When disaster strikes, co-ordination is key. Within hours of the 5.9 magnitude earthquake striking the communities of Afghanistan’s South East in the early morning of 22 June, WHO’s polio team was on the ground joining forces with UN agencies and NGOs to ensure an effective and coordinated relief effort.
As dawn broke across the provinces of Paktika and Khost, and the extent of the devastation became evident, polio teams worked across both provinces to establish communications and share reports of the length and breadth of the destruction.
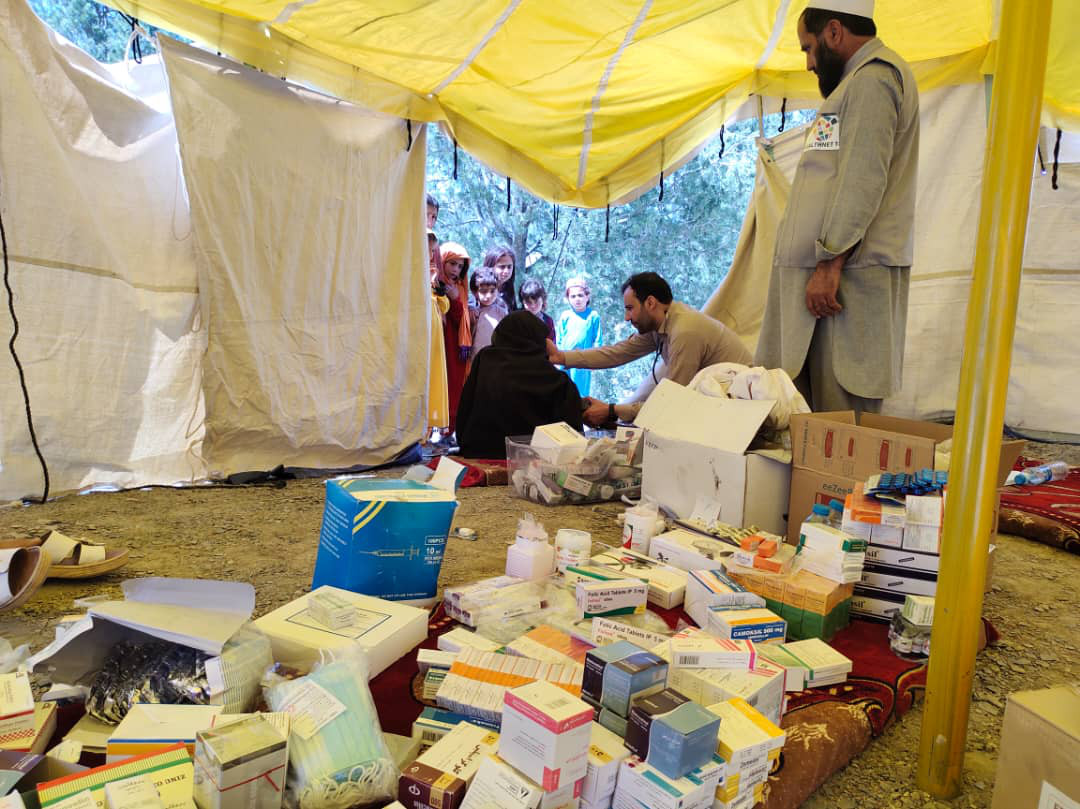
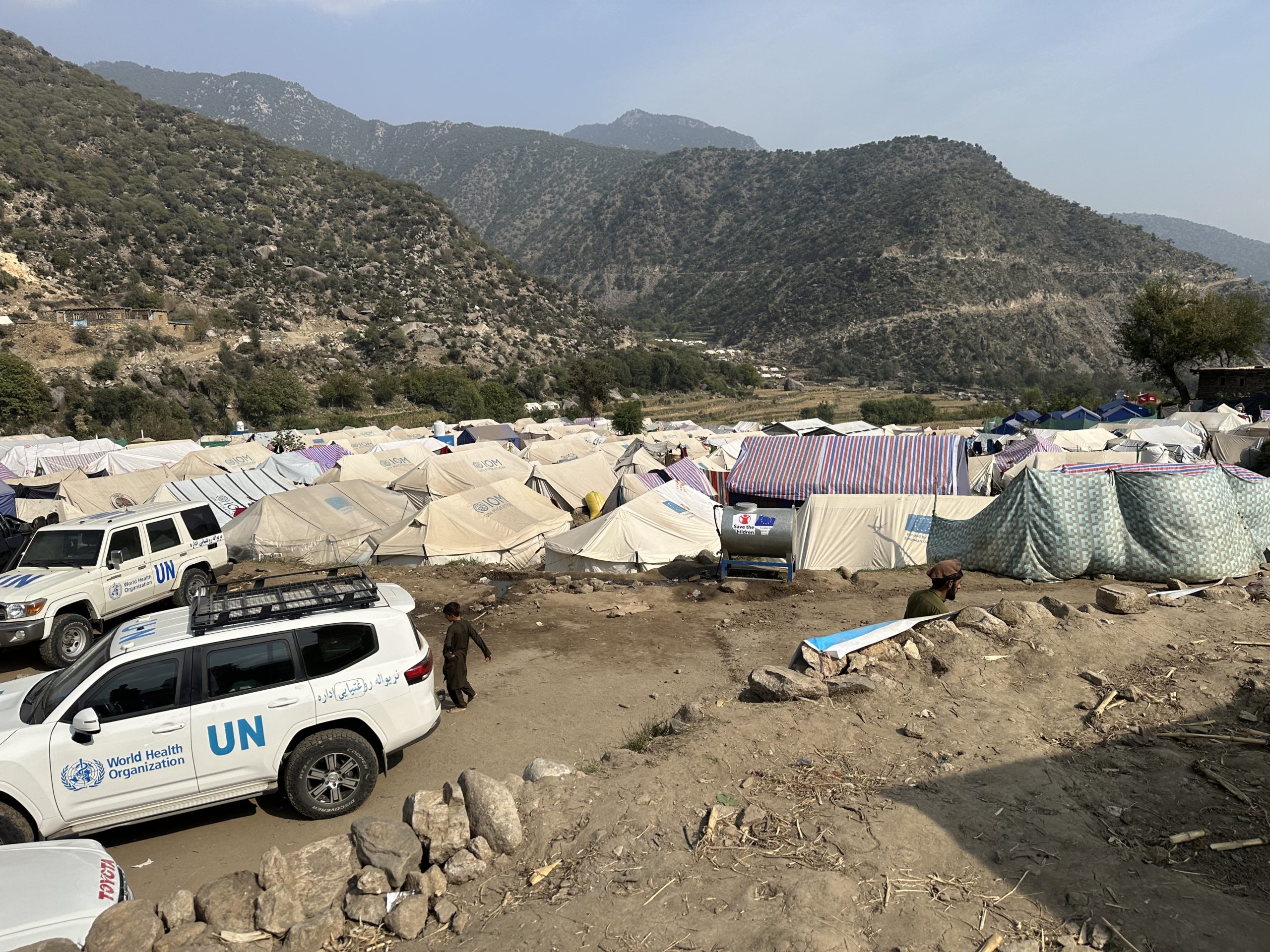
