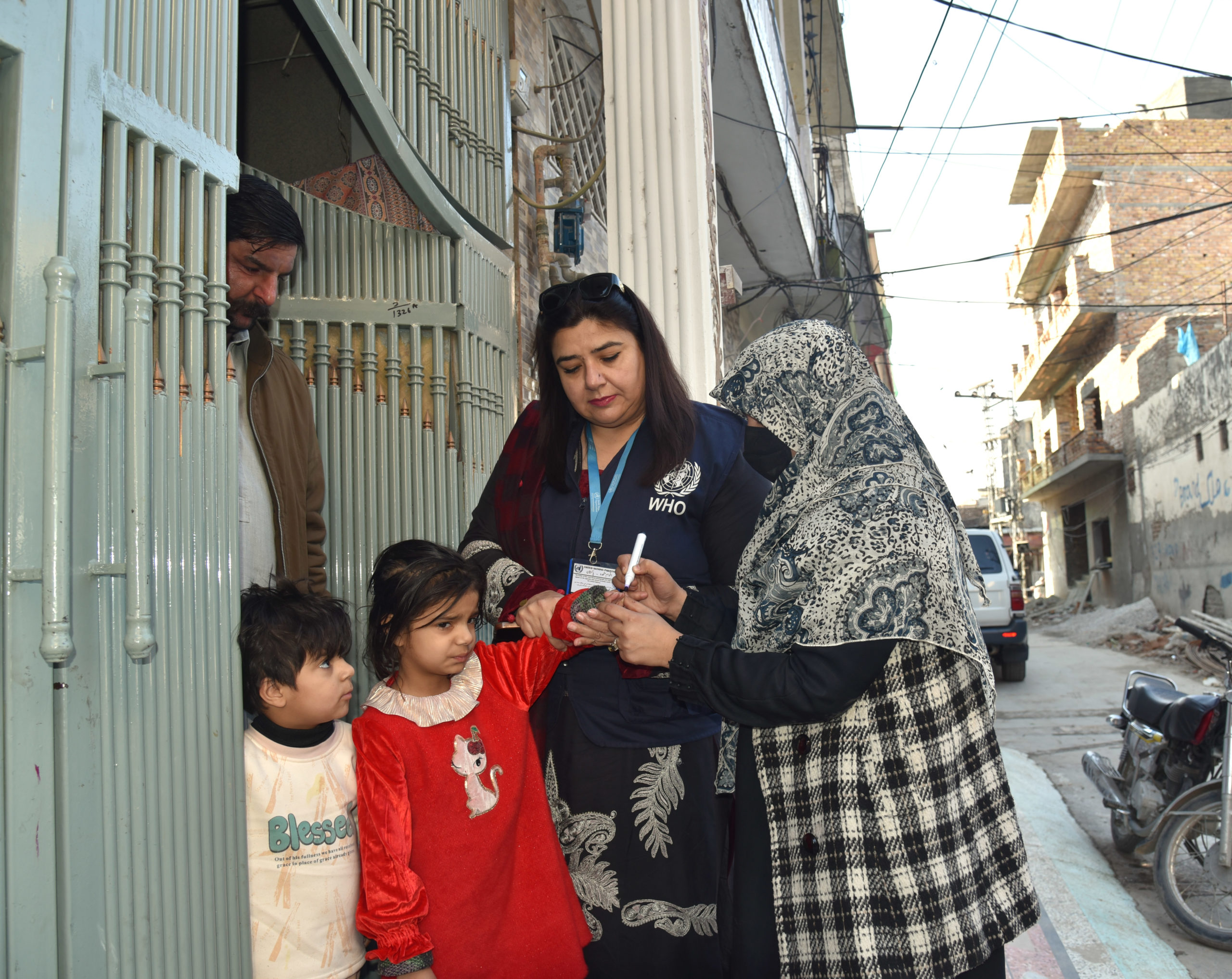
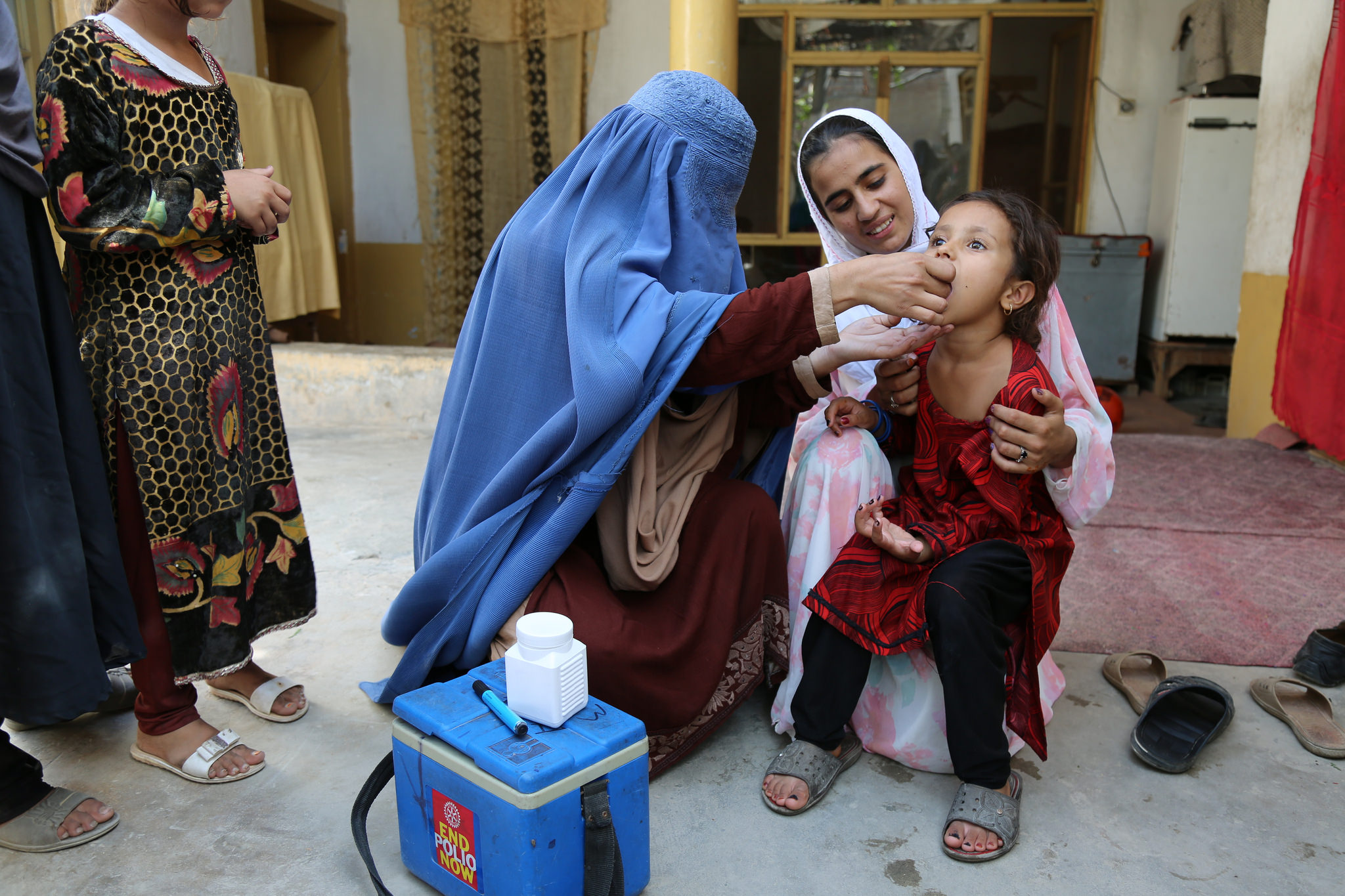
In October 2022, the Technical Advisory Group (TAG) for Afghanistan and Pakistan met in Muscat, Oman, to conduct a thorough review of ongoing polio eradication efforts in the remaining polio endemic countries. During the 6-day meeting they also provided strategic technical guidance on steering efforts towards successful interruption of the poliovirus in both countries in 2023.
Polio programmes make significant progress, despite challenges
The TAG recognized the accomplishments of the polio programmes despite longstanding humanitarian crisis in Afghanistan and unprecedented levels of flooding across Pakistan that affected almost 33 million people. The progress comes due to concerted efforts by all stakeholders across all levels, intense vaccination schedule, timely programmatic pivots to changing epidemiology and the full support of law enforcement and security agencies in implementation of polio vaccination campaigns.
Members noted the high level of sustained political commitment to polio in both countries. In Afghanistan, since the political transition, nationwide campaigns have allowed the polio programme access to almost 10 million children, 3.5 million of whom were previously inaccessible. In Pakistan, intensified vaccination activities and strategic approaches were used to reach missed children.
The TAG also acknowledged the strategic role played by the Emergency Operations Centres (EOCs) in strengthening coordination and providing programmatic oversight at the national and regional levels.
Promising epidemiological trends provide a window of opportunity
Remarkable improvements in epidemiology in Afghanistan and Pakistan provide a window of opportunity for interrupting transmission of wild poliovirus. In Pakistan, the virus is endemic only in the southern districts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, and in Afghanistan both cases have been reported from the eastern region. However, no cross-border transmission was recorded in 2022.
