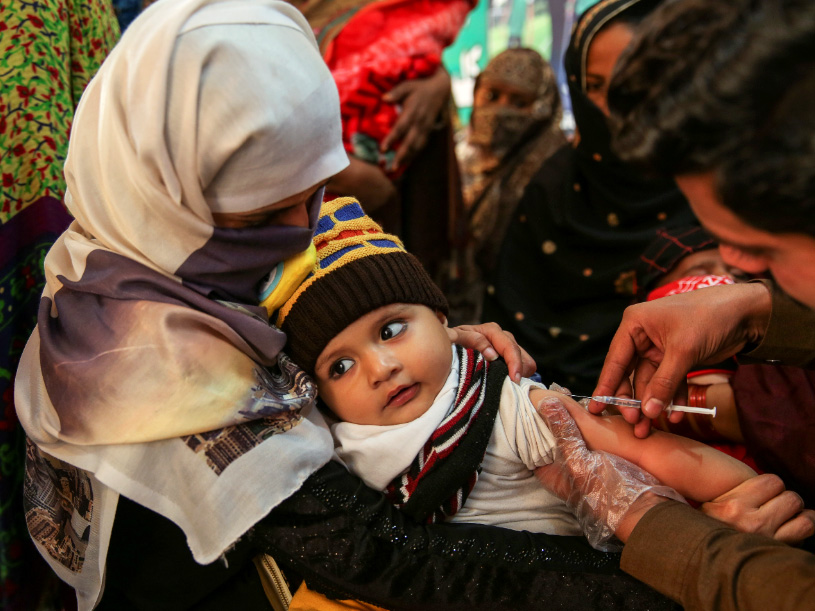
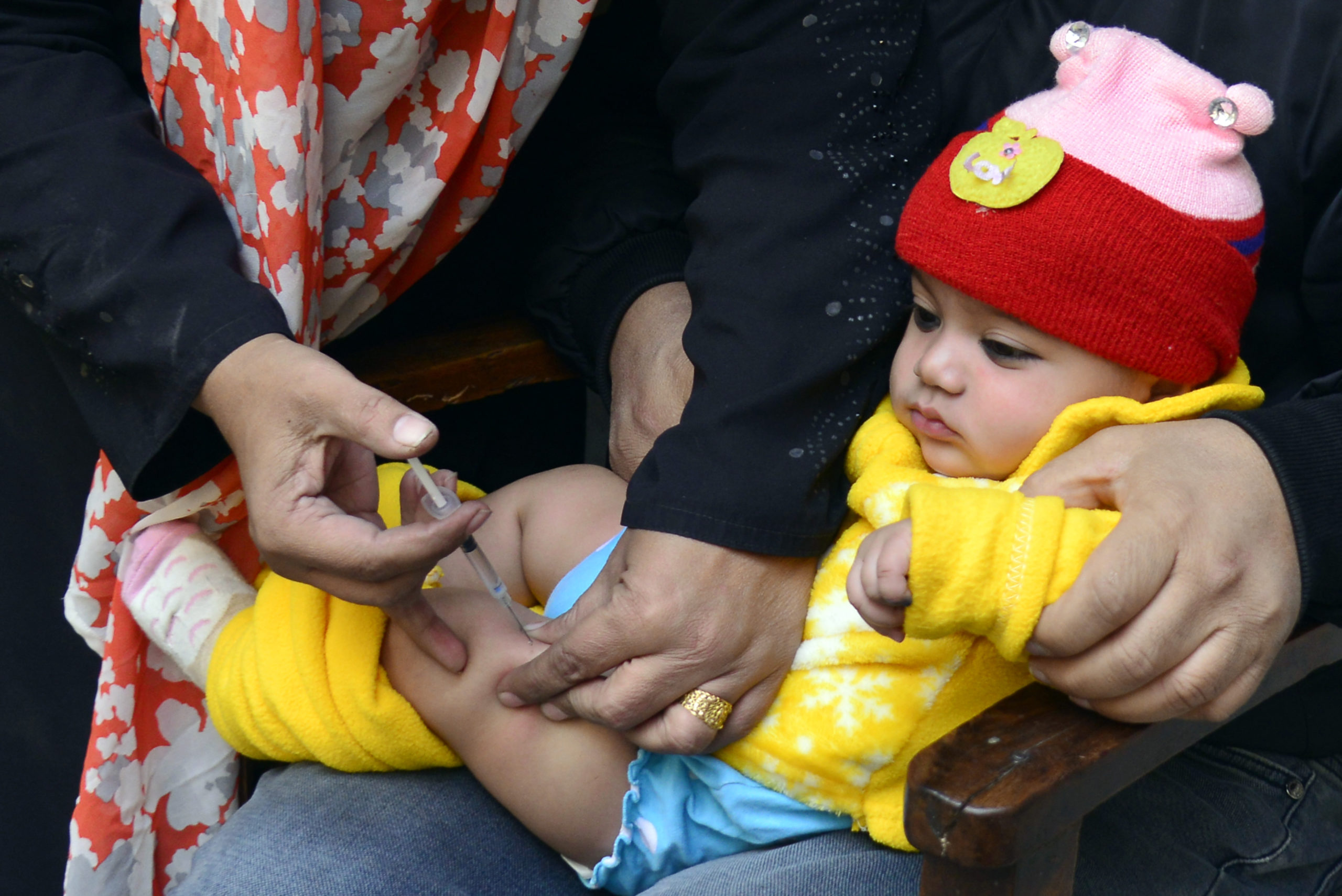
Pakistan’s routine immunization programme Expanded Programme on Immunization will carry out a nationwide measles vaccination campaign targeting around 31.8 million children aged 9-59 months from 15 to 27 October to respond to an ongoing measles outbreak in Pakistan. Over 30 000 measles cases have been reported this year, compared with around 24 000 cases in 2017.
Pakistan typically encounters a measles outbreak every 8 to 10 years, and the Federal Ministry of Health works proactively to stop these outbreaks with regular vaccination campaigns. Although the Polio Eradication Initiative and the Expanded Programme on Immunization are separate entities, they work together to improve immunization outcomes in Pakistan. Achieving strong essential immunization coverage is a critical step in bringing Pakistan closer to ending polio, and once this goal is reached, in maintaining polio-free status.
Many of the areas at highest risk for polio are also at high risk for measles. During the upcoming measles campaign, the polio programme will lend its human, physical and operational resources, knowledge and expertise to achieve the highest possible measles immunization coverage across the country.
Reaching more children through stronger collaboration
The collaboration between polio and routine immunization programmes has made a significant difference in vaccination efforts across dense urban environments as well as scattered rural settings. A key factor for success has been the polio programme’s highly-skilled workforce of community vaccinators, front-line health workers and social mobilizers.
During every round of country-wide polio vaccination campaigns, around 260 000 front-line health workers vaccinate more than 38 million children under the age of 5 across Pakistan. With vital on-the-ground experience in some of the most challenging settings, they are determined to ensure that the lessons learned in polio are transferred to other health interventions.
