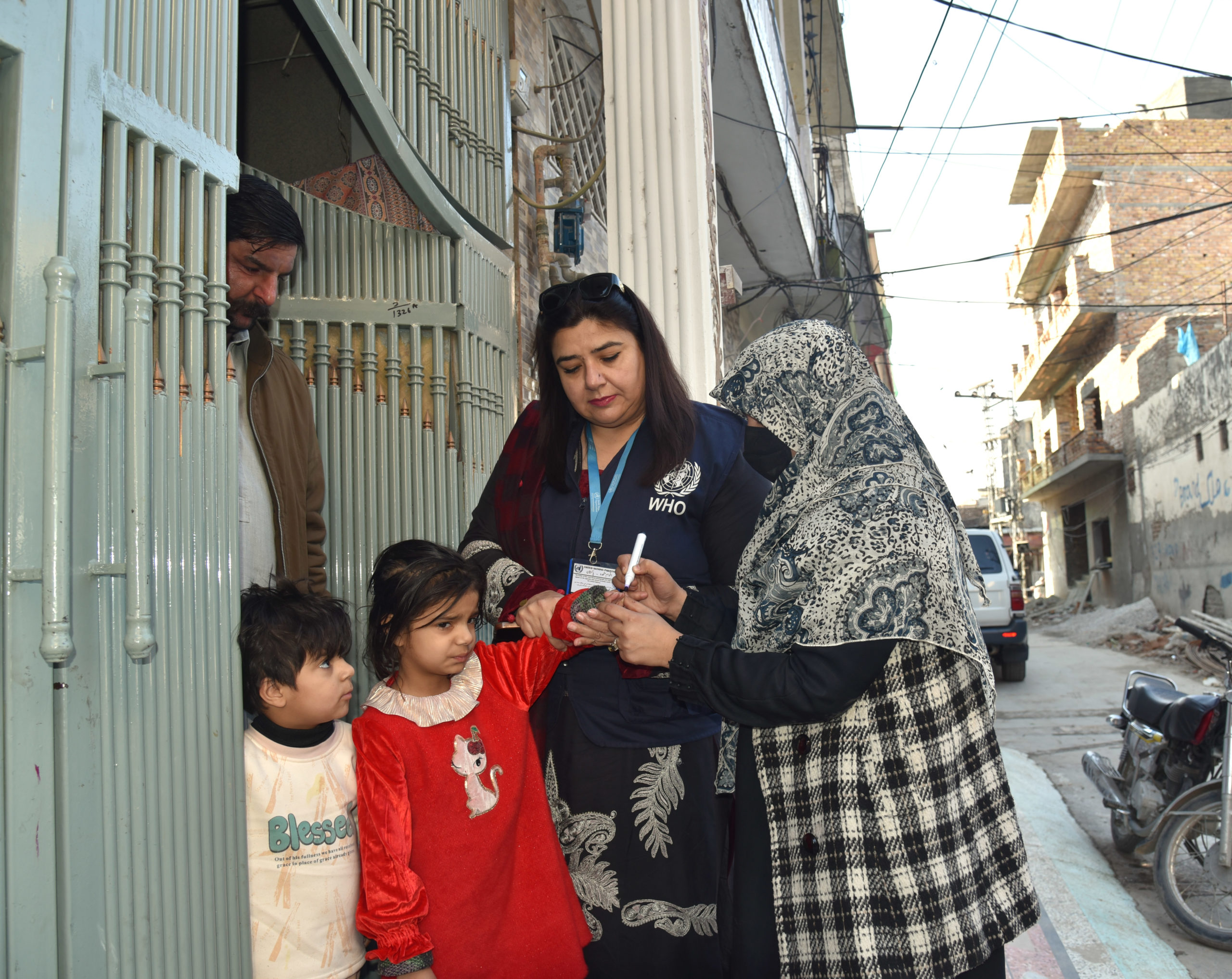
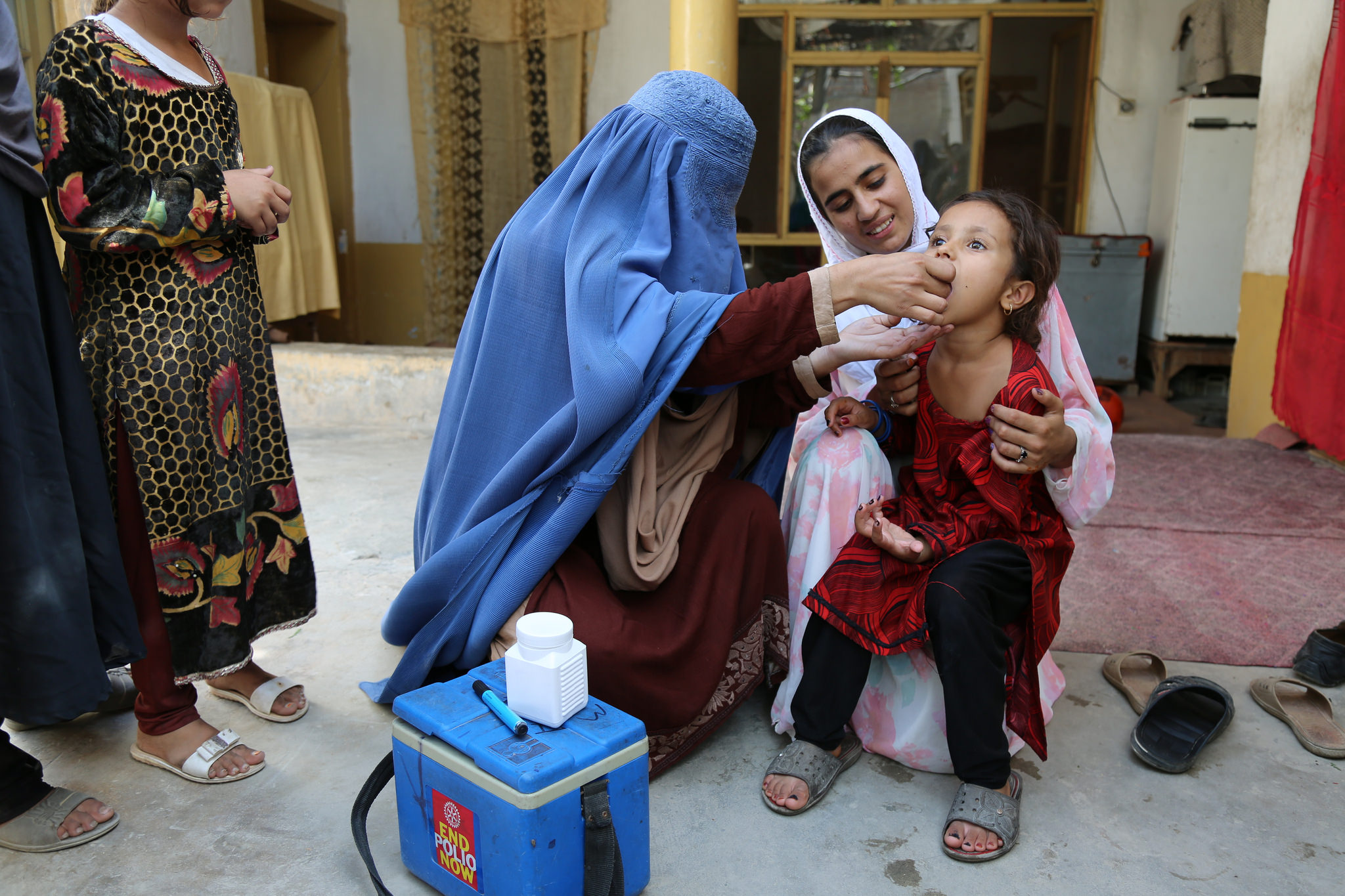
The Horn of Africa is officially polio-free, with Sudan, Kenya and Uganda having reported no wild poliovirus cases for more than a year.

Johann Hattingh/UNMIS
In the first half of 2009, an outbreak of wild poliovirus that originated in northern Nigeria spread from southern Sudan to Port Sudan, Kenya and Uganda. The cases in Port Sudan sparked particular international concern as it was from this area that, from 2004 to 2006, wild poliovirus type 1 spread to re-infect several countries, including Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Yemen and Indonesia.
However, the implementation of swiftly conducted mop-up campaigns followed by multiple immunization activities, all supported by high-level political commitment, stopped the outbreak within six months – and the region has now stayed polio-free for more than 12 months since the last case.
Recognizing that the epicentre of the outbreak was in southern Sudan, the President of the Government of Southern Sudan, His Excellency General Salva Kiir Mayardit, launched a ‘President Action Plan for Polio Eradication’, directing all state governments, county and district heads to personally oversee the quality of outbreak operations in their areas. Multiple immunization activities were held, and Sudan’s last case was reported on 27 June 2009.
Uganda drew praise for the speed with which it fully implemented the international polio outbreak response standards, conducting a mop-up immunization activity around the index case within days of it being confirmed, followed by multiple high-quality immunization activities, with no cases reported since 10 May 2009.
Kenya, which had been polio-free since 1984, implemented the Short Interval Additional Dose strategy, providing multiple doses of oral polio vaccine two weeks apart to the highest-risk populations in Turkana. The result was immediate, with the last case in Kenya reported on 30 July 2009. Ethiopia has been free of wild poliovirus since 2008 and Somalia since 2007.
The outbreak response was made possible by $500,000 in emergency grants by Rotary International.