Islamabad – As he rode his motorbike out of the relative safety of Bannu city on a September morning, Danyal Sikandri was nervous. It was his first day on a new assignment, and he was riding out into the district outskirts with colleague Yasir Shah in search of a reclusive group of people – nomads.
Their task was to find nomadic settlements and vaccinate the children there against polio and other vaccine-preventable diseases. Sikandri has been involved with the Pakistan Polio Eradication Programme since 2019, first as vaccinator and then area in-charge. Therefore, he was no stranger to interacting with people. But with this assignment, he didn’t know what to expect, since he would be travelling long distances to find people who might not speak the same language, might be unwelcoming or worse, he could end up in an area which may not be secure.
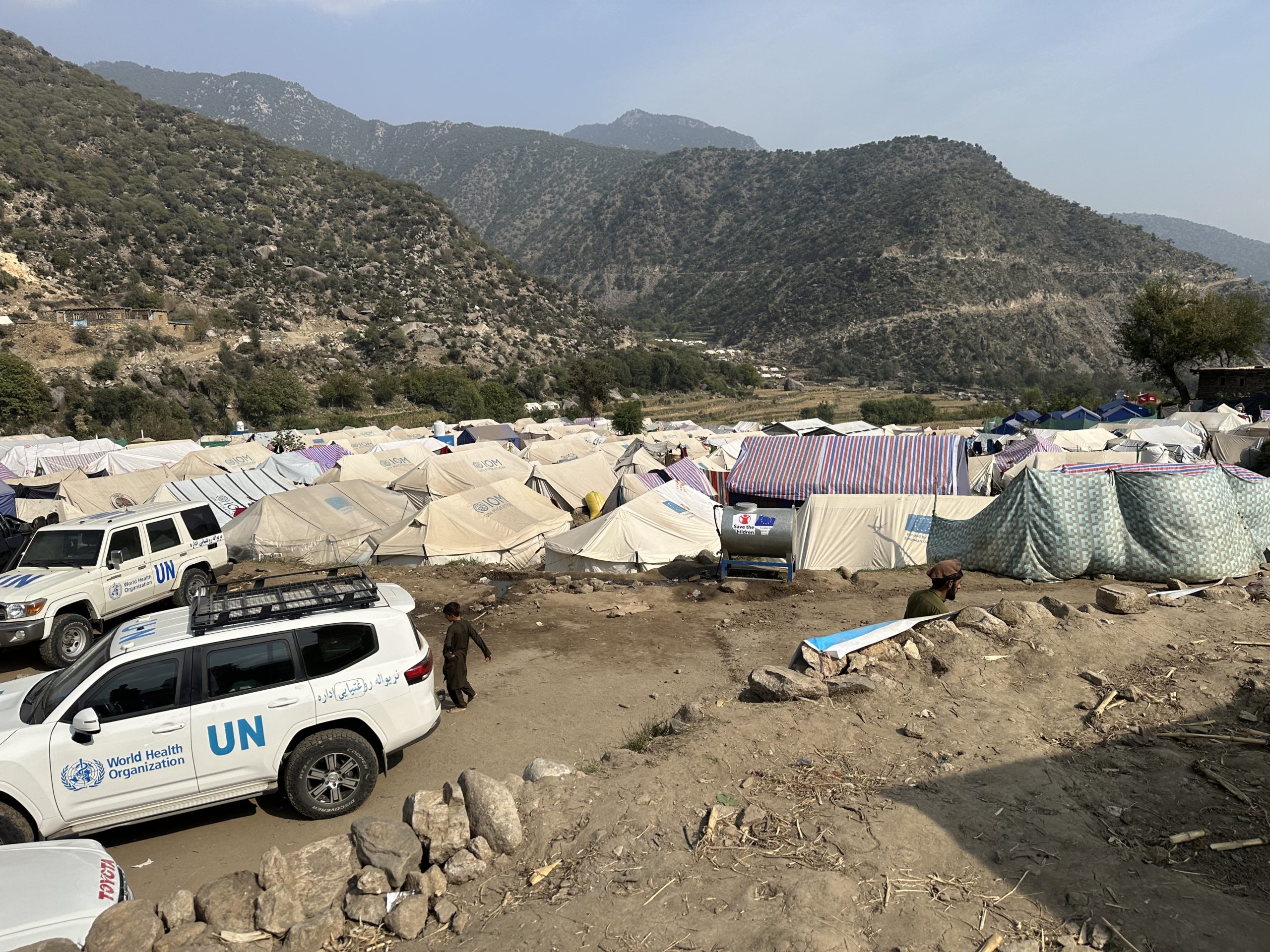
After travelling for about 36 kilometers, the team found a nomadic settlement in Domel. A group of families clustered together in makeshift tents made of plastic sheets and cloth. Sikandri approached the elders and explained why they were there. The nomads, who had come from Afghanistan and were temporarily camped in Domel, warmly welcomed the vaccinators in their midst.
