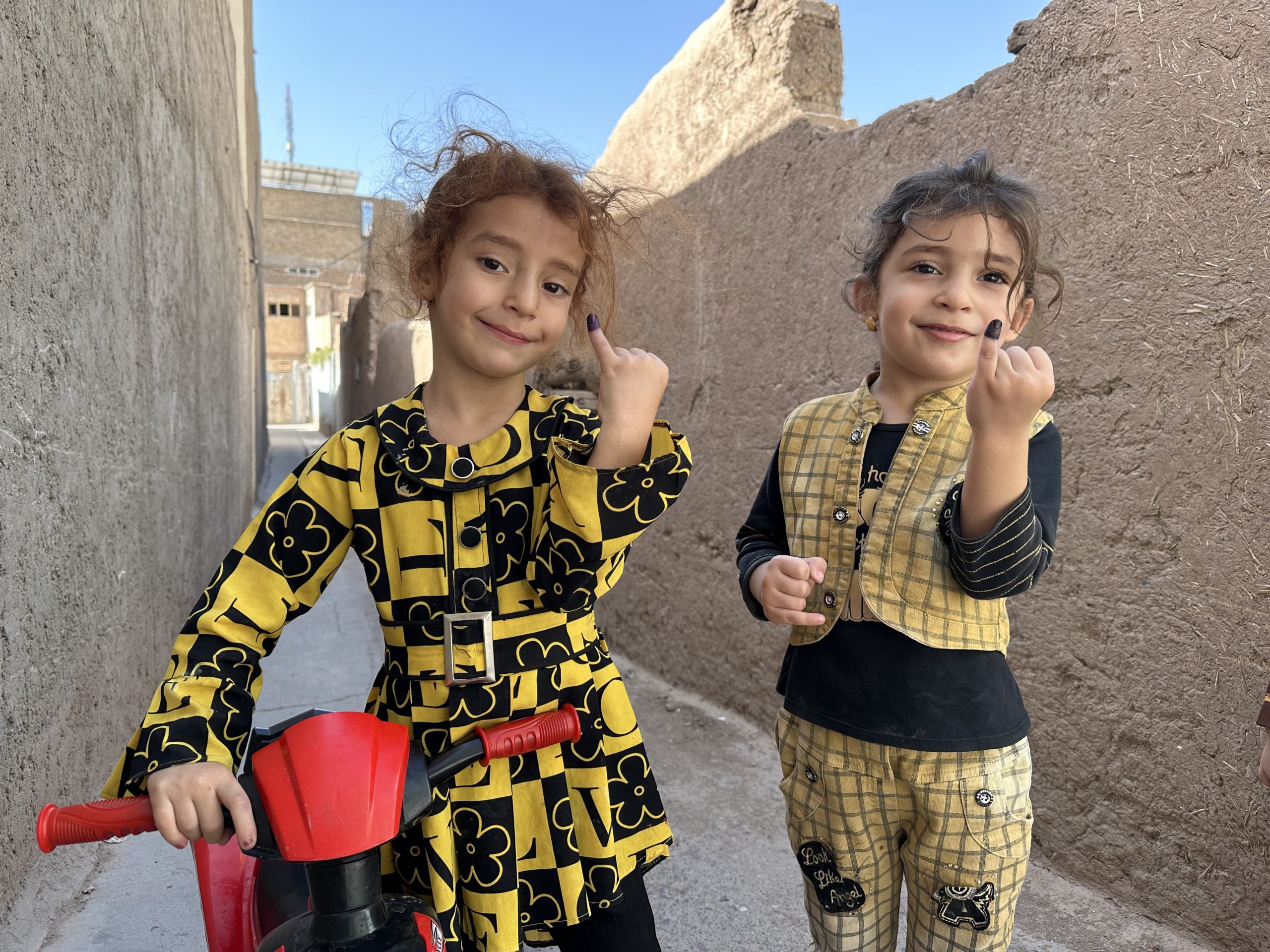
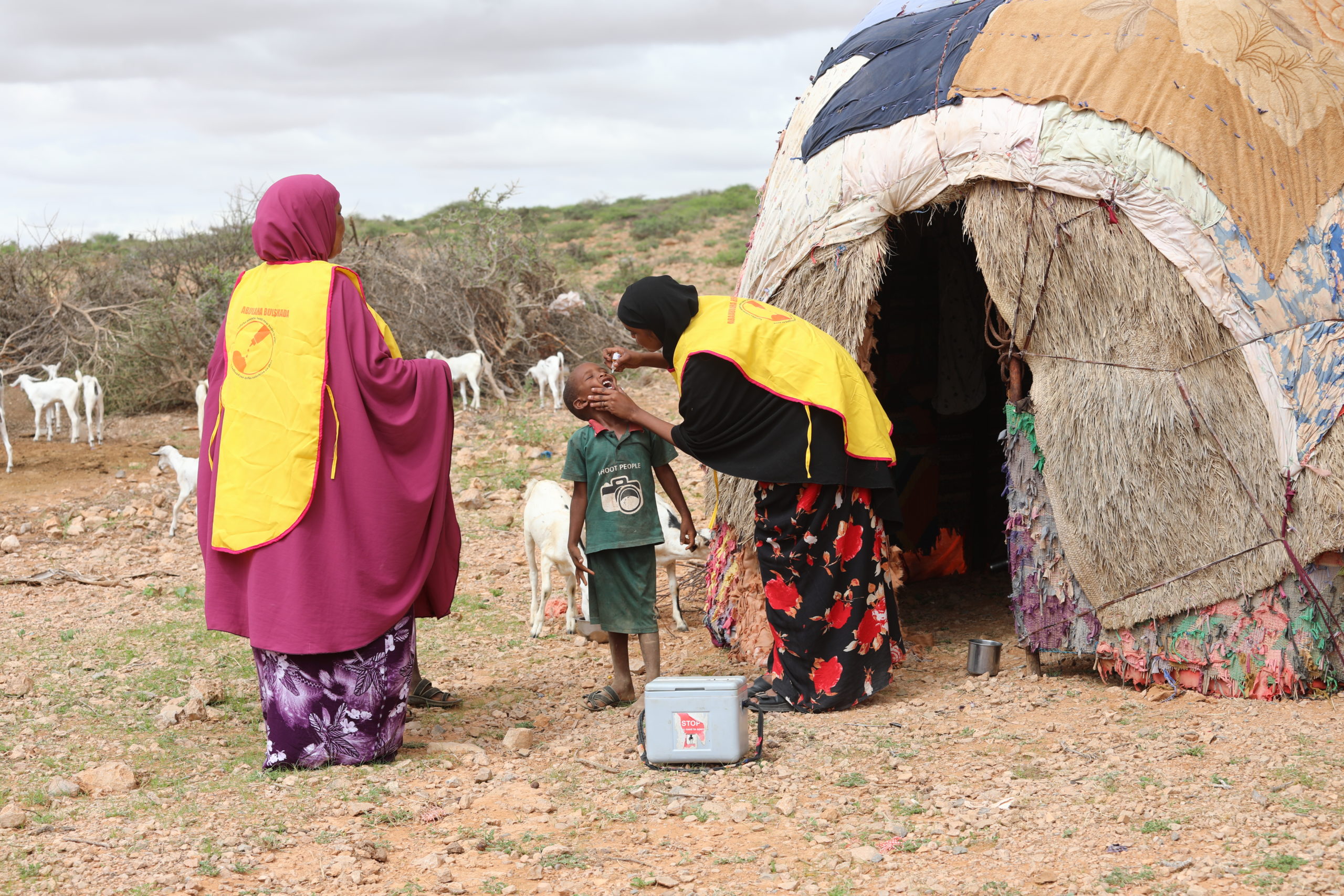
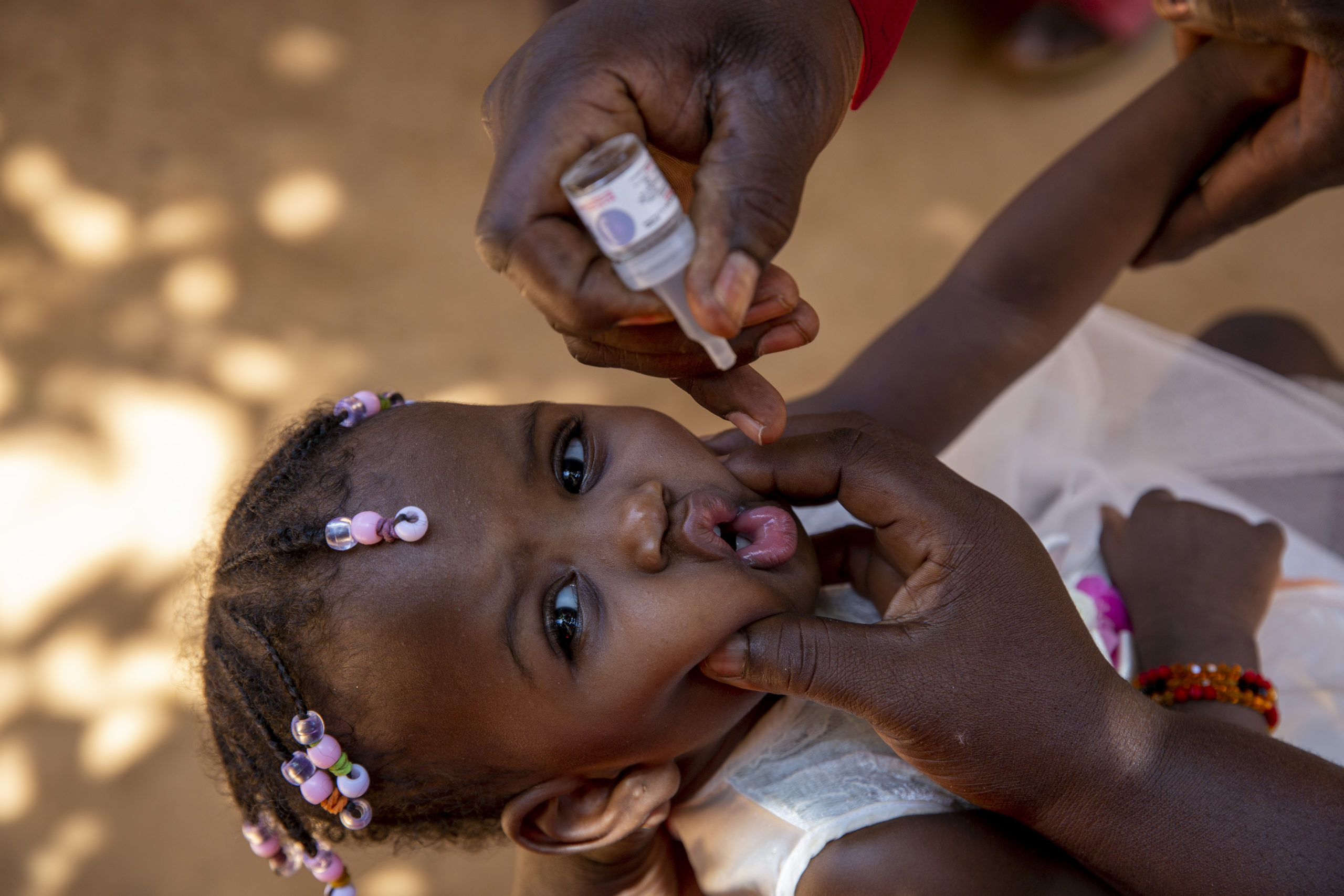
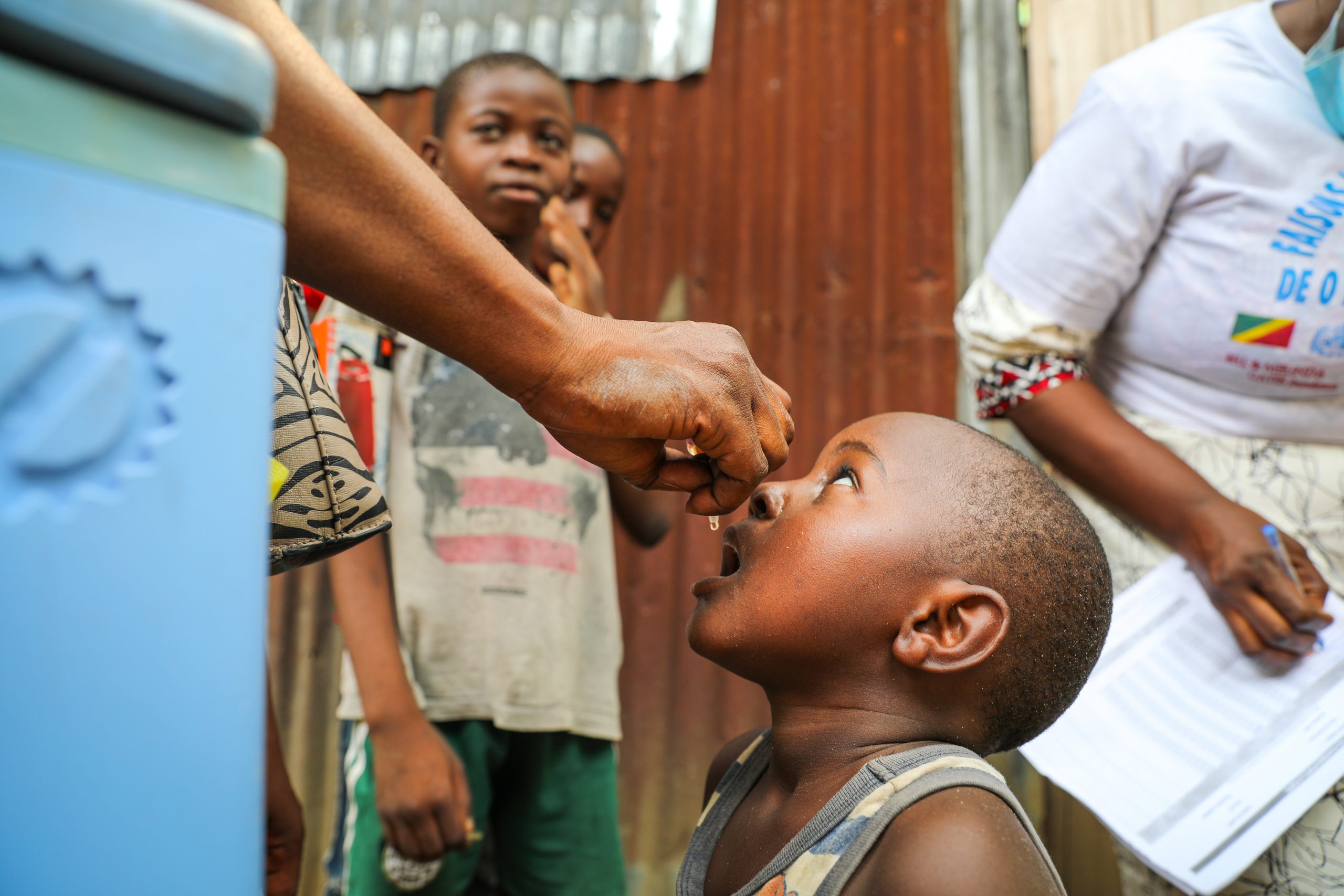Stopping any polio outbreak starts with vaccine procurement, transport by airplanes and trucks, distribution involving complex logistics, and eventually the oral administration of the vaccine by drops in the mouths of every eligible child.
However, there is another, lesser known but equally important process that must also take place to halt transmission of the poliovirus. It begins with a humble stool sample – a thumb-sized smudge of poop – taken from a child with acute flaccid paralysis (AFP), then delivered to the nearest laboratory that can test the sample specifically for poliovirus.
But nowhere in Yemen is there any such lab. So the long and arduous journey of any stool sample from a Yemeni child to a receiving lab can take up to several days – following an easterly route, to the neighboring country of Oman.
An explanation of how stool samples are transported over such a distance starts with why: monitoring children under 15 years of age for signs of AFP, which is the most common sign of poliovirus infection. The Global Polio Eradication Initiative has set a benchmark of at least three AFP cases per 100,000 children under 15 years of age, a standard that Yemen has consistently met, thanks to the effectiveness of its surveillance system. This achievement is all the more remarkable considering that Yemen is entering its ninth year of internal conflict, with resulting population displacements, widespread food and fuel shortages, and a devastated health system (in which only 46% of hospitals and health facilities are only partially functioning or completely out of service).