With the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, continued wild polio transmission in the remaining endemic countries and spreading outbreaks of circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses type 2 (cVDPV2), this year began with many challenges facing polio eradication efforts. But amid this new reality, countries and partners of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) intensified their efforts to protect children from lifelong paralysis.
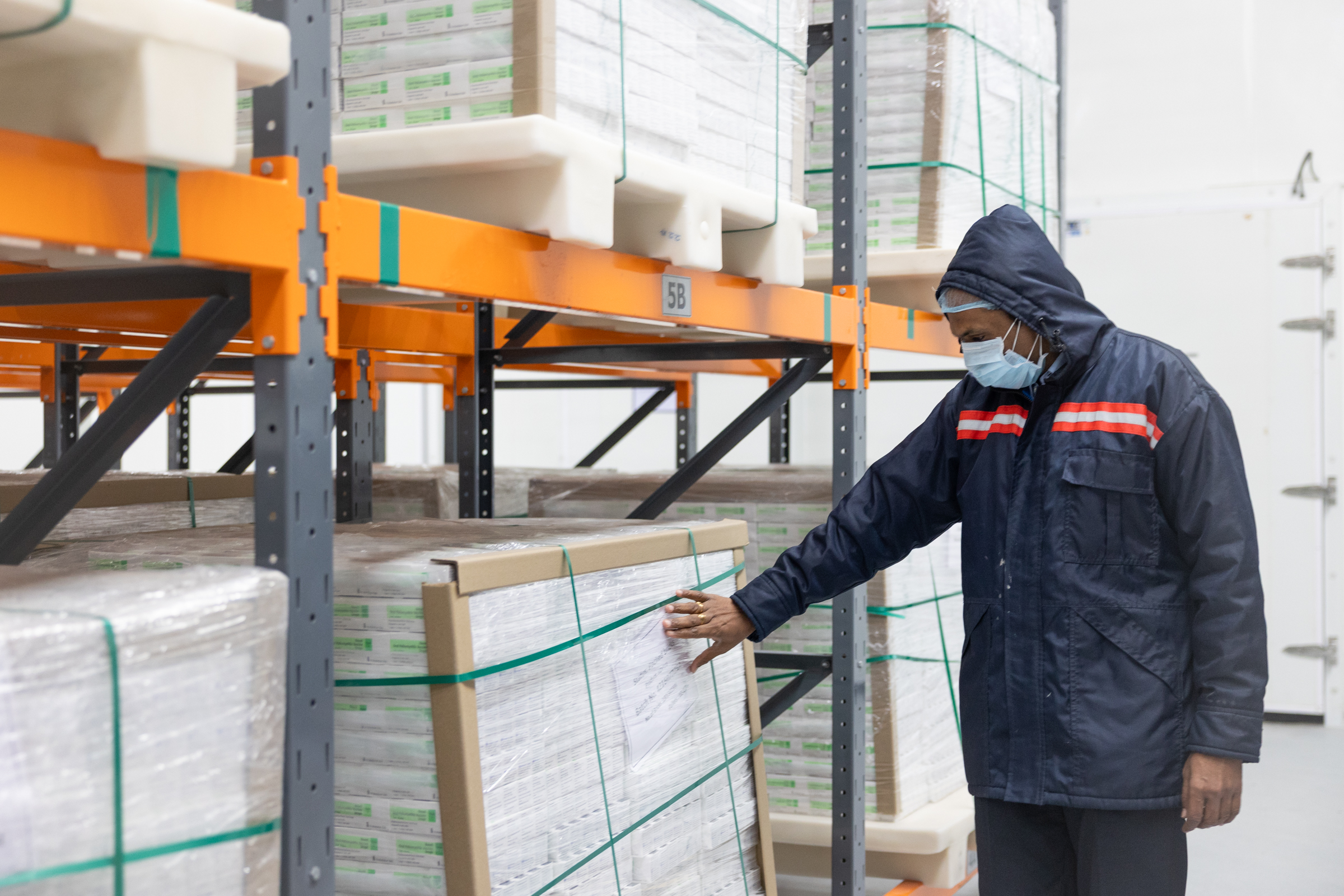
In June, the GPEI launched the new GPEI Strategy 2022-2026, which lays out the roadmap to achieving a lasting world free of all forms of polioviruses through stronger community engagement, a renewed focus on gender equity and the rollout of new tools and technologies. These new tools include the novel oral polio vaccine type 2 (nOPV2), which began deployment under Emergency Use Listing (EUL) as part of the GPEI’s broader polio vaccine repository to curb cVDPV2 transmission. In August, the WHO African Region celebrated one year since it was certified wild polio-free, and countries recommitted to strong cVDPV2 outbreak response across the continent with the support of the GPEI.