In addition to the limited geographical spread, the biodiversity of the genetic clusters is also at an all-time low: down from 8 in 2020 to 2 in 2022 in Afghanistan and from 11 in 2020 to one in 2022 in Pakistan.
Moreover, there has been no detection of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) in either country in the last year. The last cVDPV2 case in Afghanistan had onset of paralysis on 9 July 2021, and the last cVDPV2 case in Pakistan had onset of paralysis on 23 April 2021.
Given the promising epidemiological trends seen in 2022, the TAG noted the possibility of full interruption of polioviruses this year. However, for the 2 programmes to succeed, the TAG proposed major strategic shifts in categorization of risks based on the epidemiological trends. The group of experts’ recommendations include context-specific tactics and technical guidance on activities to prioritize until mid-2023, when the TAGs for Afghanistan and Pakistan will meet again.
This new categorization redefines and re-demarcates the endemic zones in Afghanistan and Pakistan from the outbreak districts and the rest of the country where it is important to maintain children’s immunity. Additionally, it identifies highly vulnerable and consequential areas that are an additional risk category for Pakistan, where historically core reservoirs may play a role in establishing circulation in an event of reinfection.
The TAG also endorsed the 2023 polio supplementary immunization activities’ calendars for Afghanistan and Pakistan and emphasized continued cross-border coordination between the 2 countries, particularly in the key corridors. Finally, the TAG encouraged the continued use of strategies to integrate gender and social behavioural change communication into the programme’s activities, to reach every last child.
To read the reports from the Technical Advisory Group meeting on Afghanistan and Pakistan, click here.