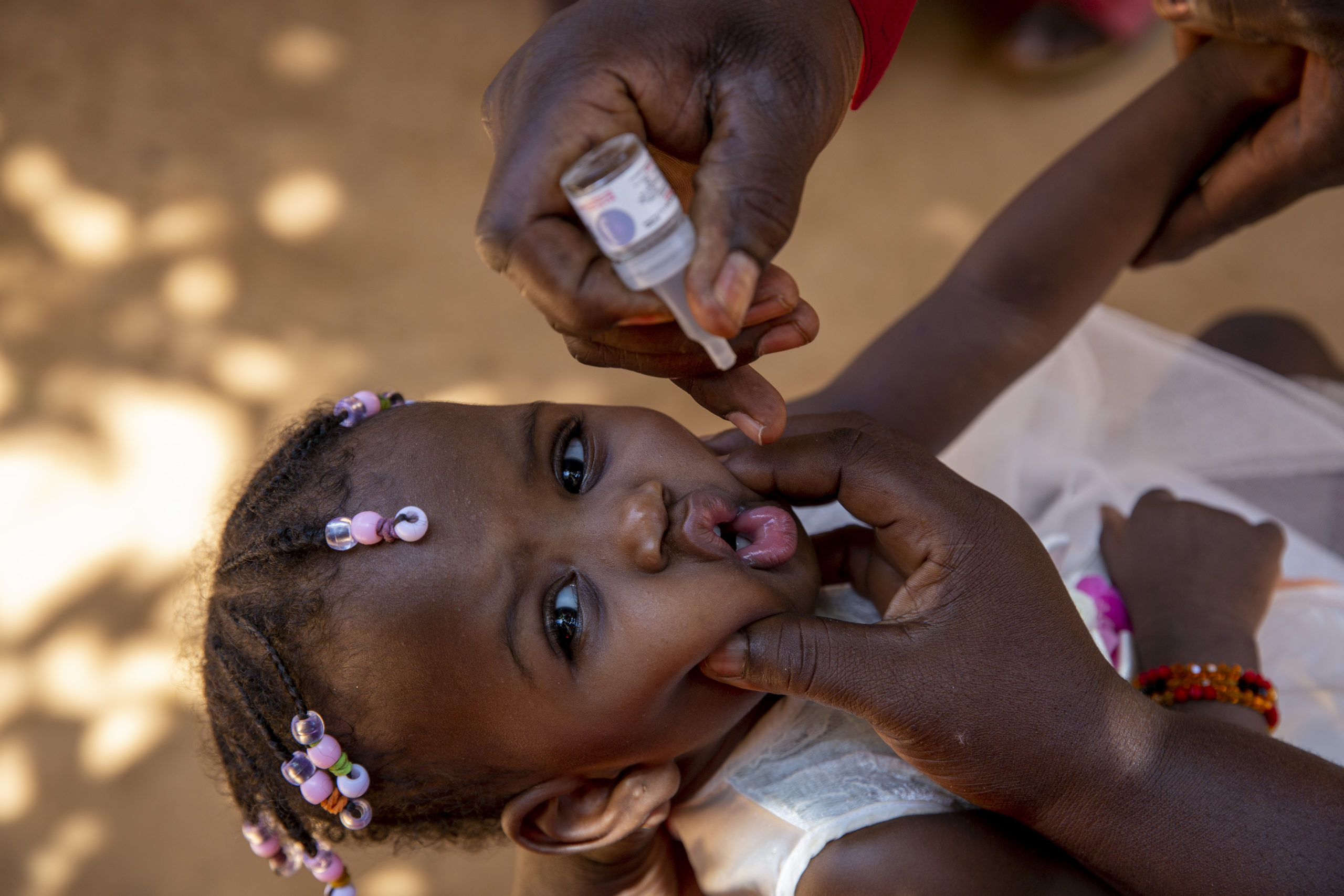
Ministry of Public Health, WHO and UNICEF working to reach all underimmunized children wherever they live, priority outreach is being directed to Southern Region.
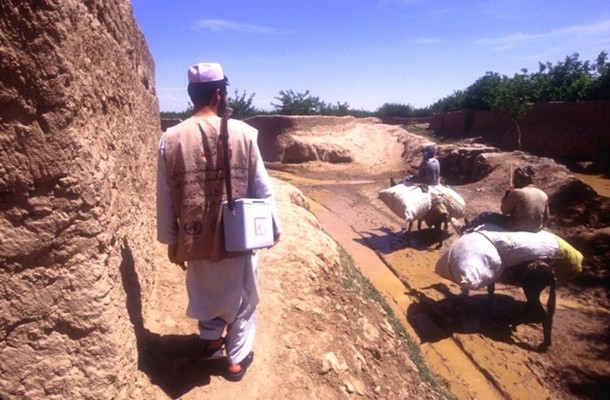

Afghanistan’s Ministry of Public Health (MoPH), with the support of World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF, is intensifying efforts to wipe out polio from the country by the end of 2012.
From 17 through 19 September, more than 55,000 medical staff and volunteers across the country went door-to-door to give two drops of oral polio vaccine (OPV) to 7.8 million children as part of the latest National Immunization Days (NIDs).
The move comes at a critical time in Afghanistan’s polio eradication effort. Although indigenous transmission is primarily restricted to key high-risk districts of Southern Region, Afghanistan has seen an increase in new cases over the past months. A total of 36 cases have now been reported in 2011, compared to 18 cases for the same period in 2010, all primarily from Southern Region.
And while the MoPH, WHO and UNICEF are working to engage all sectors of the government and society to ensure that service providers have access to all underimmunized children wherever they live in Afghanistan, priority outreach is being directed to Southern Region. “In 2009, there was no access to children for nearly a year in Marja district, Helmand province, because of ongoing military operations,” said Dr Arshad Quddus, head of WHO’s polio programme in Afghanistan. Humanitarian access in Afghanistan overall has shrunk in the past several years, according to the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Aid (OCHA). UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon dedicated his Rotary Polio Eradication Champion Award in 2009 to three polio staff killed in September 2008 while monitoring the UN polio campaign in Spin Boldak district of Kandahar.
To secure greater access to some communities, the UN negotiates with local leaders, such as tribal elders and teachers, and enlists local volunteers who are trained and monitored by health supervisors. The UN also relies on a “window of opportunity” strategy where children who live in areas that are only accessible for a short period of time, are reached through specially arranged and focused campaigns to deliver an additional OPV dose, an approach known as the Short Interval Additional Dose (SIAD) approach.
The success of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative is in large part due to the neutrality of the polio vaccination programme. “The programme is neutral. Irrespective of tribal or political affiliation, all children are vaccinated,” said UNICEF’s senior polio worker, Carmen Garrigos.