The team’s invaluable experience and local knowledge gained from more than two decades working among local communities in both Paktika and Khost provided the foundations of an assessment tool to map communities and assess the number and extent of casualties as well as the destruction to homes and buildings. This ensured accurate data guided a focused response in the immediate aftermath including the rapid construction of tents for shelter as well as housing ad hoc health camps.
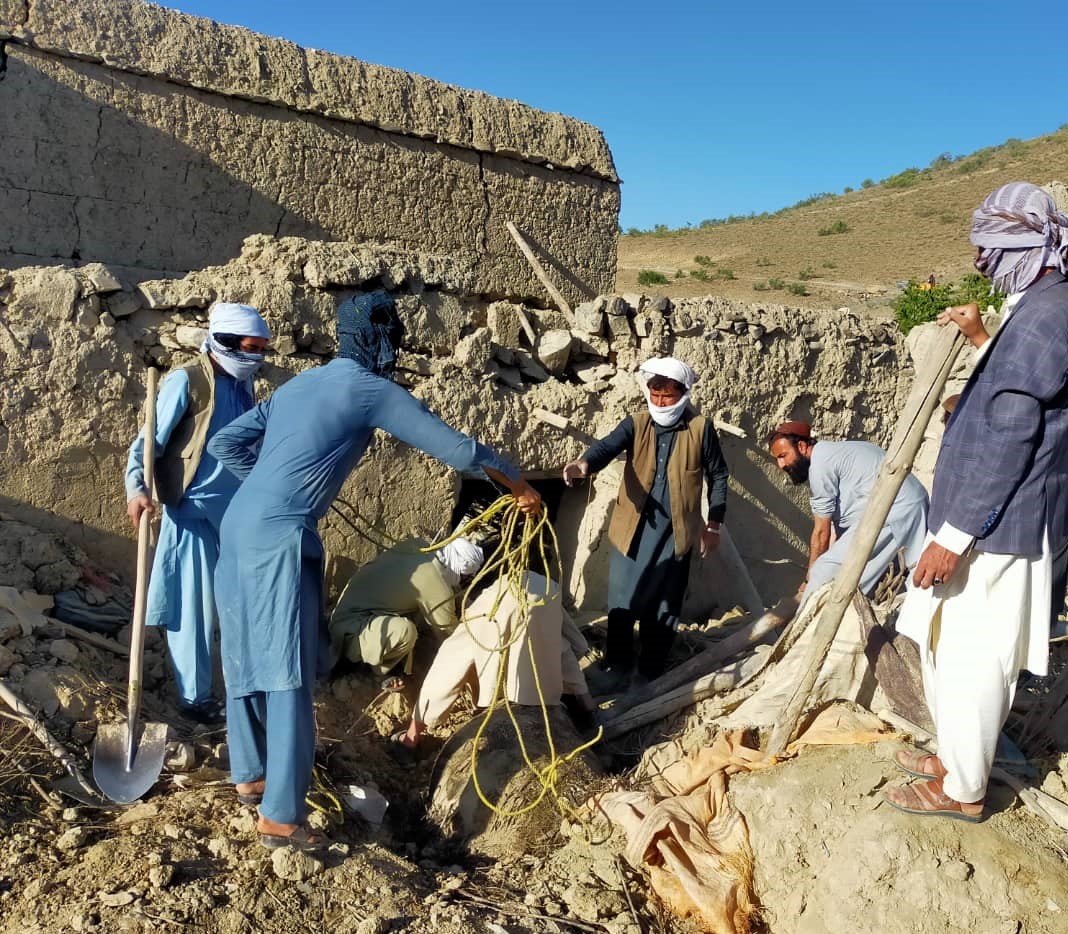

In the districts of Giyan, Geru and Barmal in Paktika, polio teams assisted in attending the injured, providing trauma care and dressing wounds. One team member was despatched to Spera district in neighbouring Khost province to assist with trauma care.