“Our front-line workers have built strong rapport in their respective communities,” said Dr. Rana Safdar, coordinator of the National Emergency Operation Centre (NEOC) for polio eradication and member of the National Measles Steering Committee.
“They understand the dynamics of the population, even as they relate to children, not only at the district level but also at the Union Council and village level. This indigenous knowledge coupled with community trust can definitely play an instrumental role for other health interventions.”
Unlike polio eradication activities, measles immunization is not carried out from door-to-door but at fixed centres at health facilities as well as through outreach sessions within communities. Children are mobilized to the vaccination sites where trained healthcare professionals administer the injectable measles vaccine. The deep local knowledge polio workers have developed and the trust they have built with their communities is vital in mobilizing caregivers to take their children for measles immunizations at nearby vaccination sites.
“The strong collaboration between the two programmes has helped us vaccinate more children. Our joint efforts are geared towards reaching every last child and they have shown significant progress so far. We hope that our synergized efforts during the upcoming measles campaign will lead us to reach every child in the target population with measles vaccine,” said Dr. Tahir Abbas Malik, from the Pakistan polio programme.
“For polio, these coordinated efforts have paved the way for increasing the coverage of persistently missed children, especially those who are on the move or reside in hard-to-reach areas. Similarly, integrated micro planning, monitoring and reporting of children who have not received essential immunization have been instrumental for achieving gains for routine immunization through enhanced coverage,” said Dr. Tahir Abbas Malik.