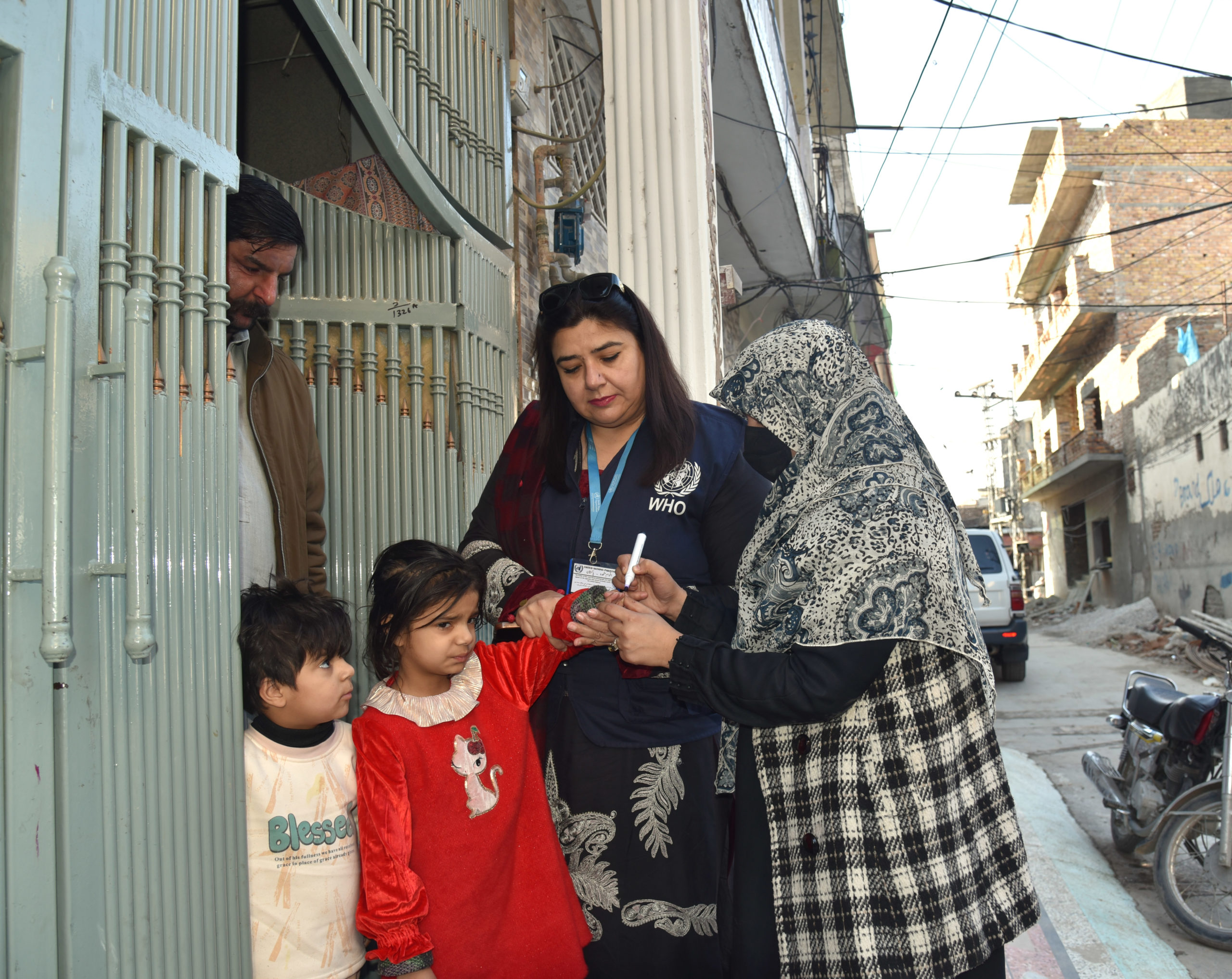
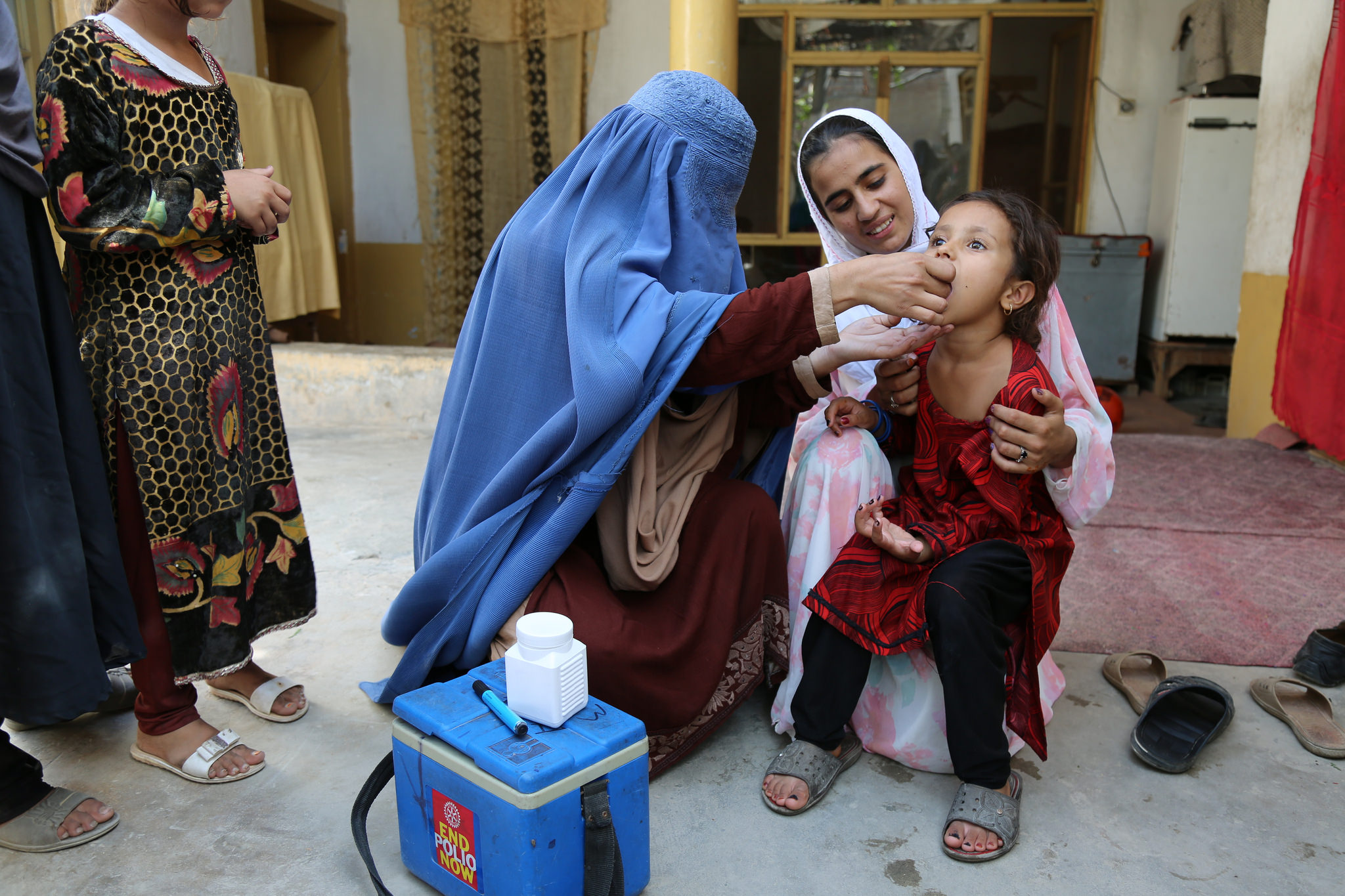
Further critical progress took place in Afghanistan – one of two final countries endemic for wild poliovirus, along with Pakistan. For the first time in more than three years, nationwide polio immunization campaigns resumed across Afghanistan reaching 8.5 million children, including 2.4 million children who were previously inaccessible.
