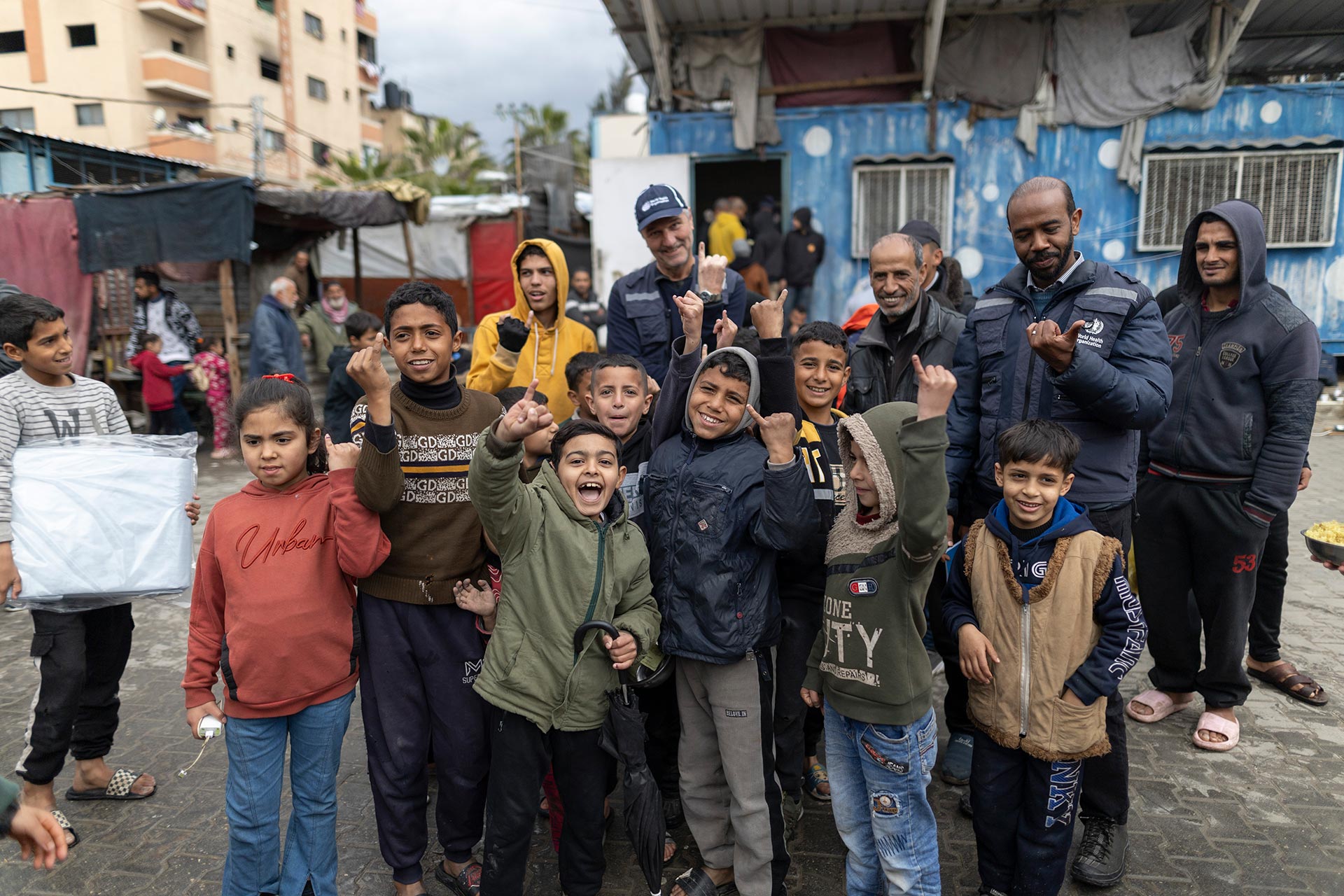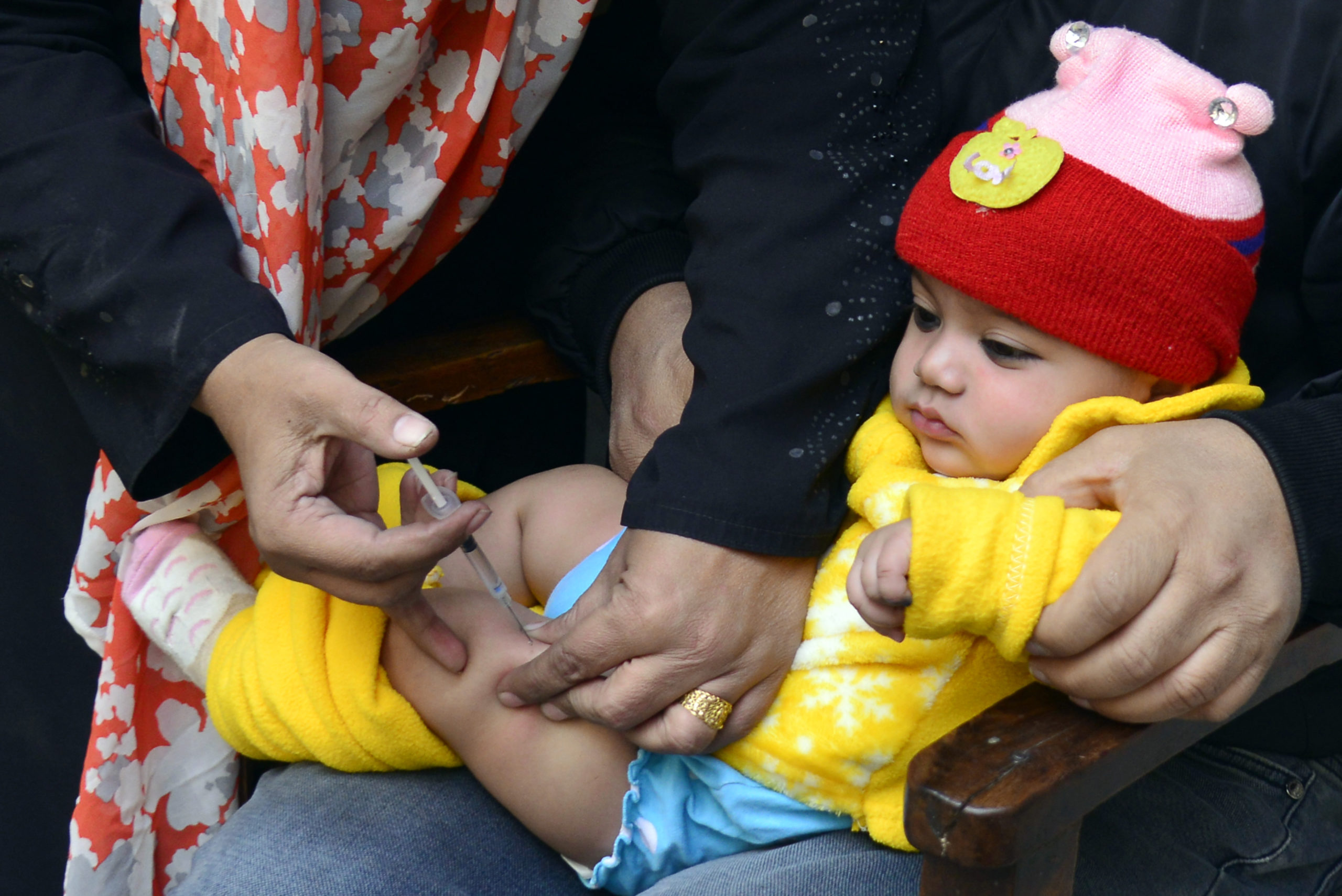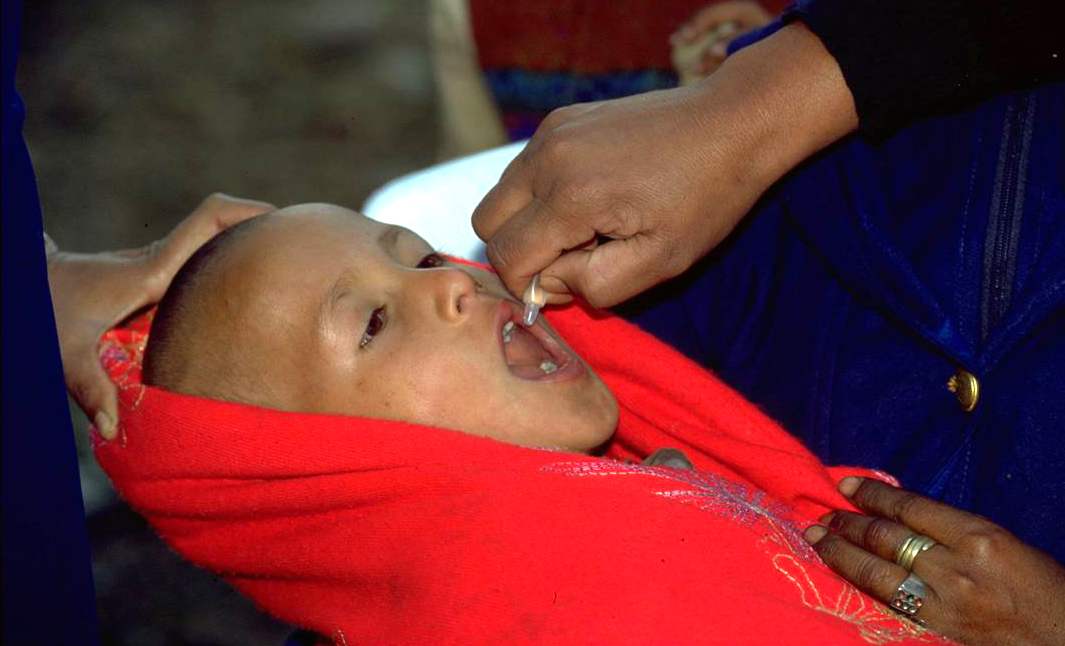
Following identification last month of an acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) case from which vaccine-derived poliovirus type 1 (VDPV1) had been isolated, genetic sequencing of two VDPV1s from two non-household contacts of the AFP case has now confirmed that VDPV1 is circulating and is being officially classified as a ‘circulating’ VDPV type 1 (cVDPV1).
The National Department of Health (NDOH) of Papua New Guinea is closely working with the GPEI partners in launching a comprehensive response. Some of the immediate steps include conducting large-scale immunization campaigns and strengthening surveillance systems that help detect the virus early. These activities are also being strengthened in neighboring provinces.
The GPEI and its partners are continuing to work with regional and country counterparts and partners in supporting the Government of Papua New Guinea and local public health authorities in conducting a full field investigation, risk assessment and to support the planning, implementation and monitoring of the outbreak response.
For more information:
Contact Oliver Rosenbauer, Communications Officer, Global Polio Eradication Initiative, tel: +41 79 500 6536