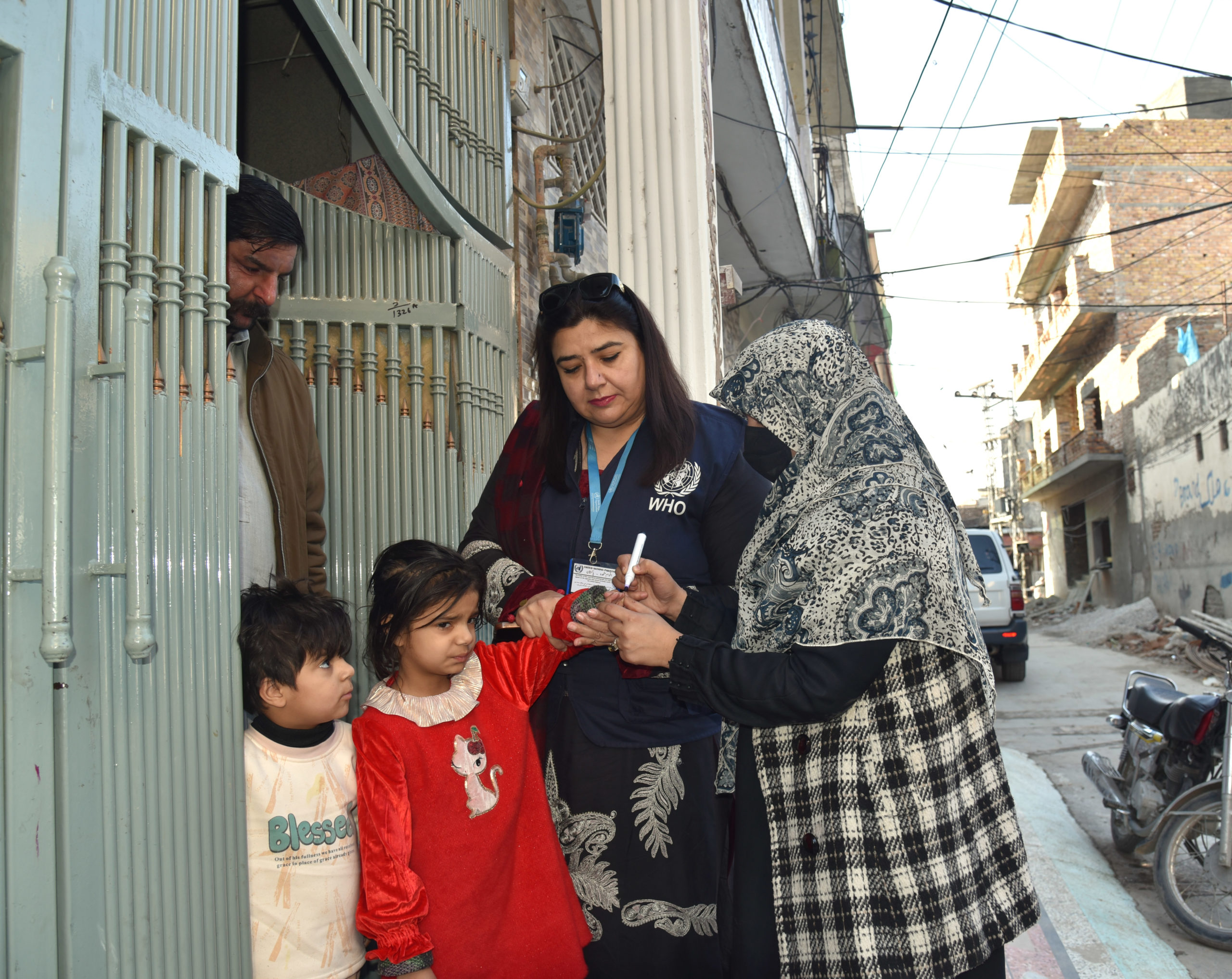
Rising up into the sky, a tower block’s outline trembles in the heat haze, even in the early morning. It’s hard to count the number of floors from the ground as the concrete block stretches up so high. Inside the door, you look around for an elevator – but there is none. Taking a deep breath and hoisting the vaccine carrier higher onto your shoulder, you begin the long climb up the stairs through the heat. At the top, many pauses for breath later, you knock on the first door. As a mother holding her baby opens it, your work for the day really begins – but there is a long way to go. To vaccinate every child in the city against polio, you and your fellow vaccinators must knock on every door in this building; on this street; in this neighbourhood; and across the entire city. It is a monumental task – and one you take on several times a year.
Cities: Uniquely challenging environments
Often it is the ability of polio vaccinators to reach the most remote and inaccessible villages, hampered by challenging weather or conflict, that is the biggest challenge to eradication. But big cities, while more easily accessible, can pose an equal challenge.
Dr Mohammed Sibak Abouzeid, has been working to stop polio in Egypt since 1999, planning and organising polio eradication campaigns and evaluating whether enough children were reached in each campaign so that the next one can be better. Over 40% of Egypt’s population lives in urban environments.
“While my colleagues in the countryside are battling challenging terrain, weather and long journeys, we have a different set of barriers: slums, high rise buildings, marginalised communities and big populations that can change overnight,” says Dr Mohammed. “But our goal is the same: to reach every single child, no matter where they live.”
One critical tactical shift to ensure all floors of a tower block were covered was to ensure vaccinators first walked to the top floor, and then knocked on every door coming down, rather than the other way around, which meant the very top floors were missed.
A playground for polio
Cities provide an easy environment in which for polio to spread. The poliovirus spreads between humans through faeces, so wherever sanitation systems or hygiene practices are poor, or many people live in close quarters, the virus is able to spread rapidly.

The city of Karachi is one of the remaining strongholds of the virus. People move in and out of Pakistan’s biggest city constantly: these ever changing populations make it difficult to know how many children need to be vaccinated and where they live. Many children are born every day, giving the virus many opportunities to hide in the unvaccinated guts of infants who have not received at least three doses of polio vaccine. Given the informal nature of many of the slums within this city, the lack of infrastructure such as health care centres can make it especially difficult to get vaccines to every child.
Slums have another consequence for polio eradication; with high levels of poverty, malnutrition and diarrhoea are regular threats. Malnutrition can damage the immune systems of children, meaning that even if they receive the vaccine, it might not be able to kick start the process of generating protection against the virus. Diarrhoea can lead to the vaccine leaving the body too quickly for it to begin creating antibodies; but it also can act as a vehicle to cause the poliovirus to spread further and faster.
Stopping polio in cities
Stopping polio even in these challenging environments takes ingenuity and creativity. Luckily, people like Dr Mohammed have the experience necessary to make a difference.

“To stop polio in urban environments, you need to train all vaccinators incredibly well, and give them the motivation they need to work in difficult environments. But the most important thing is to come to understand the networks that city inhabitants are a part of so that you can engage them, involve them in vaccination campaigns and find the right influencers from local communities to encourage parents to vaccinate their children.”
In cities like Cairo in Egypt and Mumbai in India, once thought to be the hardest places in the world to stop polio, such tactics were instrumental in stopping poliovirus. Indeed, they continue to be used even now in order to ensure high vaccination coverage and keep their populations protected. It may be a matter of getting the right neighbourhood religious leader to announce vaccination campaigns during a sermon, or the right midwife to tell new mothers about vaccination, but one thing is for sure: success against polio is ensured one person at a time, even in a city of millions.