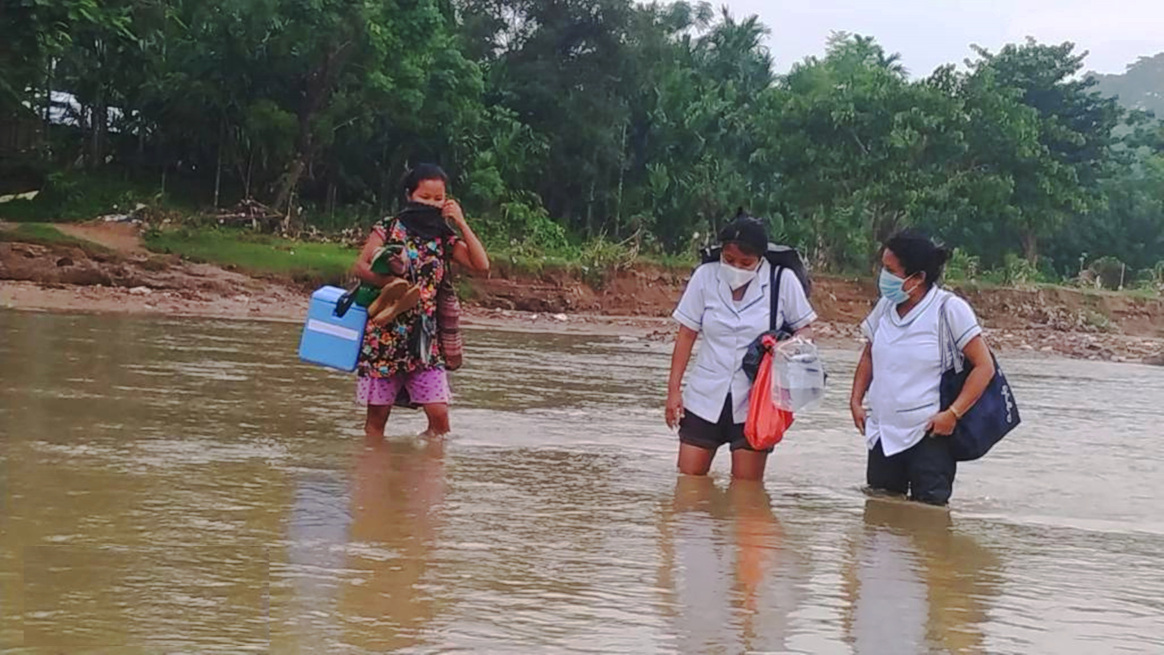
At the same time, polio programme health workers at the forefront continued to support global COVID-19 response efforts by delivering vaccines, mobilizing communities, and countering misinformation among other activities. The use of GPEI infrastructure for health emergency response has provided critical lessons for integrating polio resources into broader health systems as more countries work towards transition and the post-certification period.

Following dire predictions issued at the end of 2020, the polio programme once again proved its ability to adapt to programmatic, epidemiological and political developments. Entering 2022, there is much cause for cautious optimism – wild poliovirus transmission has slowed drastically, and cases of cVDPV2 have also declined compared to last year.
Importantly, commitment to achieving a lasting polio-free world is evident at all levels: by core GPEI partners, including among the Polio Oversight Board, which travelled to Pakistan twice in 2021; by health workers, communities and parents; and by country leaders worldwide who helped champion this year’s milestones. With the new strategy, new tools and adapted approaches, the stage is set to achieve lasting success.
To stop all forms of polio for good, the GPEI aims to capitalize on the positive epidemiological situation leading into 2022. A key opportunity to kick-start the year will be the WHO Executive Board meeting in January, where Member States plan to discuss building on the successes of this past year by fully implementing and financing the programme’s new strategy. Rotary and other key global GPEI partners are planning a renewed and intensified outreach across the broader international development community to secure the necessary financial resources to achieve success. Polio immunization campaigns will also continue in full force in both endemic and outbreak countries.
Twelve months ago, the programme was in a much different place, as WHO and UNICEF launched an Emergency Call to Action to draw attention to the need for renewed commitment. A year later, thanks to a strengthened and unified response, the GPEI is meeting the moment and is more committed than ever to end all forms of poliovirus, once and for all.