As Sikandri vaccinated 14 children in the camp that day, his nervousness dissipated, and a resolve set in – to bring life-saving vaccines to as many nomadic children as he could.
“When I met them, I saw how different their lifestyle is, since they are constantly on the move and far from health facilities,” says Sikandri. “They want to protect their children from diseases too, so they are happy to see us. They tell us that it is the first time that vaccinators have come to their tents to vaccinate their children.”
Sikandri is one half of a two-member special mobile team which works under Pakistan Polio Programme’s latest initiative to reach segments of the population with polio and essential vaccines, which they would otherwise not have access to. The nomad vaccination initiative was launched in September 2022 in the seven endemic districts of southern Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa (KP) and expanded to four districts of Punjab neighboring these districts in October. The initiative was further expanded to include more districts from Punjab in January and Balochistan in early March. A total of 80 mobile teams in 22 districts have been deployed so far to reach nomadic children.
“With this initiative, we are filling a crucial gap. In the past, we were vaccinating children on the move, in buses, on train stations and other transit points, but the children that were being left out were from nomadic populations. This initiative is a product of extensive research, where we mapped out population movements and based on that information, made mobile vaccination teams to reach nomadic children with polio as well as all essential immunization necessary for their health and safety,” said Dr Zainul Abedin Khan, the National Team Lead for WHO’s Polio Operations in Pakistan.
“This is an excellent initiative of the Government of Pakistan, with support of polio partners, to protect children who had never been vaccinated before. This initiative will keep expanding based on the movement patterns. With this, we hope that population immunity is increased, and poliovirus is interrupted permanently,” he added.
“They want to protect their children from diseases too, so they are happy to see us. They tell us that it is the first time that vaccinators have come to their tents to vaccinate their children.”
Since nomads are highly mobile, the children in these communities are missed during routine vaccination campaigns or even at transit vaccination sites because they may not be passing through formal routes. This means their immunity remains weak, they are vulnerable to disease and can potentially transmit poliovirus as they travel across country and district borders.
In 2022, the program conducted a comprehensive survey of nomadic movement patterns in February and March in 14 districts of KP, Punjab and Balochistan. The survey found that nomadic movement begins in southern KP in September and ends in March, with the nomads setting up temporary camps as they pass through various districts.
“It is difficult for our door-to-door vaccination teams to reach them since a majority of nomads live on district borders or peripheries and it is not even known when they are coming,” said Muhammad Asif Javaid, who leads the program’s High-Risk and Mobile Population Unit (HRMU) and is spearheading this initiative. “They are frequently on the move, staying in places temporarily, never settling, so they miss the opportunity to receive polio and routine immunization.”
In the first phase of implementation, two special mobile teams – consisting of a trained vaccinator and a team assistant – were deployed in each of the seven districts of southern KP and four districts of Punjab. Subsequently, the project was expanded to cover 22 districts of the country.
Union council staff collect data on nomads visiting their areas. This information along with weekly micro-plans and targets are provided to vaccinators, who travel across their assigned UCs to visit these settlements. They provide polio and other essential vaccinations to children in the camps and issue vaccination cards to the families to ensure the data remains on record.
Javaid said that these teams are also helping with surveillance for cases of acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) by asking families and looking for any children who might have AFP, and then ensuring that it is reported to relevant authorities for further testing.
As of March 31, more than 114,600 children under the age of five had received the oral polio vaccine, 71,206 had received the inactivated polio vaccine, while nearly 20,000 routine immunization antigens have been administered to eligible children, under this initiative.
“Currently the program is actively working to vaccinate chronically missed children and is focusing on reaching missed populations rather than prioritizing geography alone,” Dr Zainul Abedin Khan added.
The task is challenging for vaccinators, who travel many kilometers out of urban centers to find nomadic settlements. They might run out of fuel, the settlement might have packed up and left by the time they arrive, or they may encounter hostility, but the vaccinators take it in their stride, happy to be safeguarding children’s futures.
For Sikandri, the experience has been rewarding. He has seen areas of his native district now that he had never seen before, and he feels his communication skills have improved since he began working on this project.
“We have received a lot of love from these people. When we vaccinate their children, they are thankful and pray for us. It feels good that people like them and their children are also being taken care of,” said Sikandri.
By Suzanna Masih,
Communications Officer, WHO Pakistan (Video by NEOC)