Polio teams turned a helping hand wherever needed including digging for survivors, building tents, unpacking trucks and distributing shipments of WHO emergency and surgical kits, medical supplies and equipment, and the heartbreaking task of preparing and assisting in transporting the dead for burial.
With the very real risk of increased communicable diseases in the wake of any natural disaster, polio staff drew on the polio surveillance system to strengthen post-earthquake surveillance for acute watery diarrhea, measles, tetanus and COVID 19.
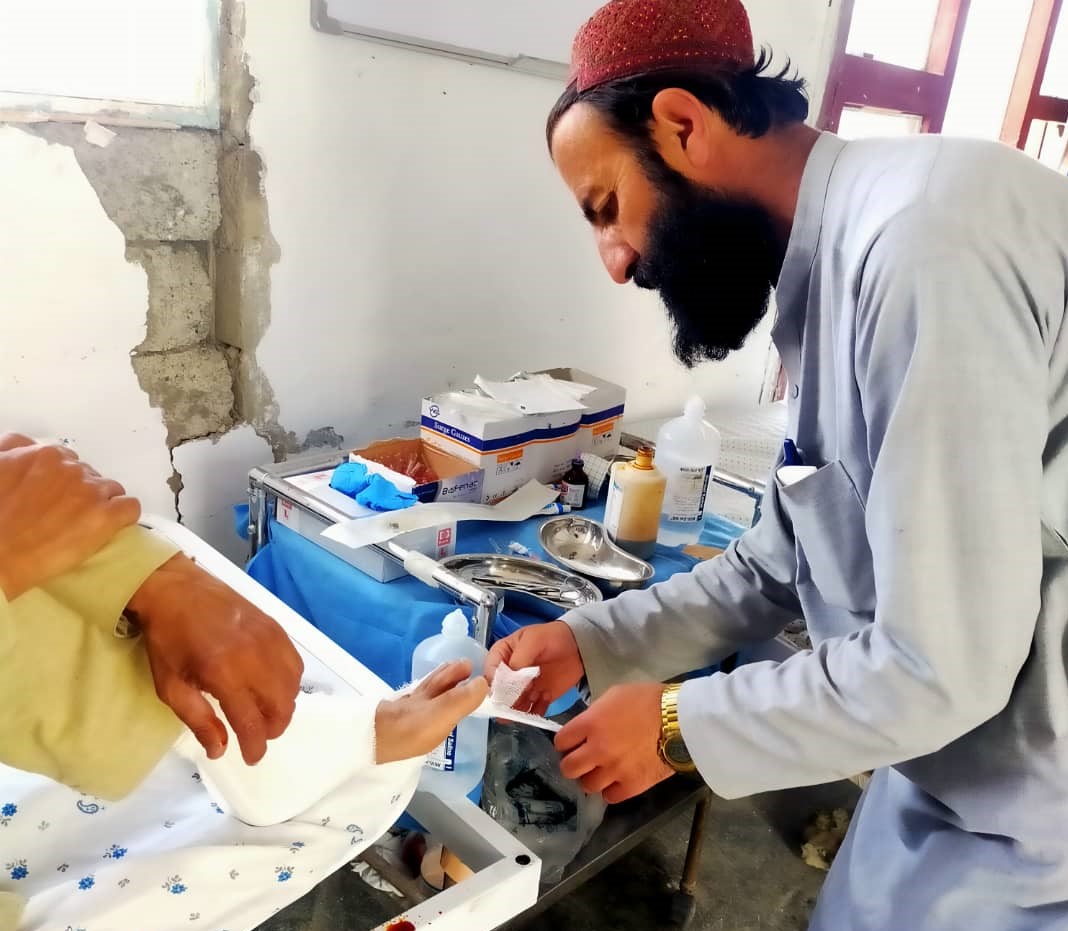

More than 1,000 people died in the quake and nearly 3,000 were injured; homes buildings and livelihoods have been destroyed. The polio team will continue to work as part of WHO Afghanistan’s earthquake response including providing trauma care, physical rehabilitation and disability assistance.
The earthquake struck five days before the start of the fifth nationwide polio vaccination campaign for 2022. The campaign was postponed for one week in Paktika province and in Spera district of Khost province and will begin on 4 July.