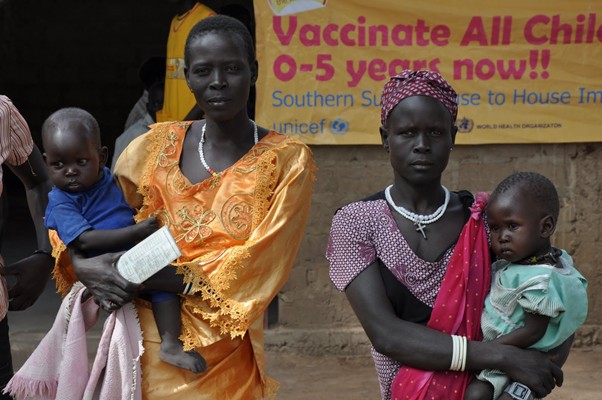
In separate and unrelated events, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPVs) have been confirmed in South Sudan and Madagascar.
In South Sudan, 2 cases due to cVDPV type 2 (cVDPV2) have been confirmed. The strains were isolated from 2 acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) cases in Unity state, with onset of paralysis on 9 September and 12 September 2014, respectively. In Madagascar, cVDPV type 1 (cVDPV1) has been confirmed after the virus was isolated from 1 case of AFP (onset of paralysis on 29 September 2014) and 3 healthy contacts. Emergency outbreak response in both countries is now being planned and implemented.
Circulating VDPVs are rare but well-documented strains of poliovirus which can emerge in some populations which are inadequately immunized. Due to the small risk of cVDPVs, use of OPV must be stopped to secure a lasting polio-free world. OPV will be withdrawn in a phased manner, beginning with the removal of type 2-containing OPV. The type 2 component contained in trivalent OPV accounts for 90% of all cVDPV cases.
For more on the cVDPVs in South Sudan and Madagascar
For more on OPV cessation